NEET-XII-Chemistry
09: Coordination Compounds
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
09-Coordination Compounds
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- Qstn #3Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes and
draw the structures for these isomers:
- K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2
- [Co(en)3]Cl3
- [Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2
- [Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]
Ans :- Both geometrical (cis-, trans-) isomers for
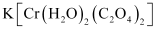 can exist. Also, optical isomers for cis-isomer exist.
can exist. Also, optical isomers for cis-isomer exist.
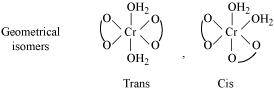
Trans-isomer is optically inactive. On the other hand, cis-isomer is optically active.
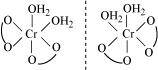
(ii) Two optical isomers for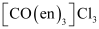 exist.
exist.
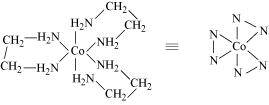
Two optical isomers are possible for this structure.

(iii)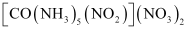
A pair of optical isomers:
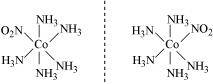
It can also show linkage isomerism.
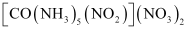 and
and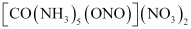
It can also show ionization isomerism.
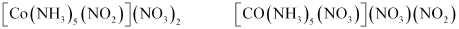
(iv) Geometrical (cis-, trans-) isomers of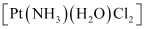 can exist.
can exist.
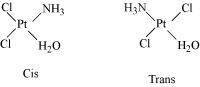
- Qstn #4Give evidence that [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4 and [Co(NH3)5SO4]Cl are ionization isomers.
Ans : When ionization isomers are dissolved in water, they ionize to give different ions. These ions then react differently with different reagents to give different products.
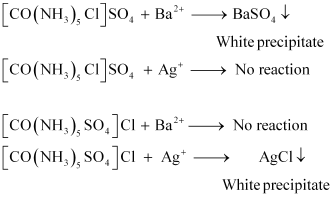
- Qstn #5Explain on the basis of valence bond theory that [Ni(CN)4]2- ion with square
planar structure is diamagnetic and the [NiCl4]2- ion with tetrahedral geometry is paramagnetic.
Ans : Ni is in the +2 oxidation state i.e., in d8 configuration.

There are 4 CN- ions. Thus, it can either have a tetrahedral geometry or square planar geometry. Since CN- ion is a strong field ligand, it causes the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons.
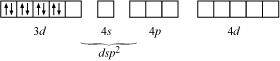
It now undergoes dsp2 hybridization. Since all electrons are paired, it is diamagnetic.
In case of [NiCl4]2-, Cl- ion is a weak field ligand. Therefore, it does not lead to the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons. Therefore, it undergoes sp3 hybridization.
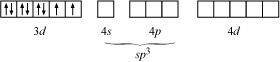
Since there are 2 unpaired electrons in this case, it is paramagnetic in nature.
- Qstn #6[NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why?
Ans : Though both [NiCl4]2- and [Ni(CO)4] are tetrahedral, their magnetic characters are different. This is due to a difference in the nature of ligands. Cl- is a weak field ligand and it does not cause the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons. Hence, [NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic.

In Ni(CO)4, Ni is in the zero oxidation state i.e., it has a configuration of 3d8 4s2.
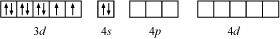
But CO is a strong field ligand. Therefore, it causes the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons. Also, it causes the 4s electrons to shift to the 3d orbital, thereby giving rise to sp3 hybridization. Since no unpaired electrons are present in this case, [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic.
- Qstn #7[Fe(H2O)6]3+ is strongly paramagnetic whereas [Fe(CN)6]3- is weakly paramagnetic. Explain.
Ans : In both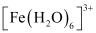 and
and  , Fe exists in the +3 oxidation state i.e., in d5 configuration.
, Fe exists in the +3 oxidation state i.e., in d5 configuration.

Since CN- is a strong field ligand, it causes the pairing of unpaired electrons. Therefore, there is only one unpaired electron left in the d-orbital.

Therefore,
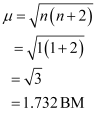
On the other hand, H2O is a weak field ligand. Therefore, it cannot cause the pairing of electrons. This means that the number of unpaired electrons is 5.
Therefore,
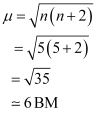
Thus, it is evident that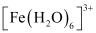 is strongly paramagnetic, while
is strongly paramagnetic, while  is weakly paramagnetic.
is weakly paramagnetic.
- Qstn #8Explain [Co(NH3)6]3+ is an inner orbital complex whereas [Ni(NH3)6]2+ is an outer orbital complex.
Ans :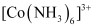

Oxidation state of cobalt = +3
Oxidation state of Ni = +2
Electronic configuration of cobalt = d6
Electronic configuration of nickel = d8
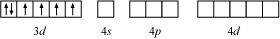
NH3 being a strong field ligand causes the pairing. Therefore, Cobalt can undergo d2sp3 hybridization.
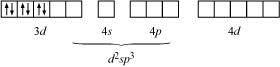
Hence, it is an inner orbital complex.
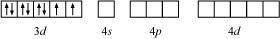
If NH3 causes the pairing, then only one 3d orbital is empty. Thus, it cannot undergo d2sp3 hybridization. Therefore, it undergoes sp3d2 hybridization.
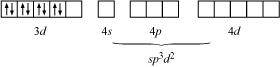
Hence, it forms an outer orbital complex.
- Qstn #9Predict the number of unpaired electrons in the square planar [Pt(CN)4]2- ion.
Ans :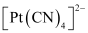
In this complex, Pt is in the +2 state. It forms a square planar structure. This means that it undergoes dsp2 hybridization. Now, the electronic configuration of Pd(+2) is 5d8.

CN- being a strong field ligand causes the pairing of unpaired electrons. Hence, there are no unpaired electrons in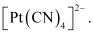
- Qstn #10The hexaquo manganese(II) ion contains five unpaired electrons, while the hexacyanoion contains only one unpaired electron. Explain using Crystal Field Theory.
Ans :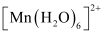
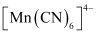
Mn is in the +2 oxidation state. Mn is in the +2 oxidation state. The electronic configuration is d5. The electronic configuration is d5. The crystal field is octahedral. Water is a weak field ligand. Therefore, the arrangement of the electrons in 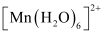 is t2g3eg2.
is t2g3eg2.The crystal field is octahedral. Cyanide is a strong field ligand. Therefore, the arrangement of the electrons in 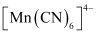 isT2g5eg0.
isT2g5eg0.
Hence, hexaaquo manganese (II) ion has five unpaired electrons, while hexacyano ion has only one unpaired electron.
- Qstn #11Calculate the overall complex dissociation equilibrium constant for the Cu(NH3)42+ ion, given that β4 for this complex is 2.1 × 1013.
Ans : β4 = 2.1 × 1013
The overall complex dissociation equilibrium constant is the reciprocal of the overall stability constant, β4.
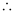
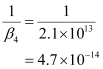
- #Section : IISECTION I Page No 258:
- Qstn #1Explain the bonding in coordination compounds in terms of Werner’s postulates.
Ans : Werner’s postulates explain the bonding in coordination compounds as follows:
(i) A metal exhibits two types of valencies namely, primary and secondary valencies. Primary valencies are satisfied by negative ions while secondary valencies are satisfied by both negative and neutral ions.
(In modern terminology, the primary valency corresponds to the oxidation number of the metal ion, whereas the secondary valency refers to the coordination number of the metal ion.
(ii) A metal ion has a definite number of secondary valencies around the central atom. Also, these valencies project in a specific direction in the space assigned to the definite geometry of the coordination compound.
(iii) Primary valencies are usually ionizable, while secondary valencies are non-ionizable.
- Qstn #2FeSO4 solution mixed with (NH4)2SO4 solution in 1:1 molar ratio gives the test of Fe2+ ion but CuSO4 solution mixed with aqueous ammonia in 1:4 molar ratio does not give the test of Cu2+ ion. Explain why?
Ans :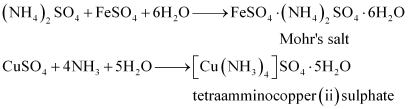
Both the compounds i.e.,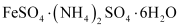 and
and 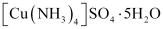 fall under the category of addition compounds with only one major difference i.e., the former is an example of a double salt, while the latter is a coordination compound.
fall under the category of addition compounds with only one major difference i.e., the former is an example of a double salt, while the latter is a coordination compound.
A double salt is an addition compound that is stable in the solid state but that which breaks up into its constituent ions in the dissolved state. These compounds exhibit individual properties of their constituents. For e.g.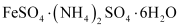 breaks into Fe2+, NH4+, and SO42- ions. Hence, it gives a positive test for Fe2+ ions.
breaks into Fe2+, NH4+, and SO42- ions. Hence, it gives a positive test for Fe2+ ions.
A coordination compound is an addition compound which retains its identity in the solid as well as in the dissolved state. However, the individual properties of the constituents are lost. This happens because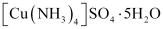 does not show the test for Cu2+. The ions present in the solution of
does not show the test for Cu2+. The ions present in the solution of 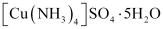 are
are 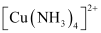 and
and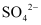 .
.
- Qstn #3-icoordination entity, () ligand, () coordination number, () coordination polyhedron, () homoleptic and () heteroleptic.Ans : Coordination entity:
A coordination entity is an electrically charged radical or species carrying a positive or negative charge. In a coordination entity, the central atom or ion is surrounded by a suitable number of neutral molecules or negative ions ( called ligands). For example:
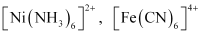 = cationic complex
= cationic complex
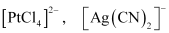 = anionic complex
= anionic complex
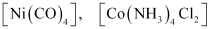 = neutral complex
= neutral complex
() Ligands
The neutral molecules or negatively charged ions that surround the metal atom in a coordination entity or a coordinal complex are known as ligands. For example,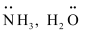 , Cl-, -OH. Ligands are usually polar in nature and possess at least one unshared pair of valence electrons.
, Cl-, -OH. Ligands are usually polar in nature and possess at least one unshared pair of valence electrons.
() Coordination number:
The total number of ligands (either neutral molecules or negative ions) that get attached to the central metal atom in the coordination sphere is called the coordination number of the central metal atom. It is also referred to as its ligancy.
For example:
(a) In the complex, K2[PtCl6], there as six chloride ions attached to Pt in the coordinate sphere. Therefore, the coordination number of Pt is 6.
(b) Similarly, in the complex [Ni(NH3)4]Cl2, the coordination number of the central atom (Ni) is 4.
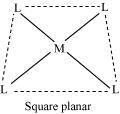
() Coordination polyhedron:
Coordination polyhedrons about the central atom can be defined as the spatial arrangement of the ligands that are directly attached to the central metal ion in the coordination sphere. For example:
(a)
(b) Tetrahedral
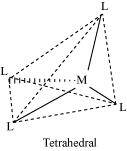
() Homoleptic complexes:
These are those complexes in which the metal ion is bound to only one kind of a donor group. For eg: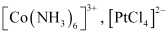 etc.
etc.
() Heteroleptic complexes:
Heteroleptic complexes are those complexes where the central metal ion is bound to more than one type of a donor group.
For e.g.: