NEET-XII-Physics
11: Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #14-aan electron, andAns : For the kinetic energy K, of an electron accelerating with a velocity v, we have the relation:

We have the relation for de Broglie wavelength as:
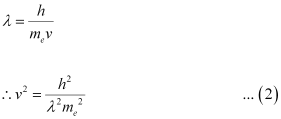
Substituting equation (2) in equation (1), we get the relation:
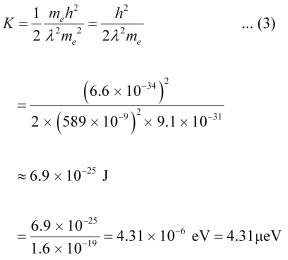
Hence, the kinetic energy of the electron is 6.9 × 10-25 J or 4.31 μeV.
- #14-ba neutron, would have the same de Broglie wavelength.Ans : Using equation (3), we can write the relation for the kinetic energy of the neutron as:
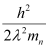
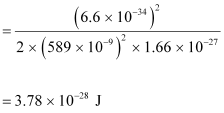
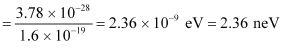
Hence, the kinetic energy of the neutron is 3.78 × 10-28 J or 2.36 neV.
- #15-aa bullet of mass 0.040 kg travelling at the speed of 1.0 km/s,Ans : Mass of the bullet, m = 0.040 kg
Speed of the bullet, v = 1.0 km/s = 1000 m/s
Planck’s constant, h = 6.6 × 10-34 Js
De Broglie wavelength of the bullet is given by the relation:
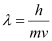
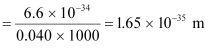
- #15-ba ball of mass 0.060 kg moving at a speed of 1.0 m/s, andAns : Mass of the ball, m = 0.060 kg
Speed of the ball, v = 1.0 m/s
De Broglie wavelength of the ball is given by the relation:
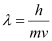
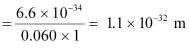

- #15-ca dust particle of mass 1.0 × 10-9 kg drifting with a speed of 2.2 m/s?Ans : Mass of the dust particle, m = 1 × 10-9 kg
Speed of the dust particle, v = 2.2 m/s
De Broglie wavelength of the dust particle is given by the relation:
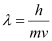
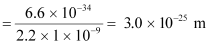
- Qstn #16An electron and a photon each have a wavelength of 1.00 nm. Find
Ans : Wavelength of an electron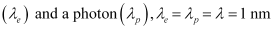
= 1 × 10-9 m
Planck’s constant, h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js
- #16-atheir momenta,Ans : The momentum of an elementary particle is given by de Broglie relation:
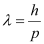
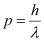
It is clear that momentum depends only on the wavelength of the particle. Since the wavelengths of an electron and a photon are equal, both have an equal momentum.
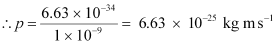
- #16-bthe energy of the photon, andAns : The energy of a photon is given by the relation:
.gif)
Where,
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
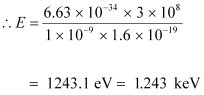
Therefore, the energy of the photon is 1.243 keV.
- #16-cthe kinetic energy of electron.Ans : The kinetic energy (K) of an electron having momentum p,is given by the relation:
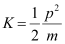
Where,
m = Mass of the electron = 9.1 × 10-31 kg
p = 6.63 × 10-25 kg m s-1
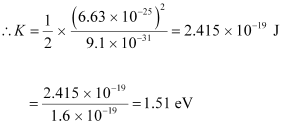
Hence, the kinetic energy of the electron is 1.51 eV.
- #17
- #17-aFor what kinetic energy of a neutron will the associated de Broglie wavelength be 1.40 × 10-10 m?Ans : De Broglie wavelength of the neutron, λ = 1.40 × 10-10 m
Mass of a neutron, mn = 1.66 × 10-27 kg
Planck’s constant, h = 6.6 × 10-34 Js
Kinetic energy (K) and velocity (v) are related as:
 ... (1)
... (1)
De Broglie wavelength (λ) and velocity (v) are related as:

Using equation (2) in equation (1), we get:
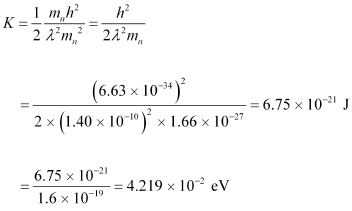
Hence, the kinetic energy of the neutron is 6.75 × 10-21 J or 4.219 × 10-2 eV.
- #17-bAlso find the de Broglie wavelength of a neutron, in thermal equilibrium with matter, having an average kinetic energy of (3/2) kT at 300 K.Ans : Temperature of the neutron, T = 300 K
Boltzmann constant, k = 1.38 × 10-23 kg m2 s-2 K-1
Average kinetic energy of the neutron:
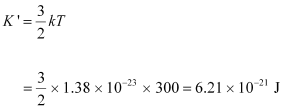
The relation for the de Broglie wavelength is given as:
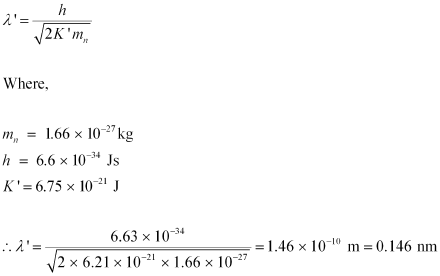
Therefore, the de Broglie wavelength of the neutron is 0.146 nm.
- Qstn #18Show that the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is equal to the de Broglie wavelength of its quantum (photon).
Ans : The momentum of a photon having energy (hν) is given as:

Where,
λ = Wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation
c = Speed of light
h = Planck’s constant
De Broglie wavelength of the photon is given as:

Where,
m = Mass of the photon
v = Velocity of the photon
Hence, it can be inferred from equations (i) and (ii) that the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation is equal to the de Broglie wavelength of the photon.
- Qstn #19What is the de Broglie wavelength of a nitrogen molecule in air at 300 K? Assume that the molecule is moving with the root-mean square speed of molecules at this temperature. (Atomic mass of nitrogen = 14.0076 u)
Ans : Temperature of the nitrogen molecule, T = 300 K
Atomic mass of nitrogen = 14.0076 u
Hence, mass of the nitrogen molecule, m = 2 × 14.0076 = 28.0152 u
But 1 u = 1.66 × 10-27 kg
∴m = 28.0152 ×1.66 × 10-27 kg
Planck’s constant, h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js
Boltzmann constant, k = 1.38 × 10-23 J K-1
We have the expression that relates mean kinetic energy of the nitrogen molecule with the root mean square speed
of the nitrogen molecule with the root mean square speed  as:
as:
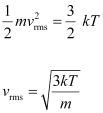
Hence, the de Broglie wavelength of the nitrogen molecule is given as:

Therefore, the de Broglie wavelength of the nitrogen molecule is 0.028 nm.