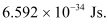NEET-XII-Physics
11: Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #3 - Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter
- Qstn #1Find the
Ans : Potential of the electrons, V = 30 kV = 3 × 104 V
Hence, energy of the electrons, E = 3 × 104 eV
Where,
e = Charge on an electron = 1.6 × 10-19 C
- #1-amaximum frequency, andAns : Maximum frequency produced by the X-rays = ν
The energy of the electrons is given by the relation:
E = hν
Where,
h = Planck’s constant = 6.626 × 10-34 Js
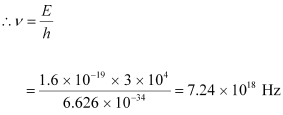
Hence, the maximum frequency of X-rays produced is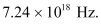
- #1-bminimum wavelength of X-rays produced by 30 kV electrons.Ans : The minimum wavelength produced by the X-rays is given as:
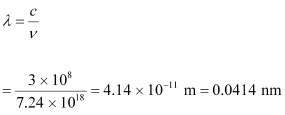
Hence, the minimum wavelength of X-rays produced is 0.0414 nm.
- Qstn #2The work function of caesium metal is 2.14 eV. When light of frequency 6 ×1014 Hz is incident on the metal surface, photoemission of electrons occurs. What is the
Ans : Work function of caesium metal,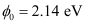
Frequency of light,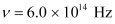
- #2-amaximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons,Ans : The maximum kinetic energy is given by the photoelectric effect as:
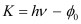
Where,
h = Planck’s constant = 6.626 × 10-34 Js
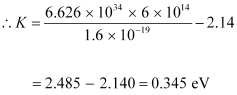
Hence, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons is 0.345 eV.
- #2-bStopping potential, andAns : For stopping potential
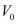 , we can write the equation for kinetic energy as:
, we can write the equation for kinetic energy as:
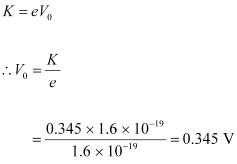
Hence, the stopping potential of the material is 0.345 V.
- #2-cmaximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons?Ans : Maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons = v
Hence, the relation for kinetic energy can be written as:
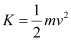
Where,
m = Mass of an electron = 9.1 × 10-31 kg
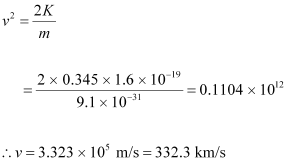
Hence, the maximum speed of the emitted photoelectrons is 332.3 km/s.
- Qstn #3The photoelectric cut-off voltage in a certain experiment is 1.5 V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted?
Ans : Photoelectric cut-off voltage, V0 = 1.5 V
The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is given as:
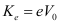
Where,
e = Charge on an electron = 1.6 × 10-19 C
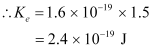
Therefore, the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the given experiment is 2.4 × 10-19 J.
- Qstn #4Monochromatic light of wavelength 632.8 nm is produced by a helium-neon laser. The power emitted is 9.42 mW.
Ans : Wavelength of the monochromatic light, λ = 632.8 nm = 632.8 × 10-9 m
Power emitted by the laser, P = 9.42 mW = 9.42 × 10-3 W
Planck’s constant, h = 6.626 × 10-34 Js
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
Mass of a hydrogen atom, m = 1.66 × 10-27 kg
- #4-aFind the energy and momentum of each photon in the light beam,Ans : The energy of each photon is given as:
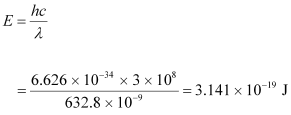
The momentum of each photon is given as:
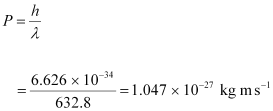
- #4-bHow many photons per second, on the average, arrive at a target irradiated by this beam? (Assume the beam to have uniform cross-section which is less than the target area), andAns : Number of photons arriving per second, at a target irradiated by the beam = n
Assume that the beam has a uniform cross-section that is less than the target area.
Hence, the equation for power can be written as:
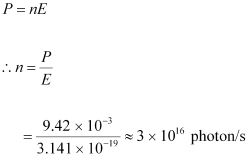
- #4-cHow fast does a hydrogen atom have to travel in order to have the same momentum as that of the photon?Ans : Momentum of the hydrogen atom is the same as the momentum of the photon,
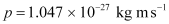
Momentum is given as:
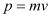
Where,
v = Speed of the hydrogen atom

- Qstn #5The energy flux of sunlight reaching the surface of the earth is 1.388 × 103 W/m2. How many photons (nearly) per square metre are incident on the Earth per second? Assume that the photons in the sunlight have an average wavelength of 550 nm.
Ans : Energy flux of sunlight reaching the surface of earth, Φ = 1.388 × 103 W/m2
Hence, power of sunlight per square metre, P = 1.388 × 103 W
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
Planck’s constant, h = 6.626 × 10-34 Js
Average wavelength of photons present in sunlight,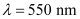
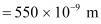
Number of photons per square metre incident on earth per second = n
Hence, the equation for power can be written as:
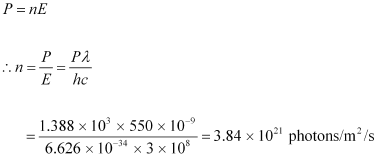
Therefore, every second, photons are incident per square metre on earth.
photons are incident per square metre on earth.
- Qstn #6In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the slope of the cut-off voltage versus frequency of incident light is found to be 4.12 × 10-15 V s. Calculate the value of Planck’s constant.
Ans : The slope of the cut-off voltage (V) versus frequency (ν) of an incident light is given as:

Where,
e = Charge on an electron = 1.6 × 10-19 C
h = Planck’s constant
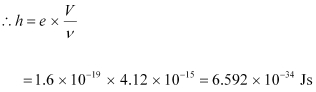
Therefore, the value of Planck’s constant is