NEET-XII-Physics
12: Atoms
- #7null (a) Using the Bohr’s model calculate the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom in the n = 1, 2, and 3 levels. (b) Calculate the orbital period in each of these levels.Ans : null (a) Let ν1 be the orbital speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom in the ground state level, n1 = 1. For charge (e) of an electron, ν1 is given by the relation,
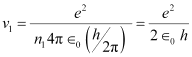
Where,
e = 1.6 × 10-19 C
∈0 = Permittivity of free space = 8.85 × 10-12 N-1 C2 m-2
h = Planck’s constant = 6.62 × 10-34 Js
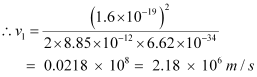
For level n2 = 2, we can write the relation for the corresponding orbital speed as:
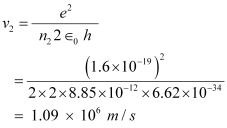
And, for n3 = 3, we can write the relation for the corresponding orbital speed as:
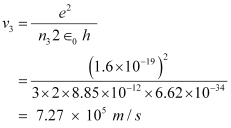
Hence, the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom in n = 1, n=2, and n=3 is 2.18 × 106 m/s, 1.09 × 106 m/s, 7.27 × 105 m/s respectively.
(b) Let T1 be the orbital period of the electron when it is in level n1 = 1.
Orbital period is related to orbital speed as:
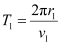
Where,
r1 = Radius of the orbit
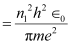
h = Planck’s constant = 6.62 × 10-34 Js
e = Charge on an electron = 1.6 × 10-19 C
∈0 = Permittivity of free space = 8.85 × 10-12 N-1 C2 m-2
m = Mass of an electron = 9.1 × 10-31 kg

For level n2 = 2, we can write the period as:

Where,
r2 = Radius of the electron in n2 = 2


And, for level n3 = 3, we can write the period as:
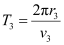
Where,
r3 = Radius of the electron in n3 = 3
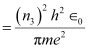
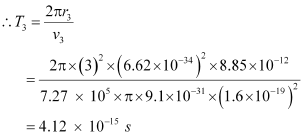
Hence, the orbital period in each of these levels is 1.52 × 10-16 s, 1.22 × 10-15 s, and 4.12 × 10-15 s respectively.
- #7-aUsing the Bohr’s model calculate the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom in the n = 1, 2, and 3 levels.Ans : Let ν1 be the orbital speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom in the ground state level, n1 = 1. For charge (e) of an electron, ν1 is given by the relation,
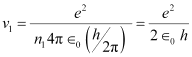
Where,
e = 1.6 × 10-19 C
∈0 = Permittivity of free space = 8.85 × 10-12 N-1 C2 m-2
h = Planck’s constant = 6.62 × 10-34 Js
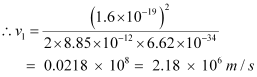
For level n2 = 2, we can write the relation for the corresponding orbital speed as:
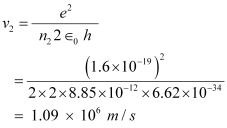
And, for n3 = 3, we can write the relation for the corresponding orbital speed as:
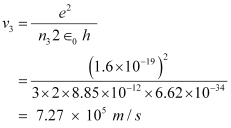
Hence, the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom in n = 1, n=2, and n=3 is 2.18 × 106 m/s, 1.09 × 106 m/s, 7.27 × 105 m/s respectively.
- #7-bCalculate the orbital period in each of these levels.Ans : Let T1 be the orbital period of the electron when it is in level n1 = 1.
Orbital period is related to orbital speed as:
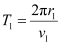
Where,
r1 = Radius of the orbit
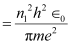
h = Planck’s constant = 6.62 × 10-34 Js
e = Charge on an electron = 1.6 × 10-19 C
∈0 = Permittivity of free space = 8.85 × 10-12 N-1 C2 m-2
m = Mass of an electron = 9.1 × 10-31 kg

For level n2 = 2, we can write the period as:

Where,
r2 = Radius of the electron in n2 = 2


And, for level n3 = 3, we can write the period as:
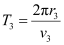
Where,
r3 = Radius of the electron in n3 = 3
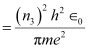
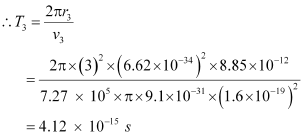
Hence, the orbital period in each of these levels is 1.52 × 10-16 s, 1.22 × 10-15 s, and 4.12 × 10-15 s respectively.