NEET-XII-Physics
11: Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter
- #12-amomentum, and
(b) de Broglie wavelength of the electrons accelerated through a potential difference of 56 V.Ans : At equilibrium, the kinetic energy of each electron is equal to the accelerating potential, i.e., we can write the relation for velocity (v) of each electron as:
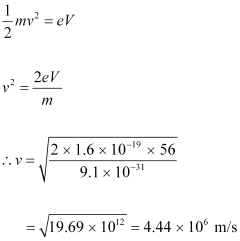
The momentum of each accelerated electron is given as:
p = mv
= 9.1 × 10-31 × 4.44 × 106
= 4.04 × 10-24 kg m s-1
Therefore, the momentum of each electron is 4.04 × 10-24 kg m s-1.
(b) De Broglie wavelength of an electron accelerating through a potential V, is given by the relation:
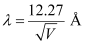
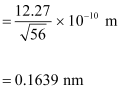
Therefore, the de Broglie wavelength of each electron is 0.1639 nm.
- #12-bde Broglie wavelength of the electrons accelerated through a potential difference of 56 V.Ans : De Broglie wavelength of an electron accelerating through a potential V, is given by the relation:
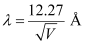
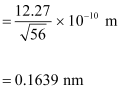
Therefore, the de Broglie wavelength of each electron is 0.1639 nm.