NEET-XII-Physics
09: Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #1 - Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
- Qstn #1A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Describe the nature and size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved?
Ans : Size of the candle, h= 2.5 cm
Image size = h’
Object distance, u= -27 cm
Radius of curvature of the concave mirror, R= -36 cm
Focal length of the concave mirror,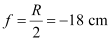
Image distance = v
The image distance can be obtained using the mirror formula:
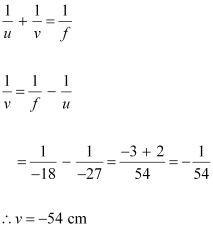
Therefore, the screen should be placed 54 cm away from the mirror to obtain a sharp image.
The magnification of the image is given as:
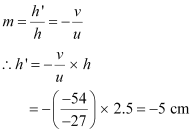
The height of the candle’s image is 5 cm. The negative sign indicates that the image is inverted and real.
If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, then the screen will have to be moved away from the mirror in order to obtain the image.
- Qstn #2A 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Give the location of the image and the magnification. Describe what happens as the needle is moved farther from the mirror.
Ans : Height of the needle, h1 = 4.5 cm
Object distance, u = -12 cm
Focal length of the convex mirror, f = 15 cm
Image distance = v
The value of v can be obtained using the mirror formula:
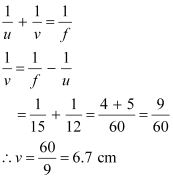
Hence, the image of the needle is 6.7 cm away from the mirror. Also, it is on the other side of the mirror.
The image size is given by the magnification formula:
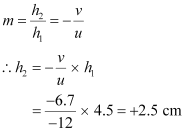
Hence, magnification of the image,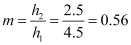
The height of the image is 2.5 cm. The positive sign indicates that the image is erect, virtual, and diminished.
If the needle is moved farther from the mirror, the image will also move away from the mirror, and the size of the image will reduce gradually.
- Qstn #3A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
Ans : Actual depth of the needle in water, h1 = 12.5 cm
Apparent depth of the needle in water, h2 = 9.4 cm
Refractive index of water = μ
The value of μcan be obtained as follows:

Hence, the refractive index of water is about 1.33.
Water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index,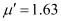
The actual depth of the needle remains the same, but its apparent depth changes. Let y be the new apparent depth of the needle. Hence, we can write the relation:
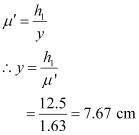
Hence, the new apparent depth of the needle is 7.67 cm. It is less than h2. Therefore, to focus the needle again, the microscope should be moved up.
∴Distance by which the microscope should be moved up = 9.4 - 7.67
= 1.73 cm
- Qstn #4Figures 9.34(a) and (b) show refraction of a ray in air incident at 60° with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in glass when the angle of incidence in water is 45° with the normal to a water-glass interface [Fig. 9.34(c)].

Ans : As per the given figure, for the glass - air interface:
Angle of incidence, i = 60°
Angle of refraction, r = 35°
The relative refractive index of glass with respect to air is given by Snell’s law as:
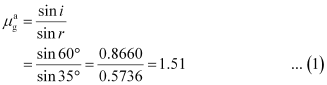
As per the given figure, for the air - water interface:
Angle of incidence, i = 60°
Angle of refraction, r = 47°
The relative refractive index of water with respect to air is given by Snell’s law as:
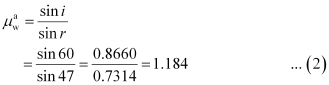
Using (1) and (2), the relative refractive index of glass with respect to water can be obtained as:
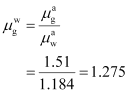
The following figure shows the situation involving the glass - water interface.

Angle of incidence, i = 45°
Angle of refraction = r
From Snell’s law, r can be calculated as:
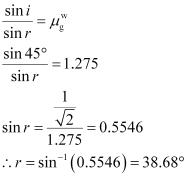
Hence, the angle of refraction at the water - glass interface is 38.68°.
- Qstn #5A small bulb is placed at the bottom of a tank containing water to a depth of 80 cm. What is the area of the surface of water through which light from the bulb can emerge out? Refractive index of water is 1.33. (Consider the bulb to be a point source.)
Ans : Actual depth of the bulb in water, d1 = 80 cm = 0.8 m
Refractive index of water,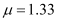
The given situation is shown in the following figure:

Where,
i = Angle of incidence
r = Angle of refraction = 90°
Since the bulb is a point source, the emergent light can be considered as a circle of radius,
Using Snell’ law, we can write the relation for the refractive index of water as:
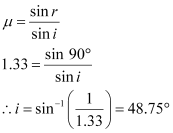
Using the given figure, we have the relation:
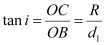
∴R = tan 48.75° × 0.8 = 0.91 m
∴Area of the surface of water = ``\pi``R2 = ``\pi`` (0.91)2 = 2.61 m2
Hence, the area of the surface of water through which the light from the bulb can emerge is approximately 2.61 m2.
- Qstn #6A prism is made of glass of unknown refractive index. A parallel beam of light is incident on a face of the prism. The angle of minimum deviation is measured to be 40°. What is the refractive index of the material of the prism? The refracting angle of the prism is 60°. If the prism is placed in water (refractive index 1.33), predict the new angle of minimum deviation of a parallel beam of light.
Ans : Angle of minimum deviation,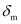 = 40°
= 40°
Angle of the prism, A = 60°
Refractive index of water, µ = 1.33
Refractive index of the material of the prism =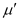
The angle of deviation is related to refractive index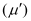 as:
as:
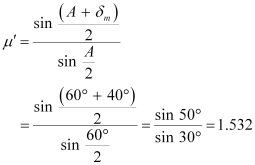
Hence, the refractive index of the material of the prism is 1.532.
Since the prism is placed in water, let be the new angle of minimum deviation for the same prism.
be the new angle of minimum deviation for the same prism.
The refractive index of glass with respect to water is given by the relation:
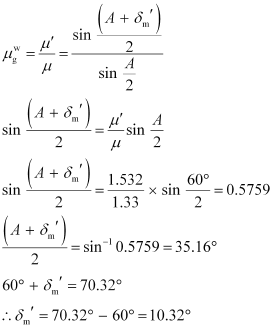
Hence, the new minimum angle of deviation is 10.32°.
- Qstn #7Double-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 20 cm?
Ans : Refractive index of glass,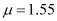
Focal length of the double-convex lens, f = 20 cm
Radius of curvature of one face of the lens = R1
Radius of curvature of the other face of the lens = R2
Radius of curvature of the double-convex lens = R
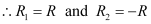
The value of R can be calculated as:
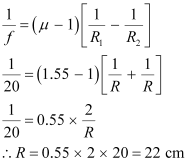
Hence, the radius of curvature of the double-convex lens is 22 cm.
- Qstn #8A beam of light converges at a point P. Now a lens is placed in the path of the convergent beam 12 cm from P. At what point does the beam converge if the lens isAns : In the given situation, the object is virtual and the image formed is real.
Object distance, u = +12 cm
- #8-aa convex lens of focal length 20 cm, andAns : Focal length of the convex lens, f = 20 cm
Image distance = v
According to the lens formula, we have the relation:
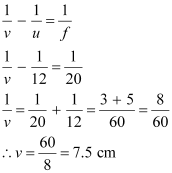
Hence, the image is formed 7.5 cm away from the lens, toward its right.
- #8-ba concave lens of focal length 16 cm?Ans : Focal length of the concave lens, f = -16 cm
Image distance = v
According to the lens formula, we have the relation:

Hence, the image is formed 48 cm away from the lens, toward its right.
- Qstn #9An object of size 3.0 cm is placed 14 cm in front of a concave lens of focal length 21 cm. Describe the image produced by the lens. What happens if the object is moved further away from the lens?
Ans : Size of the object, h1 = 3 cm
Object distance, u = -14 cm
Focal length of the concave lens, f = -21 cm
Image distance = v
According to the lens formula, we have the relation:
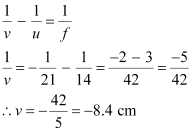
Hence, the image is formed on the other side of the lens, 8.4 cm away from it. The negative sign shows that the image is erect and virtual.
The magnification of the image is given as:

Hence, the height of the image is 1.8 cm.
If the object is moved further away from the lens, then the virtual image will move toward the focus of the lens, but not beyond it. The size of the image will decrease with the increase in the object distance.
- Qstn #10What is the focal length of a convex lens of focal length 30 cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm? Is the system a converging or a diverging lens? Ignore thickness of the lenses.
Ans : Focal length of the convex lens, f1 = 30 cm
Focal length of the concave lens, f2 = -20 cm
Focal length of the system of lenses = f
The equivalent focal length of a system of two lenses in contact is given as:
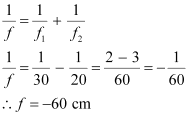
Hence, the focal length of the combination of lenses is 60 cm. The negative sign indicates that the system of lenses acts as a diverging lens.
- Qstn #11A compound microscope consists of an objective lens of focal length 2.0 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 6.25 cm separated by a distance of 15 cm. How far from the objective should an object be placed in order to obtain the final image at (a) the least distance of distinct vision (25 cm), and (b) at infinity? What is the magnifying power of the microscope in each case?
Ans : Focal length of the objective lens, f1 = 2.0 cm
Focal length of the eyepiece, f2 = 6.25 cm
Distance between the objective lens and the eyepiece, d = 15 cm
(a) Least distance of distinct vision,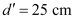
∴Image distance for the eyepiece, v2 = -25 cm
Object distance for the eyepiece = u2
According to the lens formula, we have the relation:
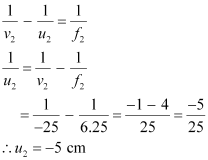
Image distance for the objective lens,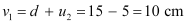
Object distance for the objective lens = u1
According to the lens formula, we have the relation:
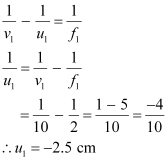
Magnitude of the object distance, = 2.5 cm
= 2.5 cm
The magnifying power of a compound microscope is given by the relation:
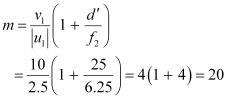
Hence, the magnifying power of the microscope is 20.
(b) The final image is formed at infinity.
∴Image distance for the eyepiece,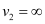
Object distance for the eyepiece = u2
According to the lens formula, we have the relation:
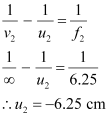
Image distance for the objective lens,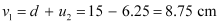
Object distance for the objective lens = u1
According to the lens formula, we have the relation:
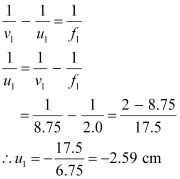
Magnitude of the object distance, = 2.59 cm
= 2.59 cm
The magnifying power of a compound microscope is given by the relation:
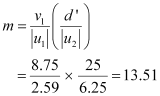
Hence, the magnifying power of the microscope is 13.51.
- Qstn #12A person with a normal near point (25 cm) using a compound microscope with objective of focal length 8.0 mm and an eyepiece of focal length 2.5 cm can bring an object placed at 9.0 mm from the objective in sharp focus. What is the separation between the two lenses? Calculate the magnifying power of the microscope,
Ans : Focal length of the objective lens, fo = 8 mm = 0.8 cm
Focal length of the eyepiece, fe = 2.5 cm
Object distance for the objective lens, uo = -9.0 mm = -0.9 cm
Least distance of distant vision, d = 25 cm
Image distance for the eyepiece, ve = -d = -25 cm
Object distance for the eyepiece =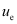
Using the lens formula, we can obtain the value of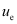 as:
as:
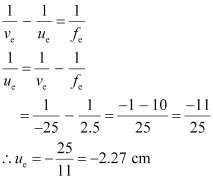
We can also obtain the value of the image distance for the objective lens using the lens formula.
using the lens formula.
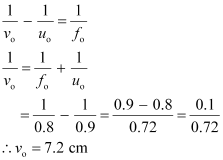
The distance between the objective lens and the eyepiece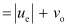
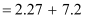
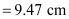
The magnifying power of the microscope is calculated as:
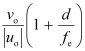

Hence, the magnifying power of the microscope is 88.