NEET-XII-Physics
08: Electromagnetic Waves
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #8-aDetermine, B0, ω, k, and λ.Ans : Magnitude of magnetic field strength is given as:
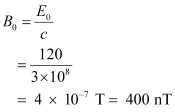
Angular frequency of source is given as:
ω = 2``\pi``ν
= 2``\pi`` × 50 × 106
= 3.14 × 108 rad/s
Propagation constant is given as:
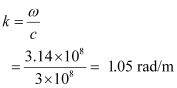
Wavelength of wave is given as:
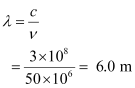
- #8-bFind expressions for E and B.Ans : Suppose the wave is propagating in the positive x direction. Then, the electric field vector will be in the positive y direction and the magnetic field vector will be in the positive z direction. This is because all three vectors are mutually perpendicular.
Equation of electric field vector is given as:
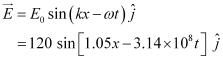
And, magnetic field vector is given as:

- Qstn #9The terminology of different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum is given in the text. Use the formula E = hν (for energy of a quantum of radiation: photon) and obtain the photon energy in units of eV for different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. In what way are the different scales of photon energies that you obtain related to the sources of electromagnetic radiation?
Ans : Energy of a photon is given as:
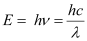
Where,
h = Planck’s constant = 6.6 × 10-34 Js
c = Speed of light = 3 × 108 m/s
λ = Wavelength of radiation
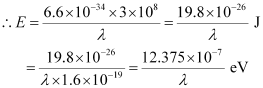
The given table lists the photon energies for different parts of an electromagnetic spectrum for differentλ.
-
λ (m) 103 1 10-3 10-6 10-8 10-10 10-12 E (eV) 12.375 × 10-10 12.375 × 10-7 12.375 × 10-4 12.375 × 10-1 12.375 × 101 12.375 × 103 12.375 × 105
The photon energies for the different parts of the spectrum of a source indicate the spacing of the relevant energy levels of the source.
-
- Qstn #10In a plane electromagnetic wave, the electric field oscillates sinusoidally at a frequency of 2.0 × 1010 Hz and amplitude 48 V m-1.
Ans : Frequency of the electromagnetic wave, ν = 2.0 × 1010 Hz
Electric field amplitude, E0 = 48 V m-1
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
- #10-aWhat is the wavelength of the wave?Ans : Wavelength of a wave is given as:

- #10-bWhat is the amplitude of the oscillating magnetic field?Ans : Magnetic field strength is given as:
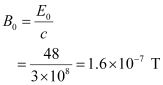
- #10-cShow that the average energy density of the E field equals the average energy density of the B field. [c = 3 × 108 m s-1.]Ans : Energy density of the electric field is given as:

And, energy density of the magnetic field is given as:
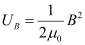
Where,
∈0 = Permittivity of free space
μ0 = Permeability of free space
We have the relation connecting E and B as:
E = cB ... (1)
Where,
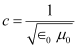 ... (2)
... (2)
Putting equation (2) in equation (1), we get
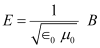
Squaring both sides, we get
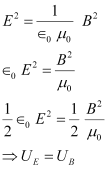
- Qstn #11Suppose that the electric field part of an electromagnetic wave in vacuum is E = {(3.1 N/C) cos [(1.8 rad/m) y + (5.4 × 106 rad/s)t]}
 .
.
- #11-aWhat is the direction of propagation?Ans : From the given electric field vector, it can be inferred that the electric field is directed along the negative x direction. Hence, the direction of motion is along the negative y direction i.e.,
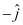 .
.
- #11-bWhat is the wavelength λ?Ans : It is given that,
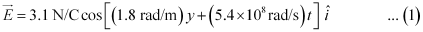
The general equation for the electric field vector in the positive x direction can be written as:

On comparing equations (1) and (2), we get
Electric field amplitude, E0 = 3.1 N/C
Angular frequency, ω = 5.4 × 108 rad/s
Wave number, k = 1.8 rad/m
Wavelength,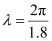 = 3.490 m
= 3.490 m
- #11-cWhat is the frequency ν?Ans : Frequency of wave is given as:
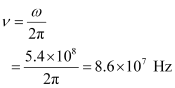
- #11-dWhat is the amplitude of the magnetic field part of the wave?Ans : Magnetic field strength is given as:
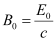
Where,
c = Speed of light = 3 × 108 m/s

- #11-eWrite an expression for the magnetic field part of the wave.Ans : On observing the given vector field, it can be observed that the magnetic field vector is directed along the negative z direction. Hence, the general equation for the magnetic field vector is written as:
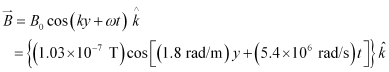
- Qstn #12About 5% of the power of a 100 W light bulb is converted to visible radiation. What is the average intensity of visible radiation
Ans : Power rating of bulb, P = 100 W
It is given that about 5% of its power is converted into visible radiation.
 Power of visible radiation,
Power of visible radiation,
Hence, the power of visible radiation is 5W.
- #12-aat a distance of 1 m from the bulb?Ans : Distance of a point from the bulb, d = 1 m
Hence, intensity of radiation at that point is given as:
