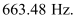NEET-XII-Physics
07: Alternating Current
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- Qstn #15A 100 μF capacitor in series with a 40 ``\Omega`` resistance is connected to a 110 V, 60 Hz supply.
Ans : Capacitance of the capacitor, C = 100 μF = 100 × 10-6 F
Resistance of the resistor, R = 40 ``\Omega``
Supply voltage, V = 110 V
- #15-aWhat is the maximum current in the circuit?Ans : Frequency of oscillations, ν= 60 Hz
Angular frequency,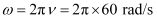
For a RC circuit, we have the relation for impedance as:
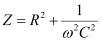
Peak voltage, V0 =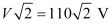
Maximum current is given as:
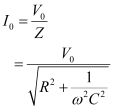
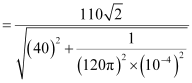
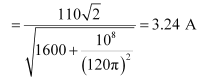
- #15-bWhat is the time lag between the current maximum and the voltage maximum?Ans : In a capacitor circuit, the voltage lags behind the current by a phase angle ofΦ. This angle is given by the relation:
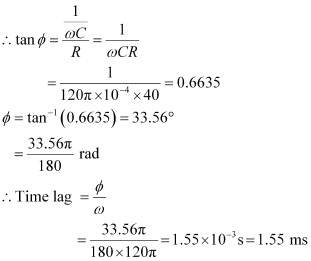
Hence, the time lag between maximum current and maximum voltage is 1.55 ms.
- Qstn #16Obtain the answers to (a) and (b) in Exercise 7.15 if the circuit is connected to a 110 V, 12 kHz supply? Hence, explain the statement that a capacitor is a conductor at very high frequencies. Compare this behaviour with that of a capacitor in a dc circuit after the steady state.
Ans : Capacitance of the capacitor, C = 100 μF = 100 × 10-6 F
Resistance of the resistor, R = 40 ``\Omega``
Supply voltage, V = 110 V
Frequency of the supply, ν = 12 kHz = 12 × 103 Hz
Angular Frequency, ω = 2 ``\pi``ν= 2 × ``\pi`` × 12 × 10303
= 24``\pi`` × 103 rad/s
Peak voltage,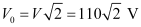
Maximum current,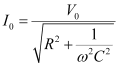
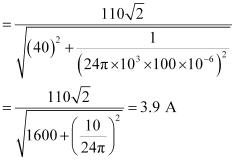
For an RC circuit, the voltage lags behind the current by a phase angle of Φ given as:

Hence, Φ tends to become zero at high frequencies. At a high frequency, capacitor C acts as a conductor.
In a dc circuit, after the steady state is achieved, ω = 0. Hence, capacitor C amounts to an open circuit.
- Qstn #17Keeping the source frequency equal to the resonating frequency of the series LCR circuit, if the three elements, L, C and R are arranged in parallel, show that the total current in the parallel LCR circuit is minimum at this frequency. Obtain the current rms value in each branch of the circuit for the elements and source specified in Exercise 7.11 for this frequency.
Ans : An inductor (L), a capacitor (C), and a resistor (R) is connected in parallel with each other in a circuit where,
L = 5.0 H
C = 80 μF = 80 × 10-6 F
R = 40 ``\Omega``
Potential of the voltage source, V = 230 V
Impedance (Z) of the given parallel LCR circuit is given as:
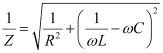
Where,
ω = Angular frequency
At resonance,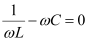
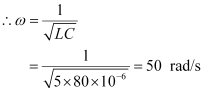
Hence, the magnitude of Z is the maximum at 50 rad/s. As a result, the total current is minimum.
Rms current flowing through inductor L is given as:
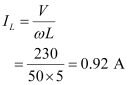
Rms current flowing through capacitor C is given as:
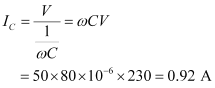
Rms current flowing through resistor R is given as:
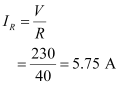
- Qstn #18A circuit containing a 80 mH inductor and a 60 μF capacitor in series is connected to a 230 V, 50 Hz supply. The resistance of the circuit is negligible.
Ans : Inductance, L = 80 mH = 80 × 10-3 H
Capacitance, C = 60 μF = 60 × 10-6 F
Supply voltage, V = 230 V
Frequency, ν = 50 Hz
Angular frequency, ω = 2``\pi``ν= 100 ``\pi`` rad/s
Peak voltage, V0 =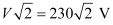
- #18-aObtain the current amplitude and rms values.Ans : Maximum current is given as:
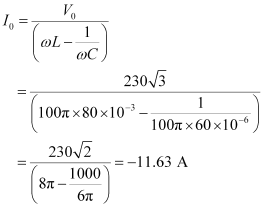
The negative sign appears because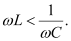
Amplitude of maximum current,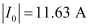
Hence, rms value of current,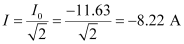
- #18-bObtain the rms values of potential drops across each element.Ans : Potential difference across the inductor,
VL= I × ωL
= 8.22 × 100 ``\pi`` × 80 × 10-3
= 206.61 V
Potential difference across the capacitor,

- #18-cWhat is the average power transferred to the inductor?Ans : Average power consumed by the inductor is zero as actual voltage leads the current by
 .
.
- #18-dWhat is the average power transferred to the capacitor?Ans : Average power consumed by the capacitor is zero as voltage lags current by
 .
.
- #18-eWhat is the total average power absorbed by the circuit? [‘Average’ implies ‘averaged over one cycle’.]Ans : The total power absorbed (averaged over one cycle) is zero.
- Qstn #19Suppose the circuit in Exercise 7.18 has a resistance of 15 ``\Omega``. Obtain the average power transferred to each element of the circuit, and the total power absorbed.
Ans : Average power transferred to the resistor = 788.44 W
Average power transferred to the capacitor = 0 W
Total power absorbed by the circuit = 788.44 W
Inductance of inductor, L = 80 mH = 80 × 10-3 H
Capacitance of capacitor, C = 60 μF = 60 × 10-6 F
Resistance of resistor, R = 15 ``\Omega``
Potential of voltage supply, V = 230 V
Frequency of signal, ν = 50 Hz
Angular frequency of signal, ω = 2``\pi``ν= 2``\pi`` × (50) = 100``\pi`` rad/s
The elements are connected in series to each other. Hence, impedance of the circuit is given as:
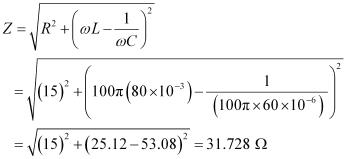
Current flowing in the circuit,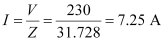
Average power transferred to resistance is given as:
PR= I2R
= (7.25)2 × 15 = 788.44 W
Average power transferred to capacitor, PC = Average power transferred to inductor, PL = 0
Total power absorbed by the circuit:
= PR + PC + PL
= 788.44 + 0 + 0 = 788.44 W
Hence, the total power absorbed by the circuit is 788.44 W.
- Qstn #20A series LCR circuit with L = 0.12 H, C = 480 nF, R = 23 ``\Omega`` is connected to a 230 V variable frequency supply.
(a) What is the source frequency for which current amplitude is maximum. Obtain this maximum value.
(b) What is the source frequency for which average power absorbed by the circuit is maximum. Obtain the value of this maximum power.
(c) For which frequencies of the source is the power transferred to the circuit half the power at resonant frequency? What is the current amplitude at these frequencies?
(d) What is the Q-factor of the given circuit?
(a) What is the source frequency for which current amplitude is maximum. Obtain this maximum value.
(b) What is the source frequency for which average power absorbed by the circuit is maximum. Obtain the value of this maximum power.
(c) For which frequencies of the source is the power transferred to the circuit half the power at resonant frequency? What is the current amplitude at these frequencies?
(d) What is the Q-factor of the given circuit?Ans : Inductance, L = 0.12 H
Capacitance, C = 480 nF = 480 × 10-9 F
Resistance, R = 23 ``\Omega``
Supply voltage, V = 230 V
Peak voltage is given as:
V0 = = 325.22 V
= 325.22 V
(a) Current flowing in the circuit is given by the relation,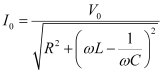
Where,
I0 = maximum at resonance
At resonance, we have
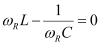
Where,
ωR = Resonance angular frequency
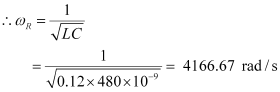
∴Resonant frequency,
And, maximum current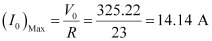
(b) Maximum average power absorbed by the circuit is given as:
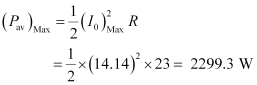
Hence, resonant frequency ( ) is
) is 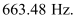


(c) The power transferred to the circuit is half the power at resonant frequency.
Frequencies at which power transferred is half, =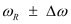
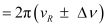
Where,
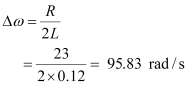
Hence, change in frequency,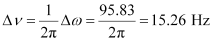
∴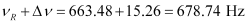
And,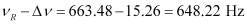
Hence, at 648.22 Hz and 678.74 Hz frequencies, the power transferred is half.
At these frequencies, current amplitude can be given as:
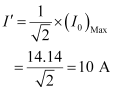
(d) Q-factor of the given circuit can be obtained using the relation,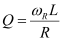
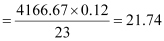
Hence, the Q-factor of the given circuit is 21.74.
(a) Current flowing in the circuit is given by the relation,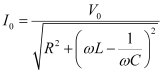
Where,
I0 = maximum at resonance
At resonance, we have
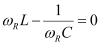
Where,
ωR = Resonance angular frequency
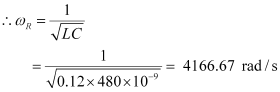
∴Resonant frequency,
And, maximum current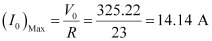
(b) Maximum average power absorbed by the circuit is given as:
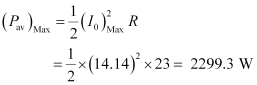
Hence, resonant frequency ( ) is
) is 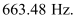


(c) The power transferred to the circuit is half the power at resonant frequency.
Frequencies at which power transferred is half, =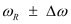
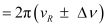
Where,
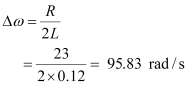
Hence, change in frequency,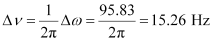
∴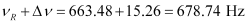
And,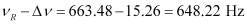
Hence, at 648.22 Hz and 678.74 Hz frequencies, the power transferred is half.
At these frequencies, current amplitude can be given as:
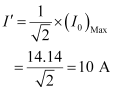
(d) Q-factor of the given circuit can be obtained using the relation,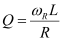
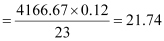
Hence, the Q-factor of the given circuit is 21.74.
- #20-aWhat is the source frequency for which current amplitude is maximum. Obtain this maximum value.Ans : Current flowing in the circuit is given by the relation,
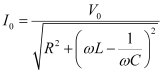
Where,
I0 = maximum at resonance
At resonance, we have
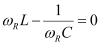
Where,
ωR = Resonance angular frequency
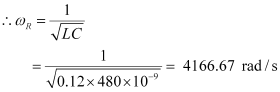
∴Resonant frequency,
And, maximum current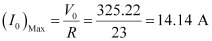
- #20-bWhat is the source frequency for which average power absorbed by the circuit is maximum. Obtain the value of this maximum power.Ans : Maximum average power absorbed by the circuit is given as:
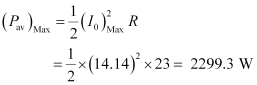
Hence, resonant frequency ( ) is
) is