NEET-XII-Physics
07: Alternating Current
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #Chapter 7 - Alternating Current
- Qstn #1A 100 ``\Omega`` resistor is connected to a 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply.
Ans : Resistance of the resistor, R = 100 ``\Omega``
Supply voltage, V = 220 V
Frequency, ν = 50 Hz
- #1-aWhat is the rms value of current in the circuit?Ans : The rms value of current in the circuit is given as:
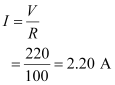
- #1-bWhat is the net power consumed over a full cycle?Ans : The net power consumed over a full cycle is given as:
P = VI
= 220 × 2.2 = 484 W
- #2
- #2-aThe peak voltage of an ac supply is 300 V. What is the rms voltage?Ans : Peak voltage of the ac supply, V0 = 300 V
Rms voltage is given as:
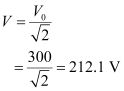
- #2-bThe rms value of current in an ac circuit is 10 A. What is the peak current?Ans : Therms value of current is given as:
I = 10 A
Now, peak current is given as:
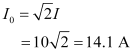
- Qstn #3A 44 mH inductor is connected to 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply. Determine the rms value of the current in the circuit.
Ans : Inductance of inductor, L = 44 mH = 44 × 10-3 H
Supply voltage, V = 220 V
Frequency, ν = 50 Hz
Angular frequency, ω=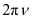
Inductive reactance, XL = ω L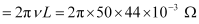
Rms value of current is given as:
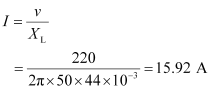
Hence, the rms value of current in the circuit is 15.92 A.
- Qstn #4A 60 μF capacitor is connected to a 110 V, 60 Hz ac supply. Determine the rms value of the current in the circuit.
Ans : Capacitance of capacitor, C = 60 μF = 60 × 10-6 F
Supply voltage, V = 110 V
Frequency, ν = 60 Hz
Angular frequency, ω=.gif)
Capacitive reactance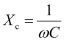
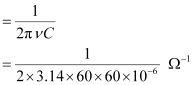
Rms value of current is given as:
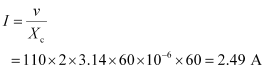
Hence, the rms value of current is 2.49 A.
- Qstn #5In Exercises 7.3 and 7.4, what is the net power absorbed by each circuit over a complete cycle. Explain your answer.
Ans : In the inductive circuit,
Rms value of current, I = 15.92 A
Rms value of voltage, V = 220 V
Hence, the net power absorbed can be obtained by the relation,
P = VI cos Φ
Where,
Φ = Phase difference between V and I
For a pure inductive circuit, the phase difference between alternating voltage and current is 90° i.e., Φ= 90°.
Hence, P = 0 i.e., the net power is zero.
In the capacitive circuit,
Rms value of current, I = 2.49 A
Rms value of voltage, V = 110 V
Hence, the net power absorbed can ve obtained as:
P = VI Cos Φ
For a pure capacitive circuit, the phase difference between alternating voltage and current is 90° i.e., Φ= 90°.
Hence, P = 0 i.e., the net power is zero.
- Qstn #6Obtain the resonant frequency ωr of a series LCR circuit with L = 2.0 H, C = 32 μF and R = 10 ``\Omega``. What is the Q-value of this circuit?
Ans : Inductance, L = 2.0 H
Capacitance, C = 32 μF = 32 × 10-6 F
Resistance, R = 10 ``\Omega``
Resonant frequency is given by the relation,
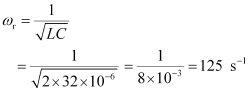
Now, Q-value of the circuit is given as:
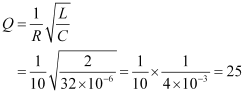
Hence, the Q-Value of this circuit is 25.
- Qstn #7A charged 30 μF capacitor is connected to a 27 mH inductor. What is the angular frequency of free oscillations of the circuit?
Ans : Capacitance, C = 30μF = 30×10-6F
Inductance, L = 27 mH = 27 × 10-3 H
Angular frequency is given as:
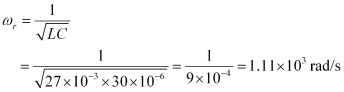
Hence, the angular frequency of free oscillations of the circuit is 1.11 × 103 rad/s.
- Qstn #8Suppose the initial charge on the capacitor in Exercise 7.7 is 6 mC. What is the total energy stored in the circuit initially? What is the total energy at later time?
Ans : Capacitance of the capacitor, C = 30 μF = 30×10-6 F
Inductance of the inductor, L = 27 mH = 27 × 10-3 H
Charge on the capacitor, Q = 6 mC = 6 × 10-3 C
Total energy stored in the capacitor can be calculated by the relation,
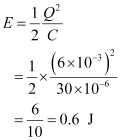
Total energy at a later time will remain the same because energy is shared between the capacitor and the inductor.
- Qstn #9A series LCR circuit with R = 20 ``\Omega``, L = 1.5 H and C = 35 μF is connected to a variable-frequency 200 V ac supply. When the frequency of the supply equals the natural frequency of the circuit, what is the average power transferred to the circuit in one complete cycle?
Ans : At resonance, the frequency of the supply power equals the natural frequency of the given LCR circuit.
Resistance, R = 20 ``\Omega``
Inductance, L = 1.5 H
Capacitance, C = 35 μF = 30 × 10-6 F
AC supply voltage to the LCR circuit, V = 200 V
Impedance of the circuit is given by the relation,
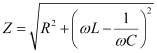
At resonance,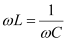
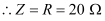
Current in the circuit can be calculated as:
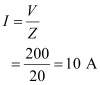
Hence, the average power transferred to the circuit in one complete cycle= VI
= 200 × 10 = 2000 W.
- Qstn #10A radio can tune over the frequency range of a portion of MW broadcast band: (800 kHz to 1200 kHz). If its LC circuit has an effective inductance of 200 μH, what must be the range of its variable capacitor?
[Hint: For tuning, the natural frequency i.e., the frequency of free oscillations of the LC circuit should be equal to the frequency of the radiowave.]
Ans : The range of frequency (ν) of a radio is 800 kHz to 1200 kHz.
Lower tuning frequency, ν1 = 800 kHz = 800 × 103 Hz
Upper tuning frequency, ν2 = 1200 kHz = 1200× 103 Hz
Effective inductance of circuit L = 200 μH = 200 × 10-6 H
Capacitance of variable capacitor for ν1 is given as:
C1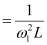
Where,
ω1 = Angular frequency for capacitor C1
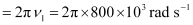
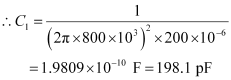
Capacitance of variable capacitor for ν2,
C2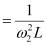
Where,
ω2 = Angular frequency for capacitor C2
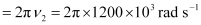
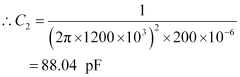
Hence, the range of the variable capacitor is from 88.04 pF to 198.1 pF.