NEET-XII-Chemistry
01: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- #10Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halides with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
() 1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
() 2-Chloro-2-methylbutane
() 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane.
() 1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
() 2-Chloro-2-methylbutane
() 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane.Ans : null ()(2).png)
In the given compound, there are two types ofβ-hydrogen atoms are present. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of this compound gives twoalkenes.
.png) ​
​
()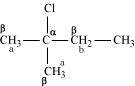
In the given compound, there are two different sets of equivalent β-hydrogen atoms labelled as a and b. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of the compound yields two alkenes.
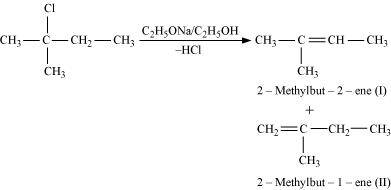
Saytzeff’s rule implies that in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to a doubly bonded carbon atoms is preferably produced.
Therefore, alkene (I) i.e., 2-methylbut-2-ene is the major product in this reaction.
() 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
In the given compound, there are two different sets of equivalent β-hydrogen atoms labelled as a and b. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of the compound yields two alkenes.
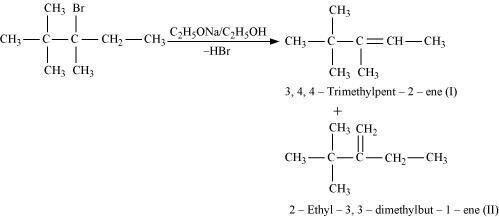
According to Saytzeff’s rule, in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atom is preferably formed.
Hence, alkene (I) i.e., 3,4,4-trimethylpent-2-ene is the major product in this reaction.
()(2).png)
In the given compound, there are two types ofβ-hydrogen atoms are present. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of this compound gives twoalkenes.
.png) ​
​
()
In the given compound, there are two different sets of equivalent β-hydrogen atoms labelled as a and b. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of the compound yields two alkenes.

Saytzeff’s rule implies that in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to a doubly bonded carbon atoms is preferably produced.
Therefore, alkene (I) i.e., 2-methylbut-2-ene is the major product in this reaction.
() 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
In the given compound, there are two different sets of equivalent β-hydrogen atoms labelled as a and b. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of the compound yields two alkenes.

According to Saytzeff’s rule, in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atom is preferably formed.
Hence, alkene (I) i.e., 3,4,4-trimethylpent-2-ene is the major product in this reaction.
- #10-i1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexaneAns :
(2).png)
In the given compound, there are two types ofβ-hydrogen atoms are present. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of this compound gives twoalkenes.
.png) ​
​
- #10-ii2-Chloro-2-methylbutaneAns :

In the given compound, there are two different sets of equivalent β-hydrogen atoms labelled as a and b. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of the compound yields two alkenes.

Saytzeff’s rule implies that in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to a doubly bonded carbon atoms is preferably produced.
Therefore, alkene (I) i.e., 2-methylbut-2-ene is the major product in this reaction.
- #10-iii2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane.Ans :
 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
In the given compound, there are two different sets of equivalent β-hydrogen atoms labelled as a and b. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of the compound yields two alkenes.

According to Saytzeff’s rule, in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atom is preferably formed.
Hence, alkene (I) i.e., 3,4,4-trimethylpent-2-ene is the major product in this reaction.