NEET-XII-Chemistry
01: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- Qstn #9-ii(CH3)3CCl or CH3ClAns :
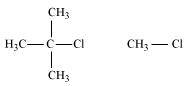
The SN2 mechanism involves the attack of the nucleophile at the atom bearing the leaving group. But, in case of (CH3)3CCl, the attack of the nucleophile at the carbon atom is hindered because of the presence of bulky substituents on that carbon atom bearing the leaving group. On the other hand, there are no bulky substituents on the carbon atom bearing the leaving group in CH3Cl. Hence, CH3Cl reacts faster than (CH3)3CCl in SN2 reaction with OH-.
- Qstn #10Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halides with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
- Qstn #10-i1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexaneAns :
(2).png)
In the given compound, there are two types ofβ-hydrogen atoms are present. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of this compound gives twoalkenes.
.png) ​
​
- Qstn #10-ii2-Chloro-2-methylbutaneAns :
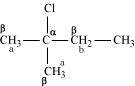
In the given compound, there are two different sets of equivalent β-hydrogen atoms labelled as a and b. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of the compound yields two alkenes.
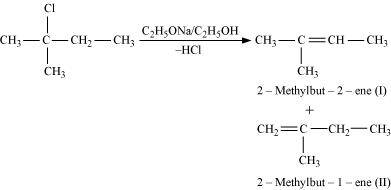
Saytzeff’s rule implies that in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to a doubly bonded carbon atoms is preferably produced.
Therefore, alkene (I) i.e., 2-methylbut-2-ene is the major product in this reaction.
- Qstn #10-iii2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane.Ans :
 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
In the given compound, there are two different sets of equivalent β-hydrogen atoms labelled as a and b. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of the compound yields two alkenes.
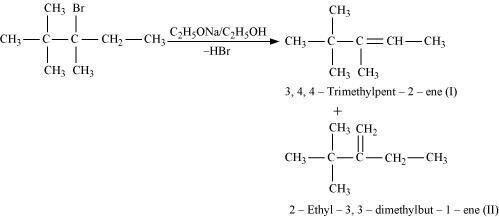
According to Saytzeff’s rule, in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atom is preferably formed.
Hence, alkene (I) i.e., 3,4,4-trimethylpent-2-ene is the major product in this reaction.

.png)
.png)

.png)