NEET-XII-Chemistry
05: Biomolecules
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
No item to list.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #5 - Biomolecules
- #Section : ISECTION I Page No 412:
- Qstn #1Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water. Explain.
Ans : A glucose molecule contains five -OH groups while a sucrose molecule contains eight -OH groups. Thus, glucose and sucrose undergo extensive H-bonding with water.
Hence, these are soluble in water.
But cyclohexane and benzene do not contain -OH groups. Hence, they cannot undergo H-bonding with water and as a result, are insoluble in water.
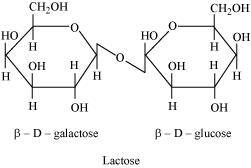
- Qstn #2What are the expected products of hydrolysis of lactose?
Ans : Lactose is composed of β-D galactose and β-D glucose. Thus, on hydrolysis, it gives β-D galactose and β-D glucose.
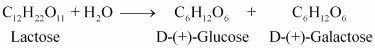
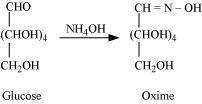
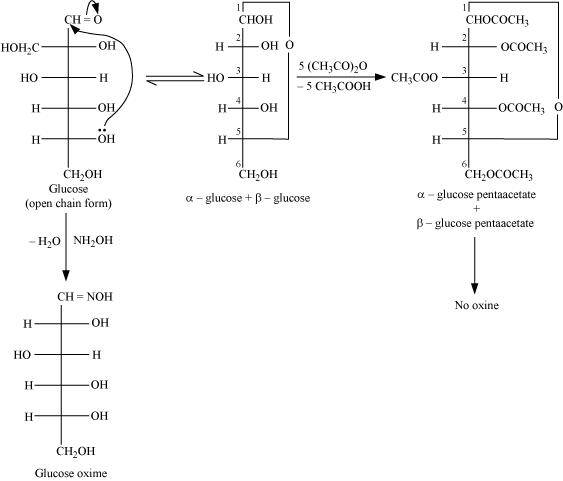
- Qstn #3How do you explain the absence of aldehyde group in the pentaacetate of D-glucose?
Ans : D-glucose reacts with hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to form an oxime because of the presence of aldehydic (-CHO) group or carbonyl carbon. This happens as the cyclic structure of glucose forms an open chain structure in an aqueous medium, which then reacts with NH2OH to give an oxime.
But pentaacetate of D-glucose does not react with NH2OH. This is because pentaacetate does not form an open chain structure.
- Qstn #4The melting points and solubility in water of amino acids are generally higher than that of the corresponding halo acids. Explain.
Ans : Both acidic (carboxyl) as well as basic (amino) groups are present in the same molecule of amino acids. In aqueous solutions, the carboxyl group can lose a proton and the amino group can accept a proton, thus giving rise to a dipolar ion known as a zwitter ion.
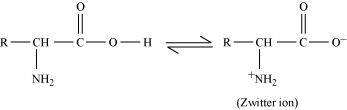
Due to this dipolar behaviour, they have strong electrostatic interactions within them and with water. But halo-acids do not exhibit such dipolar behaviour.
For this reason, the melting points and the solubility of amino acids in water is higher than those of the corresponding halo-acids.
- Qstn #5Where does the water present in the egg go after boiling the egg?
Ans : When an egg is boiled, the proteins present inside the egg get denatured and coagulate. After boiling the egg, the water present in it is absorbed by the coagulated protein through H-bonding.
- Qstn #6Why cannot vitamin C be stored in our body?
Ans : Vitamin C cannot be stored in our body because it is water soluble. As a result, it is readily excreted in the urine.
- Qstn #7What products would be formed when a nucleotide from DNA containing thymine is hydrolysed?
Ans : When a nucleotide from the DNA containing thymine is hydrolyzed, thymine β-D-2-deoxyribose and phosphoric acid are obtained as products.
- Qstn #8When RNA is hydrolysed, there is no relationship among the quantities of different bases obtained. What does this fact suggest about the structure of RNA?
Ans : A DNA molecule is double-stranded in which the pairing of bases occurs. Adenine always pairs with thymine, while cytosine always pairs with guanine. Therefore, on hydrolysis of DNA, the quantity of adenine produced is equal to that of thymine and similarly, the quantity of cytosine is equal to that of guanine.
But when RNA is hydrolyzed, there is no relationship among the quantities of the different bases obtained. Hence, RNA is single-stranded.
- #Section : IISECTION I Page No 423:
- Qstn #1What are monosaccharides?
Ans : Monosaccharides are carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolysed further to give simpler units of polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone.
Monosaccharides are classified on the bases of number of carbon atoms and the functional group present in them. Monosaccharides containing an aldehyde group are known as aldoses and those containing a keto group are known as ketoses. Monosaccharides are further classified as trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses, and heptoses according to the number of carbon atoms they contain. For example, a ketose containing 3 carbon atoms is called ketotriose and an aldose containing 3 carbon atoms is called aldotriose.
- Qstn #2What are reducing sugars?
Ans : Reducing sugars are carbohydrates that reduce Fehling’s solution and Tollen’s reagent. All monosaccharides and disaccharides, excluding sucrose, are reducing sugars.
- Qstn #3Write two main functions of carbohydrates in plants.
Ans : Two main functions of carbohydrates in plants are:
( i) Polysaccharides such as starch serve as storage molecules.
(ii) Cellulose, a polysaccharide, is used to build the cell wall.
- Qstn #4Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides.
Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, maltose, galactose, fructose and lactose
Ans : Monosaccharides:
Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, galactose, fructose
Disaccharides:
Maltose, lactose