NEET-XII-Chemistry
07: The p-Block Elements
- Qstn #7Illustrate how copper metal can give different products on reaction with HNO3.
Ans : Concentrated nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent. It is used for oxidizing most metals. The products of oxidation depend on the concentration of the acid, temperature, and also on the material undergoing oxidation.
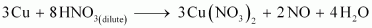
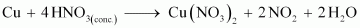
- Qstn #9The HNH angle value is higher than HPH, HAsH and HSbH angles. Why? [Hint: Can be explained on the basis of sp3 hybridisation in NH3 and only s-p bonding between hydrogen and other elements of the group].
Ans : Hydride NH3 PH3 AsH3 SbH3
H-M-H angle 107° 92° 91° 90°
The above trend in the H-M-H bond angle can be explained on the basis of the electronegativity of the central atom. Since nitrogen is highly electronegative, there is high electron density around nitrogen. This causes greater repulsion between the electron pairs around nitrogen, resulting in maximum bond angle. We know that electronegativity decreases on moving down a group. Consequently, the repulsive interactions between the electron pairs decrease, thereby decreasing the H-M-H bond angle.
- Qstn #10Why does R3P=O exist but R3N=O does not (R = alkyl group)?
Ans : N (unlike P) lacks the d-orbital. This restricts nitrogen to expand its coordination number beyond four. Hence, R3N=O does not exist.
- Qstn #11Explain why NH3 is basic while BiH3 is only feebly basic.
Ans : NH3 is distinctly basic while BiH3 is feebly basic.
Nitrogen has a small size due to which the lone pair of electrons is concentrated in a small region. This means that the charge density per unit volume is high. On moving down a group, the size of the central atom increases and the charge gets distributed over a large area decreasing the electron density. Hence, the electron donating capacity of group 15 element hydrides decreases on moving down the group.
- Qstn #12Nitrogen exists as diatomic molecule and phosphorus as P4. Why?
Ans : Nitrogen owing to its small size has a tendency to form p``\pi``-p``\pi`` multiple bonds with itself. Nitrogen thus forms a very stable diatomic molecule, N2. On moving down a group, the tendency to form p``\pi``-p``\pi`` bonds decreases (because of the large size of heavier elements). Therefore, phosphorus (like other heavier metals) exists in the P4 state.
- Qstn #13Write main differences between the properties of white phosphorus and red phosphorus.
Ans :White phosphorus
Red Phosphorus
It is a soft and waxy solid. It possesses a garlic smell. It is a hard and crystalline solid, without any smell. It is poisonous. It is non-poisonous. It is insoluble in water but soluble in carbon disulphide. It is insoluble in both water and carbon disulphide. It undergoes spontaneous combustion in air. It is relatively less reactive. In both solid and vapour states, it exists as a P4 molecule. 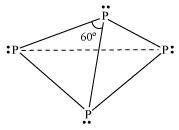
It exists as a chain of tetrahedral P4 units. 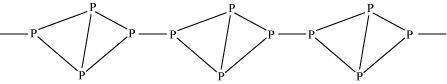
- Qstn #14Why does nitrogen show catenation properties less than phosphorus?
Ans : Catenation is much more common in phosphorous compounds than in nitrogen compounds. This is because of the relative weakness of the N-N single bond as compared to the P-P single bond. Since nitrogen atom is smaller, there is greater repulsion of electron density of two nitrogen atoms, thereby weakening the N-N single bond.
- Qstn #15Give the disproportionation reaction of H3PO3.
Ans : On heating, orthophosphorus acid (H3PO3) disproportionates to give orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4) and phosphine (PH3). The oxidation states of P in various species involved in the reaction are mentioned below.
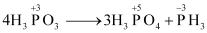
- Qstn #16Can PCl5 act as an oxidising as well as a reducing agent? Justify.
Ans : PCl5 can only act as an oxidizing agent. The highest oxidation state that P can show is +5. In PCl5, phosphorus is in its highest oxidation state (+5). However, it can decrease its oxidation state and act as an oxidizing agent.
- Qstn #17Justify the placement of O, S, Se, Te and Po in the same group of the periodic table in terms of electronic configuration, oxidation state and hydride formation.
Ans : The elements of group 16 are collectively called chalcogens.
(i) Elements of group 16 have six valence electrons each. The general electronic configuration of these elements is ns2 np4, where n varies from 2 to 6.
(ii) Oxidation state:
As these elements have six valence electrons (ns2 np4), they should display an oxidation state of -2. However, only oxygen predominantly shows the oxidation state of -2 owing to its high electronegativity. It also exhibits the oxidation state of -1 (H2O2), zero (O2), and +2 (OF2). However, the stability of the -2 oxidation state decreases on moving down a group due to a decrease in the electronegativity of the elements. The heavier elements of the group show an oxidation state of +2, +4, and +6 due to the availability of d-orbitals.
(iii) Formation of hydrides:
These elements form hydrides of formula H2E, where E = O, S, Se, Te, PO. Oxygen and sulphur also form hydrides of type H2E2. These hydrides are quite volatile in nature.
- Qstn #18Why is dioxygen a gas but sulphur a solid?
Ans : Oxygen is smaller in size as compared to sulphur. Due to its smaller size, it can effectively form p``\pi``-p``\pi`` bonds and form O2 (O==O) molecule. Also, the intermolecular forces in oxygen are weak van der Wall’s, which cause it to exist as gas. On the other hand, sulphur does not form M2 molecule but exists as a puckered structure held together by strong covalent bonds. Hence, it is a solid.
- Qstn #19Knowing the electron gain enthalpy values for O → O- and O → O2- as -141
and 702 kJ mol-1 respectively, how can you account for the formation of a
large number of oxides having O2- species and not O-?
(Hint: Consider lattice energy factor in the formation of compounds).
Ans : Stability of an ionic compound depends on its lattice energy. More the lattice energy of a compound, more stable it will be.
Lattice energy is directly proportional to the charge carried by an ion. When a metal combines with oxygen, the lattice energy of the oxide involving O2- ion is much more than the oxide involving O- ion. Hence, the oxide having O2- ions are more stable than oxides having O-. Hence, we can say that formation of O2- is energetically more favourable than formation of O-.
- Qstn #20Which aerosols deplete ozone?
Ans : Freons or chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are aerosols that accelerate the depletion of ozone. In the presence of ultraviolet radiations, molecules of CFCs break down to form chlorine-free radicals that combine with ozone to form oxygen.
- Qstn #21Describe the manufacture of H2SO4 by contact process?
Ans : Sulphuric acid is manufactured by the contact process. It involves the following steps:
Step (i):
Sulphur or sulphide ores are burnt in air to form SO2.
Step (ii):
By a reaction with oxygen, SO2 is converted into SO3 in the presence of V2O5 as a catalyst.
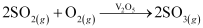
Step (iii):
SO3 produced is absorbed on H2SO4 to give H2S2O7 (oleum).
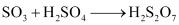
This oleum is then diluted to obtain H2SO4 of the desired concentration.
In practice, the plant is operated at 2 bar (pressure) and 720 K (temperature). The sulphuric acid thus obtained is 96-98% pure.
(1).png)