NEET-XII-Chemistry
06: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- #6 - General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- #Section : ISECTION I Page No 150:
- Qstn #1Which of the ores mentioned in Table 6.1 can be concentrated by magnetic separation method?
Ans : If the ore or the gangue can be attracted by the magnetic field, then the ore can be concentrated by the process of magnetic separation. Among the ores mentioned in table 6.1, the ores of iron such as haematite (``\ce{Fe2O3}``), magnetite (Fe3O4), siderite (``\ce{FeCO3}``), and iron pyrites (FeS2) can be separated by the process of magnetic separation.
- Qstn #2What is the significance of leaching in the extraction of aluminium?
Ans : In the extraction of aluminium, the significance of leaching is to concentrate pure alumina (Al2O3) from bauxite ore.
Bauxite usually contains silica, iron oxide, and titanium oxide as impurities. In the process of leaching, alumina is concentrated by digesting the powdered ore with a concentrated solution of NaOH at 473-523 K and 35-36 bar. Under these conditions, alumina (Al2O3) dissolves as sodium meta-aluminate and silica (SiO2) dissolves as sodium silicate leaving the impurities behind.
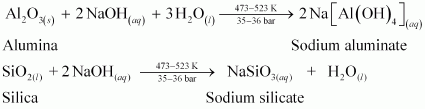
The impurities are then filtered and the solution is neutralized by passing CO2 gas. In this process, hydrated Al2O3 gets precipitated and sodium silicate remains in the solution. Precipitation is induced by seeding the solution with freshly prepared samples of hydrated Al2O3.

Hydrated alumina thus obtained is filtered, dried, and heated to give back pure alumina (Al2O3).
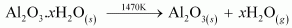
- Qstn #3The reaction,
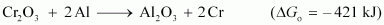
is thermodynamically feasible as is apparent from the Gibbs energy value.
Why does it not take place at room temperature?
Ans : The change in Gibbs energy is related to the equilibrium constant, K as
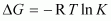 .
.
At room temperature, all reactants and products of the given reaction are in the solid state. As a result, equilibrium does not exist between the reactants and the products. Hence, the reaction does not take place at room temperature. However, at a higher temperature, chromium melts and the reaction takes place.
We also know that according to the equation
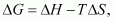
Increasing the temperature increases the value of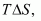 making the value of
making the value of 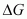 more and more negative. Therefore, the reaction becomes more and more feasible as the temperature is increased.
more and more negative. Therefore, the reaction becomes more and more feasible as the temperature is increased.
- Qstn #4Is it true that under certain conditions, Mg can reduce SiO2 and Si can reduce MgO? What are those conditions?
Ans :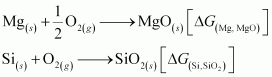
The temperature range in which is lesser than
is lesser than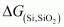 , Mg can reduce SiO2 to Si.
, Mg can reduce SiO2 to Si.
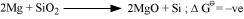
On the other hand, the temperatures range in which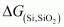 is less than
is less than , Si can reduce MgO to Mg.
, Si can reduce MgO to Mg.
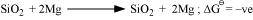
The temperature at which ΔfG curves of these two substances intersect is 1966 K. Thus, at temperatures less than 1966 K, Mg can reduce SiO2 and above 1966 K, Si can reduce MgO.
- #Section : IISECTION I Page No 163:
- Qstn #1Copper can be extracted by hydrometallurgy but not zinc. Explain.
Ans : The reduction potentials of zinc and iron are lower than that of copper. In hydrometallurgy, zinc and iron can be used to displace copper from their solution.
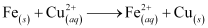
But to displace zinc, more reactive metals i.e., metals having lower reduction potentials than zinc such as Mg, Ca, K, etc. are required. But all these metals react with water with the evolution of H2 gas.
As a result, these metals cannot be used in hydrometallurgy to extract zinc.
Hence, copper can be extracted by hydrometallurgy but not zinc.
- Qstn #2What is the role of depressant in froth floatation process?
Ans : In the froth floatation process, the role of the depressants is to separate two sulphide ores by selectively preventing one ore from forming froth. For example, to separate two sulphide ores (ZnS and Pbs), NaCN is used as a depressant which selectively allows PbS to come with froth, but prevents ZnS from coming to froth. This happens because NaCN reacts with ZnS to form Na2[Zn(CN)4].

- Qstn #3Why is the extraction of copper from pyrites more difficult than that from its
oxide ore through reduction?
Ans : The Gibbs free energy of formation (ΔfG) of Cu2S is less than that of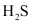 and
and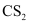 . Therefore, H2 and C cannot reduce Cu2S to Cu.
. Therefore, H2 and C cannot reduce Cu2S to Cu.
On the other hand, the Gibbs free energy of formation of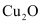 is greater than that of
is greater than that of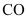 . Hence, C can reduce Cu2O to Cu.
. Hence, C can reduce Cu2O to Cu.
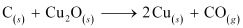
Hence, the extraction of copper from its pyrite ore is difficult than from its oxide ore through reduction.
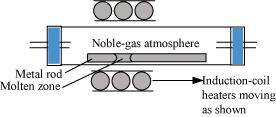
- Qstn #4-iZone refiningAns : Zone refining:
This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the rod also moves with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass onto the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times, which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. Then, the end with the impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, gallium, indium etc. can be purified by this process.
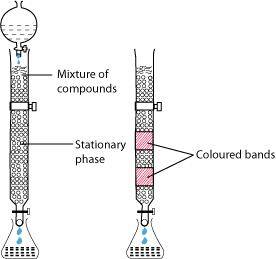
- Qstn #4-iiColumn chromatography.Ans : Column chromatography:
Column chromatography is a technique used to separate different components of a mixture. It is a very useful technique used for the purification of elements available in minute quantities. It is also used to remove the impurities that are not very different in chemical properties from the element to be purified. Chromatography is based on the principle that different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent. In chromatography, there are two phases: mobile phase and stationary phase. The stationary phase is immobile and immiscible. Al2O3 column is usually used as the stationary phase in column chromatography. The mobile phase may be a gas, liquid, or supercritical fluid in which the sample extract is dissolved. Then, the mobile phase is forced to move through the stationary phase. The component that is more strongly adsorbed on the column takes a longer time to travel through it than the component that is weakly adsorbed. The adsorbed components are then removed (eluted) using a suitable solvent (eluant).
- Qstn #5Out of C and CO, which is a better reducing agent at 673 K?
Ans : At 673 K, the value of is less than that of
is less than that of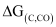 . Therefore, CO can be oxidised more easily to CO2 than C to CO. Hence, CO is a better reducing agent than C at 673 K.
. Therefore, CO can be oxidised more easily to CO2 than C to CO. Hence, CO is a better reducing agent than C at 673 K.
- Qstn #6Name the common elements present in the anode mud in electrolytic refining
of copper. Why are they so present ?
Ans : In electrolytic refining of copper, the common elements present in anode mud are selenium, tellurium, silver, gold, platinum, and antimony.
These elements are very less reactive and are not affected during the purification process. Hence, they settle down below the anode as anode mud.