NEET-XII-Chemistry
06: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Qstn #7Write down the reactions taking place in different zones in the blast furnace
during the extraction of iron.
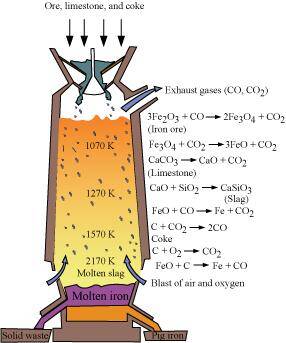
Ans : During the extraction of iron, the reduction of iron oxides takes place in the blast furnace. In this process, hot air is blown from the bottom of the furnace and coke is burnt to raise the temperature up to 2200 K in the lower portion itself. The temperature is lower in the upper part. Thus, it is the lower part where the reduction of iron oxides (Fe2O3 and Fe3O4) takes place.
The reactions taking place in the lower temperature range (500 - 800 K) in the blast furnace are:
3Fe2O3+CO→2Fe3O4+CO2Fe3O4+4CO→3Fe+4CO2Fe2O3+CO→2FeO+CO2The reactions taking place in the higher temperature range (900 - 1500 K) in the blast furnace are:
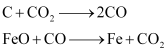
The silicate impurity of the ore is removed as slag by calcium oxide (CaO), which is formed by the decomposition of limestone (CaCO3).
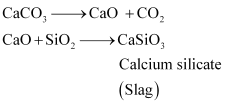
- Qstn #8Write chemical reactions taking place in the extraction of zinc from zinc blende.
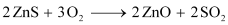
Ans : The different steps involved in the extraction of zinc from zinc blende (ZnS) are given below:
(i) Concentration of ore
First, the gangue from zinc blende is removed by the froth floatation method.

(ii) Conversion to oxide (Roasting)
Sulphide ore is converted into oxide by the process of roasting. In this process, ZnS is heated in a regular supply of air in a furnace at a temperature, which is below the melting point of Zn.
(iii) Extraction of zinc from zinc oxide (Reduction)
Zinc is extracted from zinc oxide by the process of reduction. The reduction of zinc oxide is carried out by mixing it with powdered coke and then, heating it at 673 K.
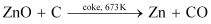
(iv) Electrolytic Refining
Zinc can be refined by the process of electrolytic refining. In this process, impure zinc is made the anode while a pure copper strip is made the cathode. The electrolyte used is an acidified solution of zinc sulphate (ZnSO4). Electrolysis results in the transfer of zinc in pure from the anode to the cathode.
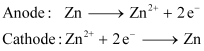
- Qstn #9State the role of silica in the metallurgy of copper.
Ans : During the roasting of pyrite ore, a mixture of FeO and Cu2O is obtained.
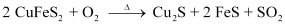
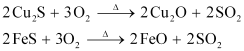
The role of silica in the metallurgy of copper is to remove the iron oxide obtained during the process of roasting as ‘slag’. If the sulphide ore of copper contains iron, then silica (SiO2) is added as flux before roasting. Then, FeO combines with silica to form iron silicate, FeSiO3 (slag).
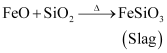
- Qstn #10What is meant by the term “chromatography”?
Ans : Chromatography is a collective term used for a family of laboratory techniques for the separation of mixtures. The term is derived from Greek words ‘chroma’ meaning ‘colour’ and ‘graphein’ meaning ‘to write’. Chromatographic techniques are based on the principle that different components are absorbed differently on an absorbent. There are several chromatographic techniques such as paper chromatography, column chromatography, gas chromatography, etc.
- Qstn #11What criterion is followed for the selection of the stationary phase in chromatography?Ans : The stationary phase is selected in such a way that the components of the sample have different solubility’s in the phase. Hence, different components have different rates of movement through the stationary phase and as a result, can be separated from each other.
- Qstn #12Describe a method for refining nickel.
Ans : Nickel is refined by Mond’s process. In this process, nickel is heated in the presence of carbon monoxide to form nickel tetracarbonyl, which is a volatile complex.
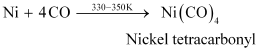
Then, the obtained nickel tetracarbonyl is decomposed by subjecting it to a higher temperature (450 - 470 K) to obtain pure nickel metal.
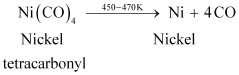
- Qstn #13How can you separate alumina from silica in bauxite ore associated with
silica? Give equations, if any.
Ans : To separate alumina from silica in bauxite ore associated with silica, first the powdered ore is digested with a concentrated NaOH solution at 473 - 523 K and 35 - 36 bar pressure. This results in the leaching out of alumina (Al2O3) as sodium aluminate and silica (SiO2) as sodium silicate leaving the impurities behind.
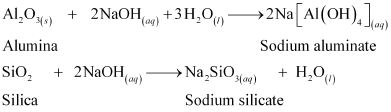
Then, CO2 gas is passed through the resulting solution to neutralize the aluminate in the solution, which results in the precipitation of hydrated alumina. To induce precipitation, the solution is seeded with freshly prepared samples of hydrated alumina.
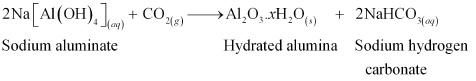
During this process, sodium silicate remains in the solution. The obtained hydrated alumina is filtered, dried, and heated to get back pure alumina.
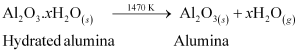
- Qstn #14Giving examples, differentiate between ‘roasting’ and ‘calcination’.
Ans : Roasting is the process of converting sulphide ores to oxides by heating the ores in a regular supply of air at a temperature below the melting point of the metal. For example, sulphide ores of Zn, Pb, and Cu are converted to their respective oxides by this process.

On the other hand, calcination is the process of converting hydroxide and carbonate ores to oxides by heating the ores either in the absence or in a limited supply of air at a temperature below the melting point of the metal. This process causes the escaping of volatile matter leaving behind the metal oxide. For example, hydroxide of Fe, carbonates of Zn, Ca, Mg are converted to their respective oxides by this process.
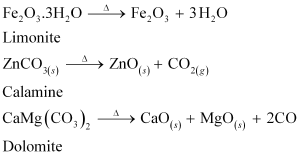
- Qstn #15How is ‘cast iron’ different from ‘pig iron”?
Ans : The iron obtained from blast furnaces is known as pig iron. It contains around 4% carbon and many impurities such as S, P, Si, Mn in smaller amounts.
Cast iron is obtained by melting pig iron and coke using a hot air blast. It contains a lower amount of carbon (3%) than pig iron. Unlike pig iron, cast iron is extremely hard and brittle.
- Qstn #16Differentiate between “minerals” and “ores”.
Ans : Minerals are naturally occurring chemical substances containing metals. They are found in the Earth’s crust and are obtained by mining.
Ores are rocks and minerals viable to be used as a source of metal.
For example, there are many minerals containing zinc, but zinc cannot be extracted profitably (conveniently and economically) from all these minerals.
Zinc can be obtained from zinc blende (ZnS), calamine (ZnCO3), Zincite (ZnO) etc.
Thus, these minerals are called ores of zinc.
- Qstn #17Why copper matte is put in silica lined converter?
Ans : Copper matte contains Cu2S and FeS. Copper matte is put in a silica-lined converter to remove the remaining FeO and FeS present in the matte as slag (FeSiO3). Also, some silica is added to the silica-lined converter. Then, a hot air blast is blown. As a result, the remaining FeS and FeO are converted to iron silicate (FeSiO3) and Cu2S is converted into metallic copper.

- Qstn #18What is the role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium?
Ans : Cryolite (Na3AlF6) has two roles in the metallurgy of aluminium:
1. To decrease the melting point of the mixture from 2323 K to 1140 K.
2. To increase the electrical conductivity of Al2O3.
- Qstn #19How is leaching carried out in case of low grade copper ores?
Ans : In case of low grade copper ores, leaching is carried out using acid or bacteria in the presence of air. In this process, copper goes into the solution as Cu2+ ions.
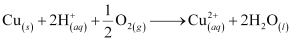
The resulting solution is treated with scrap iron or H2 to get metallic copper.
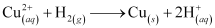
- Qstn #20Why is zinc not extracted from zinc oxide through reduction using CO?
Ans : The standard Gibbs free energy of formation of ZnO from Zn
is lower than that of CO2 from CO. Therefore, CO cannot reduce ZnO to Zn. Hence, Zn is not extracted from ZnO through reduction using CO.
- Qstn #21The value of
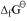 for formation of Cr2O3 is - 540 kJmol-1 and that of Al2 O3 is - 827 kJmol-1. Is the reduction of Cr2O3 possible with Al?
for formation of Cr2O3 is - 540 kJmol-1 and that of Al2 O3 is - 827 kJmol-1. Is the reduction of Cr2O3 possible with Al?
Ans : The value of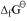 for the formation of Cr2O3 from Cr (-540 kJmol-1) is higher than that of Al2O3 from Al (-827 kJmol-1). Therefore, Al can reduce Cr2O3 to Cr. Hence, the reduction of Cr2O3 with Al is possible.
for the formation of Cr2O3 from Cr (-540 kJmol-1) is higher than that of Al2O3 from Al (-827 kJmol-1). Therefore, Al can reduce Cr2O3 to Cr. Hence, the reduction of Cr2O3 with Al is possible.
Alternatively,

Subtracting equation (ii) from (i), we have
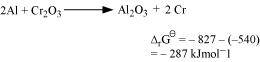
As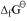 for the reduction reaction of Cr2O3 by Al is negative, this reaction is possible.
for the reduction reaction of Cr2O3 by Al is negative, this reaction is possible.