ICSE-X-Mathematics
Previous Year Paper year:2018
- #5-b [3]A man invests Rs. 22,500 in Rs. 50 shares available at 10% discount. If the dividend
paid by the company is 12%, calculate:Ans : Face Value (FV)`` = 50 \ Rs. ,\ Discount\ = 10\%``
Market Value (MV)`` = 50 - \frac{10}{100} \times 50 = 45 Rs.``
Total Investment = ``22500 \ Rs.``
- #5-b-iThe number of shares purchasedAns : Number of shares bought ``(n) = \frac{22500}{45} = 500``
- #5-b-iiThe annual dividend received.Ans : Annual dividend received ``= FV \times n \times Dividend \% = 50 \times 500 \times \frac{12}{100} = 3000 \ Rs.``
- #5-b-iiiThe rate of return he gets on his investment. Give your answer correct to the
nearest whole number.Ans : Rate of return ``= \frac{Dividend \ Received}{Total \ Investment} \times 100``
``= \frac{3000}{22500} \times 100 = 13.33\% \approx 13\%``
- #5-c [4]Use graph paper for this question (Take 2 cm = 1 unit along both x and y axis). ABCD
is a quadrilateral whose vertices are A(2, 2), B(2, -2), C(0, -1) and D(0, 1).Ans :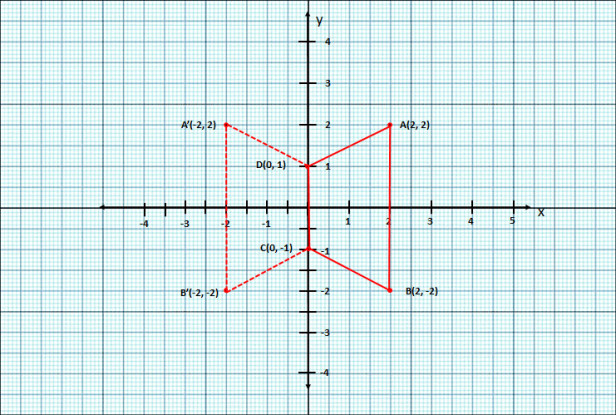 '
'
- #5-c-iReflect quadrilateral ABCD on the y-axis and name it as A'B'CD.Ans : Refer to the graph
- #5-c-iiWrite down the coordinates of A' and B'.Ans : A'(-2, 2) and B'(-2, -2)
- #5-c-iiiName two points which are invariant under the above reflection.Ans : C and D are irrelevant to the reflection
- #5-c-ivName the polygon A'B'CD.Ans : A'B'CD is a trapezium
- #6
- #6-a [3]Using properties of proportion, solve for x. Given that x is positive:
$$\frac{ 2x + \sqrt{4x^2-1}}{ 2x - \sqrt{4x^2-1}} =4$$Ans : `` \frac{2x+\sqrt{4x^2-1}}{2x-\sqrt{4x^2-1}} = 4``
Applying Componendo and Dividendo
``\frac{(2x+\sqrt{4x^2-1}) + (2x-\sqrt{4x^2-1})}{(2x+\sqrt{4x^2-1}) - (2x-\sqrt{4x^2-1})}``
``= \frac{4+1}{4-1}\frac{4x}{ 2 \sqrt{4x^2-1} } = \frac{5}{3}``
``\Rightarrow 6x = 5\sqrt{4x^2-1}``
``\Rightarrow 36x^2 = 25(4x^2 -1 )``
`` \Rightarrow 36x^2 = 100x^2 - 25``
``\Rightarrow 25 = 64 x^2``
``\Rightarrow x^2 = \frac{25}{64} \Rightarrow x = \frac{5}{8} \ or \frac{-5}{8}``
- #6-b [3]If ``A= \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 7 \\ \end{bmatrix},
B= \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 4 \\ -1 & 7 \\ \end{bmatrix},
C= \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ -1 & 4 \\ \end{bmatrix} ``
find ``AC + B^2 - 10C`` .Ans : ``AC+B^2-10C``
``= \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 7 \end{bmatrix} . \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ -1 & 4 \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 4 \\ -1 & 7 \end{bmatrix} . \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 4 \\ -1 & 7 \end{bmatrix} - 10 . \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ -1 & 4 \end{bmatrix}``
``= \begin{bmatrix} 2-3 & 12 \\ 5-7 & 28 \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} -4 & 28 \\ -7 & -4+49 \end{bmatrix} - 10 \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ -1 & 4 \end{bmatrix}``
``= \begin{bmatrix} -1 & 12 \\ -2 & 28 \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} -4 & 28 \\ -7 & 45 \end{bmatrix} - \begin{bmatrix} 10 & 0 \\ -10 & 40 \end{bmatrix}``
``= \begin{bmatrix} -15 & 40 \\ 1 & 33 \end{bmatrix}``
- #6-c [4]Prove that (1 + cot θ - cosec θ)(1+ tan θ + sec θ) = 2Ans : ``(1+cot \ \theta - cosec \ \theta)(1 + tan \ \theta + sec \ \theta) = 2``
``LHS = (1+cot \ \theta - cosec \ \theta)(1 + tan \ \theta + sec \ \theta)``
``= (1 + \frac{cos\ \theta}{sin\ \theta} - \frac{1}{sin\ \theta} )(1 + \frac{sin\ \theta}{cos\ \theta} + \frac{1}{cos\ \theta} )``
``= (\frac{sin\ \theta + cos\ \theta - 1}{sin \theta}) . ( \frac{cos\ \theta+sin\ \theta+1}{cos\ \theta})``
``= \frac{(sin\ \theta + cos\ \theta)^2-1^2}{sin\ \theta \ cos\ \theta}``
``= \frac{sin^2 \theta + cos^2 \theta - 2 sin\ \theta cos\ \theta-1}{sin\ \theta \ cos\ \theta}``
``= \frac{2 sin\ \theta cos\ \theta}{sin\ \theta \ cos\ \theta}``
= 2 = RHS
Hence Proved
- #7
- #7-a [3]Find the value of k for which the following equation has equal roots.
$$x^2 + 4kx + (k^2 - k + 2) = 0$$Ans : Given ``x^2+4kx+(k^2-k+2)=0``
Therefore ``a = 1, b = 4k \ and \ c = (k^2-k+2)``
For equal roots,``b^2 - 4ac = 0``
``\Rightarrow 16k^2 - 4(k^2-k+2)= 0``
``\Rightarrow 16k^2- 4k^2 + 4k -8 = 0``
``\Rightarrow 12k^2 + 4k - 8 = 0``
``\Rightarrow 3k^2 + k - 2 = 0``
``\Rightarrow 3k^2 + 3k - 2k - 2 = 0``
``\Rightarrow 3k (k+1) - 2 (k+1) = 0``
``\Rightarrow (k+1)(3k-2) = 0``
``\Rightarrow k = -1 \ or \ \frac{2}{3}``