NEET-XII-Physics
11: Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter
- #22An electron gun with its collector at a potential of 100 V fires out electrons in a spherical bulb containing hydrogen gas at low pressure (∼10-2 mm of Hg). A magnetic field of 2.83 × 10-4 T curves the path of the electrons in a circular orbit of radius 12.0 cm. (The path can be viewed because the gas ions in the path focus the beam by attracting electrons, and emitting light by electron capture; this method is known as the ‘fine beam tube’ method. Determine e/m from the data.
Ans : Potential of an anode, V = 100 V
Magnetic field experienced by the electrons, B = 2.83 × 10-4 T
Radius of the circular orbit r = 12.0 cm = 12.0 × 10-2 m
Mass of each electron = m
Charge on each electron = e
Velocity of each electron = v
The energy of each electron is equal to its kinetic energy, i.e.,

It is the magnetic field, due to its bending nature, that provides the centripetal force.gif) for the beam. Hence, we can write:
for the beam. Hence, we can write:
Centripetal force = Magnetic force

Putting the value of v in equation (1), we get:
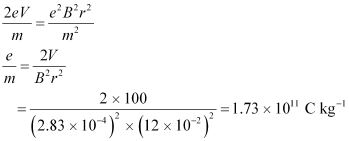
Therefore, the specific charge ratio (e/m) is