NEET-XII-Physics
09: Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
- #24For a normal eye, the far point is at infinity and the near point of distinct vision is about 25cm in front of the eye. The cornea of the eye provides a converging power of about 40 dioptres, and the least converging power of the eye-lens behind the cornea is about 20 dioptres. From this rough data estimate the range of accommodation (i.e., the range of converging power of the eye-lens) of a normal eye.
Ans : Least distance of distinct vision, d = 25 cm
Far point of a normal eye,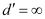
Converging power of the cornea,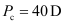
Least converging power of the eye-lens,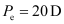
To see the objects at infinity, the eye uses its least converging power.
Power of the eye-lens, P = Pc + Pe = 40 + 20 = 60 D
Power of the eye-lens is given as:

To focus an object at the near point, object distance (u) = -d = -25 cm
Focal length of the eye-lens = Distance between the cornea and the retina
= Image distance
Hence, image distance,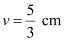
According to the lens formula, we can write:
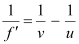
Where,
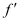 = Focal length
= Focal length
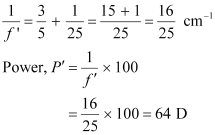
∴Power of the eye-lens = 64 - 40 = 24 D
Hence, the range of accommodation of the eye-lens is from 20 D to 24 D.