NEET-XII-Physics
09: Ray Optics And Optical Instruments
- #15Use the mirror equation to deduce that:
(a) an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror produces a real image beyond 2f.
(b) a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object.
(c) the virtual image produced by a convex mirror is always diminished in size and is located between the focus and the pole.
(d) an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror produces a virtual and enlarged image.
[Note: This exercise helps you deduce algebraically properties of
images that one obtains from explicit ray diagrams.]
Ans : null (a) For a concave mirror, the focal length (f) is negative.
∴f < 0
When the object is placed on the left side of the mirror, the object distance (u) is negative.
∴u < 0
For image distance v, we can write the lens formula as:

The object lies between f and 2f.

Using equation (1), we get:

∴ is negative, i.e., v is negative.
is negative, i.e., v is negative.
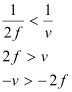
Therefore, the image lies beyond 2f.
(b) For a convex mirror, the focal length (f) is positive.
∴ f > 0
When the object is placed on the left side of the mirror, the object distance (u) is negative.
∴ u < 0
For image distance v, we have the mirror formula:

Thus, the image is formed on the back side of the mirror.
Hence, a convex mirror always produces a virtual image, regardless of the object distance.
(c) For a convex mirror, the focal length (f) is positive.
∴f > 0
When the object is placed on the left side of the mirror, the object distance (u) is negative,
∴u < 0
For image distance v, we have the mirror formula:
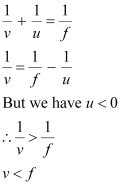
Hence, the image formed is diminished and is located between the focus (f) and the pole.
(d) For a concave mirror, the focal length (f) is negative.
∴f < 0
When the object is placed on the left side of the mirror, the object distance (u) is negative.
∴u < 0
It is placed between the focus (f) and the pole.
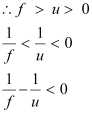
For image distance v, we have the mirror formula:

The image is formed on the right side of the mirror. Hence, it is a virtual image.
For u < 0 and v > 0, we can write:
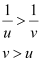
Magnification, m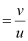 > 1
> 1
Hence, the formed image is enlarged.
- #15-aan object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror produces a real image beyond 2f.Ans : For a concave mirror, the focal length (f) is negative.
∴f < 0
When the object is placed on the left side of the mirror, the object distance (u) is negative.
∴u < 0
For image distance v, we can write the lens formula as:

The object lies between f and 2f.

Using equation (1), we get:

∴ is negative, i.e., v is negative.
is negative, i.e., v is negative.
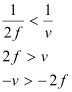
Therefore, the image lies beyond 2f.
- #15-ba convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object.Ans : For a convex mirror, the focal length (f) is positive.
∴ f > 0
When the object is placed on the left side of the mirror, the object distance (u) is negative.
∴ u < 0
For image distance v, we have the mirror formula:

Thus, the image is formed on the back side of the mirror.
Hence, a convex mirror always produces a virtual image, regardless of the object distance.
- #15-cthe virtual image produced by a convex mirror is always diminished in size and is located between the focus and the pole.Ans : For a convex mirror, the focal length (f) is positive.
∴f > 0
When the object is placed on the left side of the mirror, the object distance (u) is negative,
∴u < 0
For image distance v, we have the mirror formula:
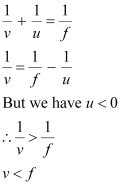
Hence, the image formed is diminished and is located between the focus (f) and the pole.
- #15-dan object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror produces a virtual and enlarged image.
[Note: This exercise helps you deduce algebraically properties of
images that one obtains from explicit ray diagrams.]
Ans : For a concave mirror, the focal length (f) is negative.
∴f < 0
When the object is placed on the left side of the mirror, the object distance (u) is negative.
∴u < 0
It is placed between the focus (f) and the pole.
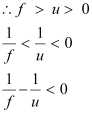
For image distance v, we have the mirror formula:

The image is formed on the right side of the mirror. Hence, it is a virtual image.
For u < 0 and v > 0, we can write:
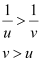
Magnification, m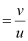 > 1
> 1
Hence, the formed image is enlarged.