NEET-XII-Physics
07: Alternating Current
- #11Figure 7.21 shows a series LCR circuit connected to a variable frequency 230 V source. L = 5.0 H, C = 80μF, R = 40 ``\Omega``
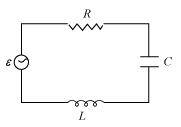
(a) Determine the source frequency which drives the circuit in resonance.
(b) Obtain the impedance of the circuit and the amplitude of current at the resonating frequency.
(c) Determine the rms potential drops across the three elements of the circuit. Show that the potential drop across the LC combination is zero at the resonating frequency.
(a) Determine the source frequency which drives the circuit in resonance.
(b) Obtain the impedance of the circuit and the amplitude of current at the resonating frequency.
(c) Determine the rms potential drops across the three elements of the circuit. Show that the potential drop across the LC combination is zero at the resonating frequency.Ans : Inductance of the inductor, L = 5.0 H
Capacitance of the capacitor, C = 80 μF = 80 × 10-6 F
Resistance of the resistor, R = 40 ``\Omega``
Potential of the variable voltage source, V = 230 V
(a) Resonance angular frequency is given as:
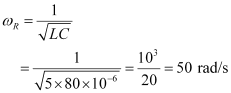
Hence, the circuit will come in resonance for a source frequency of 50 rad/s.
(b) Impedance of the circuit is given by the relation,
.gif)
At resonance,

Amplitude of the current at the resonating frequency is given as: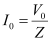
Where,
V0 = Peak voltage
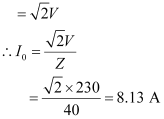
Hence, at resonance, the impedance of the circuit is 40 ``\Omega`` and the amplitude of the current is 8.13 A.
(c) Rms potential drop across the inductor,
(VL)rms = I × ωRL
Where,
I = rms current
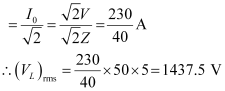
Potential drop across the capacitor,
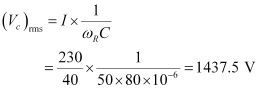
Potential drop across the resistor,
(VR)rms = IR
=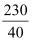 × 40 = 230 V
× 40 = 230 V
Potential drop across the LC combination,
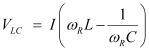
At resonance,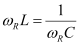
∴VLC= 0
Hence, it is proved that the potential drop across the LC combination is zero at resonating frequency.
(a) Resonance angular frequency is given as:

Hence, the circuit will come in resonance for a source frequency of 50 rad/s.
(b) Impedance of the circuit is given by the relation,
.gif)
At resonance,

Amplitude of the current at the resonating frequency is given as: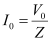
Where,
V0 = Peak voltage
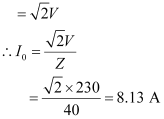
Hence, at resonance, the impedance of the circuit is 40 ``\Omega`` and the amplitude of the current is 8.13 A.
(c) Rms potential drop across the inductor,
(VL)rms = I × ωRL
Where,
I = rms current
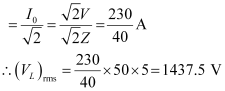
Potential drop across the capacitor,
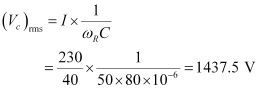
Potential drop across the resistor,
(VR)rms = IR
=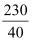 × 40 = 230 V
× 40 = 230 V
Potential drop across the LC combination,
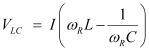
At resonance,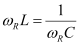
∴VLC= 0
Hence, it is proved that the potential drop across the LC combination is zero at resonating frequency.
- #11-aDetermine the source frequency which drives the circuit in resonance.Ans : Resonance angular frequency is given as:

Hence, the circuit will come in resonance for a source frequency of 50 rad/s.
- #11-bObtain the impedance of the circuit and the amplitude of current at the resonating frequency.Ans : Impedance of the circuit is given by the relation,
.gif)
At resonance,

Amplitude of the current at the resonating frequency is given as: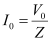
Where,
V0 = Peak voltage
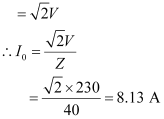
Hence, at resonance, the impedance of the circuit is 40 ``\Omega`` and the amplitude of the current is 8.13 A.
- #11-cDetermine the rms potential drops across the three elements of the circuit. Show that the potential drop across the LC combination is zero at the resonating frequency.Ans : Rms potential drop across the inductor,
(VL)rms = I × ωRL
Where,
I = rms current
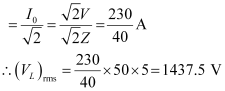
Potential drop across the capacitor,
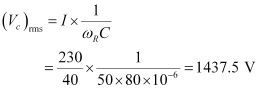
Potential drop across the resistor,
(VR)rms = IR
=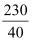 × 40 = 230 V
× 40 = 230 V
Potential drop across the LC combination,
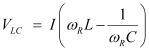
At resonance,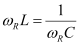
∴VLC= 0
Hence, it is proved that the potential drop across the LC combination is zero at resonating frequency.