NEET-XII-Physics
06: Electromagnetic Induction
- #6A circular coil of radius 8.0 cm and 20 turns is rotated about its vertical diameter with an angular speed of 50 rad s-1 in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 3.0×10-2 T. Obtain the maximum and average emf induced in the coil. If the coil forms a closed loop of resistance 10``\Omega``, calculate the maximum value of current in the coil. Calculate the average power loss due to Joule heating. Where does this power come from?
Ans : Max induced emf = 0.603 V
Average induced emf = 0 V
Max current in the coil = 0.0603 A
Average power loss = 0.018 W
(Power comes from the external rotor)
Radius of the circular coil, r = 8 cm = 0.08 m
Area of the coil, A = ``\pi``r2 = ``\pi`` × (0.08)2 m2
Number of turns on the coil, N = 20
Angular speed, ω = 50 rad/s
Magnetic field strength, B = 3 × 10-2 T
Resistance of the loop, R = 10 ``\Omega``
Maximum induced emf is given as:
e = Nω AB
= 20 × 50 × ``\pi`` × (0.08)2 × 3 × 10-2
= 0.603 V
The maximum emf induced in the coil is 0.603 V.
Over a full cycle, the average emf induced in the coil is zero.
Maximum current is given as:
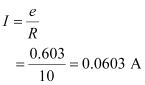
Average power loss due to joule heating:
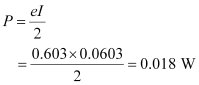
The current induced in the coil produces a torque opposing the rotation of the coil. The rotor is an external agent. It must supply a torque to counter this torque in order to keep the coil rotating uniformly. Hence, dissipated power comes from the external rotor.