NEET-XII-Physics
04: Moving Charges And Magnetism
- #19An electron emitted by a heated cathode and accelerated through a potential difference of 2.0 kV, enters a region with uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T. Determine the trajectory of the electron if the field (a) is transverse to its initial velocity, (b) makes an angle of 30° with the initial velocity.Ans : Magnetic field strength, B = 0.15 T
Charge on the electron, e = 1.6 × 10-19 C
Mass of the electron, m = 9.1 × 10-31 kg
Potential difference, V = 2.0 kV = 2 × 103 V
Thus, kinetic energy of the electron = eV

Where,
v = velocity of the electron
(a) Magnetic force on the electron provides the required centripetal force of the electron. Hence, the electron traces a circular path of radius r.
Magnetic force on the electron is given by the relation,
B ev
Centripetal force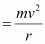

From equations (1) and (2), we get
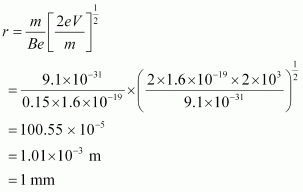
Hence, the electron has a circular trajectory of radius 1.0 mm normal to the magnetic field.
(b) When the field makes an angle θ of 30° with initial velocity, the initial velocity will be,
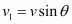
From equation (2), we can write the expression for new radius as:

Hence, the electron has a helical trajectory of radius 0.5 mm along the magnetic field direction.
- #19-ais transverse to its initial velocity,Ans : Magnetic force on the electron provides the required centripetal force of the electron. Hence, the electron traces a circular path of radius r.
Magnetic force on the electron is given by the relation,
B ev
Centripetal force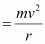

From equations (1) and (2), we get
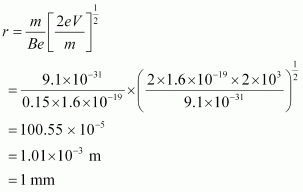
Hence, the electron has a circular trajectory of radius 1.0 mm normal to the magnetic field.
- #19-bmakes an angle of 30° with the initial velocity.Ans : When the field makes an angle θ of 30° with initial velocity, the initial velocity will be,
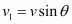
From equation (2), we can write the expression for new radius as:

Hence, the electron has a helical trajectory of radius 0.5 mm along the magnetic field direction.