NEET-XII-Physics
03: Current Electricity
- #11A storage battery of emf 8.0 V and internal resistance 0.5 ``\Omega`` is being charged by a 120 V dc supply using a series resistor of 15.5 ``\Omega``. What is the terminal voltage of the battery during charging? What is the purpose of having a series resistor in the charging circuit?
Ans : Emf of the storage battery, E = 8.0 V
Internal resistance of the battery, r = 0.5 ``\Omega``
DC supply voltage, V = 120 V
Resistance of the resistor, R = 15.5 ``\Omega``
Effective voltage in the circuit = V1
R is connected to the storage battery in series. Hence, it can be written as
V1 = V - E
V1 = 120 - 8 = 112 V
Current flowing in the circuit = I, which is given by the relation,
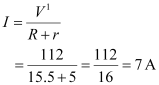
Voltage across resistor R given by the product, IR = 7 × 15.5 = 108.5 V
DC supply voltage = Terminal voltage of battery + Voltage drop across R
Terminal voltage of battery = 120 - 108.5 = 11.5 V
A series resistor in a charging circuit limits the current drawn from the external source. The current will be extremely high in its absence. This is very dangerous.