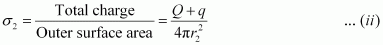NEET-XII-Physics
02: Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #7-aWhat is the total capacitance of the combination?Ans : Capacitances of the given capacitors are
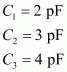
For the parallel combination of the capacitors, equivalent capacitor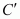 is given by the algebraic sum,
is given by the algebraic sum,
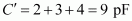
Therefore, total capacitance of the combination is 9 pF.
- #7-bDetermine the charge on each capacitor if the combination is connected to a 100 V supply.Ans : Supply voltage, V = 100 V
The voltage through all the three capacitors is same = V = 100 V
Charge on a capacitor of capacitance C and potential difference V is given by the relation,
q = VC ... (i)
For C = 2 pF,
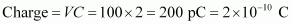
For C = 3 pF,
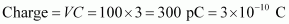
For C = 4 pF,
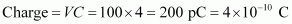
- Qstn #8In a parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates, each plate has an area of 6 × 10-3 m2 and the distance between the plates is 3 mm. Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor. If this capacitor is connected to a 100 V supply, what is the charge on each plate of the capacitor?
Ans : Area of each plate of the parallel plate capacitor, A = 6 × 10-3 m2
Distance between the plates, d = 3 mm = 3 × 10-3 m
Supply voltage, V = 100 V
Capacitance C of a parallel plate capacitor is given by,
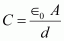
Where,
.gif) = Permittivity of free space
= Permittivity of free space
= 8.854 × 10-12 N-1 m-2 C-2
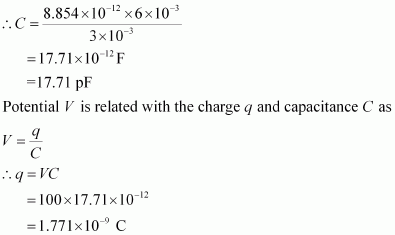
Therefore, capacitance of the capacitor is 17.71 pF and charge on each plate is 1.771 × 10-9 C.
Page No 88:
- Qstn #9Explain what would happen if in the capacitor given in Exercise 2.8, a 3 mm thick mica sheet (of dielectric constant = 6) were inserted between the plates,
- #9-aWhile the voltage supply remained connected.Ans : Dielectric constant of the mica sheet, k = 6
Initial capacitance, C = 1.771 × 10-11 F
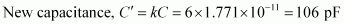
Supply voltage, V = 100 V
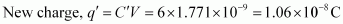
Potential across the plates remains 100 V.
- #9-bAfter the supply was disconnected.Ans : Dielectric constant, k = 6
Initial capacitance, C = 1.771 × 10-11 F
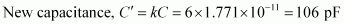
If supply voltage is removed, then there will be no effect on the amount of charge in the plates.
Charge = 1.771 × 10-9 C
Potential across the plates is given by,
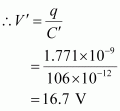
- Qstn #10A 12 pF capacitor is connected to a 50V battery. How much electrostatic energy is stored in the capacitor?
Ans : Capacitor of the capacitance, C = 12 pF = 12 × 10-12 F
Potential difference, V = 50 V
Electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor is given by the relation,
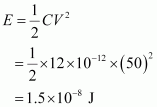
Therefore, the electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor is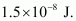
- Qstn #11A 600 pF capacitor is charged by a 200 V supply. It is then disconnected from the supply and is connected to another uncharged 600 pF capacitor. How much electrostatic energy is lost in the process?
Ans : Capacitance of the capacitor, C = 600 pF
Potential difference, V = 200 V
Electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor is given by,

If supply is disconnected from the capacitor and another capacitor of capacitance C = 600 pF is connected to it, then equivalent capacitance (C’) of the combination is given by,

New electrostatic energy can be calculated as
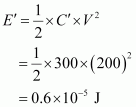
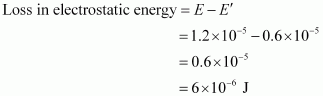
Therefore, the electrostatic energy lost in the process is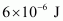 .
.
- Qstn #12A charge of 8 mC is located at the origin. Calculate the work done in taking a small charge of -2 × 10-9 C from a point P (0, 0, 3 cm) to a point Q (0, 4 cm, 0), via a point R (0, 6 cm, 9 cm).
Ans : Charge located at the origin, q = 8 mC= 8 × 10-3 C
Magnitude of a small charge, which is taken from a point P to point R to point Q, q1 = - 2 × 10-9 C
All the points are represented in the given figure.

Point P is at a distance, d1 = 3 cm, from the origin along z-axis.
Point Q is at a distance, d2 = 4 cm, from the origin along y-axis.
Potential at point P,
Potential at point Q,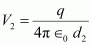
Work done (W) by the electrostatic force is independent of the path.
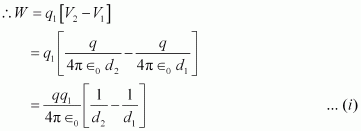

Therefore, work done during the process is 1.27 J.
- Qstn #13A cube of side b has a charge q at each of its vertices. Determine the potential and electric field due to this charge array at the centre of the cube.
Ans : Length of the side of a cube = b
Charge at each of its vertices = q
A cube of side b is shown in the following figure.

d = Diagonal of one of the six faces of the cube
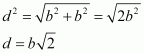
l = Length of the diagonal of the cube

The electric potential (V) at the centre of the cube is due to the presence of eight charges at the vertices.

Therefore, the potential at the centre of the cube is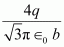 .
.
The electric field at the centre of the cube, due to the eight charges, gets cancelled. This is because the charges are distributed symmetrically with respect to the centre of the cube. Hence, the electric field is zero at the centre.
- Qstn #14Two tiny spheres carrying charges 1.5 μC and 2.5 μC are located 30 cm apart. Find the potential and electric field:
Ans : Two charges placed at points A and B are represented in the given figure. O is the mid-point of the line joining the two charges.
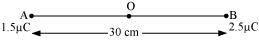
Magnitude of charge located at A, q1 = 1.5 μC
Magnitude of charge located at B, q2 = 2.5 μC
Distance between the two charges, d = 30 cm = 0.3 m
- #14-aat the mid-point of the line joining the two charges, andAns : Let V1 and E1 are the electric potential and electric field respectively at O.
V1 = Potential due to charge at A + Potential due to charge at B
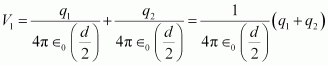
Where,
∈0 = Permittivity of free space
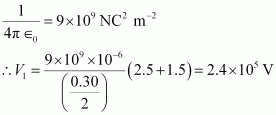
E1 = Electric field due to q2 - Electric field due to q1

Therefore, the potential at mid-point is 2.4 × 105 V and the electric field at mid-point is 4× 105 V m-1. The field is directed from the larger charge to the smaller charge.
- #14-bat a point 10 cm from this midpoint in a plane normal to the line and passing through the mid-point.Ans : Consider a point Z such that normal distanceOZ = 10 cm = 0.1 m, as shown in the following figure.

V2 and E2 are the electric potential and electric field respectively at Z.
It can be observed from the figure that distance,
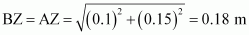
V2= Electric potential due to A + Electric Potential due to B
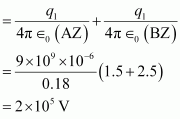
Electric field due to q at Z,

Electric field due to q2 at Z,
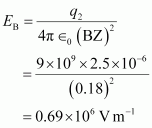
The resultant field intensity at Z,
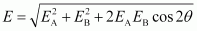
Where, 2θis the angle, ∠AZ B
From the figure, we obtain
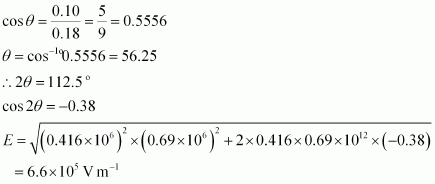
Therefore, the potential at a point 10 cm (perpendicular to the mid-point) is 2.0 × 105 V and electric field is 6.6 ×105 V m-1.
- #15-aA charge q is placed at the centre of the shell. What is the surface charge density on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell?Ans : Charge placed at the centre of a shell is +q. Hence, a charge of magnitude -q will be induced to the inner surface of the shell. Therefore, total charge on the inner surface of the shell is -q.
Surface charge density at the inner surface of the shell is given by the relation,

A charge of +q is induced on the outer surface of the shell. A charge of magnitude Q is placed on the outer surface of the shell. Therefore, total charge on the outer surface of the shell is Q + q. Surface charge density at the outer surface of the shell,