NEET-XII-Physics
02: Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #Chapter 2 - Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance
- Qstn #1Two charges 5 × 10-8 C and -3 × 10-8 C are located 16 cm apart. At what point(s) on the line joining the two charges is the electric potential zero? Take the potential at infinity to be zero.
Ans : There are two charges,
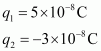
Distance between the two charges, d = 16 cm = 0.16 m
Consider a point P on the line joining the two charges, as shown in the given figure.
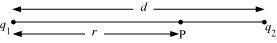
r = Distance of point P from charge q1
Let the electric potential (V) at point P be zero.
Potential at point P is the sum of potentials caused by charges q1 and q2 respectively.
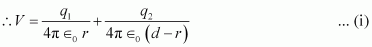
Where,
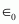 = Permittivity of free space
= Permittivity of free space
For V = 0, equation (i) reduces to
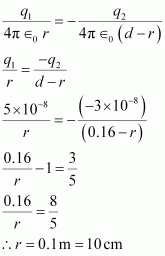
Therefore, the potential is zero at a distance of 10 cm from the positive charge between the charges.
Suppose point P is outside the system of two charges at a distance s from the negative charge, where potential is zero, as shown in the following figure.
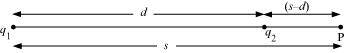
For this arrangement, potential is given by,
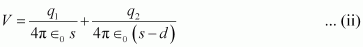
For V = 0, equation (ii) reduces to
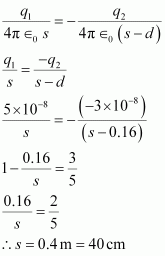
Therefore, the potential is zero at a distance of 40 cm from the positive charge outside the system of charges.
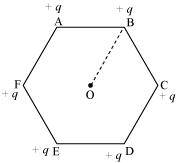
- Qstn #2A regular hexagon of side 10 cm has a charge 5 µC at each of its vertices. Calculate the potential at the centre of the hexagon.
Ans : The given figure shows six equal amount of charges, q, at the vertices of a regular hexagon.
Where,
Charge, q = 5 µC = 5 × 10-6 C
Side of the hexagon, l = AB = BC = CD = DE = EF = FA = 10 cm
Distance of each vertex from centre O, d = 10 cm
Electric potential at point O,
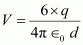
Where,
.gif) = Permittivity of free space
= Permittivity of free space
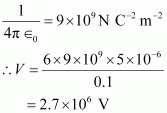
Therefore, the potential at the centre of the hexagon is 2.7 × 106 V.
- #3-aIdentify an equipotential surface of the system.Ans : The situation is represented in the given figure.

An equipotential surface is the plane on which total potential is zero everywhere. This plane is normal to line AB. The plane is located at the mid-point of line AB because the magnitude of charges is the same.
- #3-bWhat is the direction of the electric field at every point on this surface?Ans : The direction of the electric field at every point on this surface is normal to the plane in the direction of AB.
- Qstn #4A spherical conductor of radius 12 cm has a charge of 1.6 × 10-7C distributed uniformly on its surface. What is the electric field
- #4-aInside the sphereAns : Radius of the spherical conductor, r = 12 cm = 0.12 m
Charge is uniformly distributed over the conductor, q = 1.6 × 10-7 C
Electric field inside a spherical conductor is zero. This is because if there is field inside the conductor, then charges will move to neutralize it.
- #4-bJust outside the sphereAns : Electric field E just outside the conductor is given by the relation,
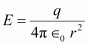
Where,
.gif) = Permittivity of free space
= Permittivity of free space
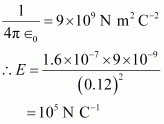
Therefore, the electric field just outside the sphere is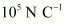 .
.
- #4-cAt a point 18 cm from the centre of the sphere?Ans : Electric field at a point 18 m from the centre of the sphere = E1
Distance of the point from the centre, d = 18 cm = 0.18 m
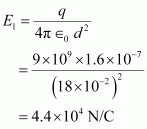
Therefore, the electric field at a point 18 cm from the centre of the sphere is
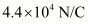 .
.
- Qstn #5A parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates has a capacitance of 8 pF (1pF = 10-12 F). What will be the capacitance if the distance between the plates is reduced by half, and the space between them is filled with a substance of dielectric constant 6?
Ans : Capacitance between the parallel plates of the capacitor, C = 8 pF
Initially, distance between the parallel plates was d and it was filled with air. Dielectric constant of air, k = 1
Capacitance, C, is given by the formula,

Where,
A = Area of each plate
.gif) = Permittivity of free space
= Permittivity of free space
If distance between the plates is reduced to half, then new distance, d’ =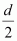
Dielectric constant of the substance filled in between the plates,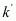 = 6
= 6
Hence, capacitance of the capacitor becomes
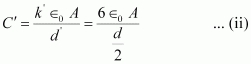
Taking ratios of equations (i) and (ii), we obtain
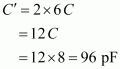
Therefore, the capacitance between the plates is 96 pF.
- #6-aWhat is the total capacitance of the combination?Ans : Capacitance of each of the three capacitors, C = 9 pF
Equivalent capacitance (C’) of the combination of the capacitors is given by the relation,
1C’=1C+1C+1C⇒1C’=19+19+19=13⇒C’=3pFTherefore, total capacitance of the combination is
3pF.
- #6-bWhat is the potential difference across each capacitor if the combination is connected to a 120 V supply?Ans : Supply voltage, V = 120 V
Potential difference (V‘) across each capacitor is equal to one-third of the supply voltage.
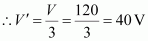
Therefore, the potential difference across each capacitor is 40 V.