NEET-XII-Chemistry
06: Polymers
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
No item to list.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #6 - Polymers
- #Section : ISECTION I Page No 428:
- Qstn #1What are polymers?
Ans : Polymers are high molecular mass macromolecules, which consist of repeating structural units derived from monomers. Polymers have a high molecular mass (103 - 107 u). In a polymer, various monomer units are joined by strong covalent bonds. These polymers can be natural as well as synthetic. Polythene, rubber, and nylon 6, 6 are examples of polymers.
- Qstn #2How are polymers classified on the basis of structure?
Ans : Addition polymers:
Polyvinyl chloride, polythene
Condensation polymers:
Terylene, bakelite
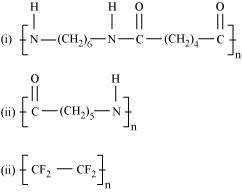
- #3-iAns : Hexamethylenediamine
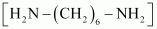 and adipic acid
and adipic acid 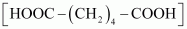
- #3-iiAns :
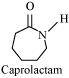
- #3-iiiAns : Tetrafluoroethene
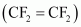
- Qstn #4Classify the following as addition and condensation polymers: Terylene, Bakelite, Polyvinyl chloride, Polythene.
Ans : Addition polymers:
Polyvinyl chloride, polythene
Condensation polymers:
Terylene, bakelite
- Qstn #5Explain the difference between Buna-N and Buna-S.
Ans : Buna - N is a copolymer of 1, 3-butadiene and acrylonitrile.
Buna - S is a copolymer of 1, 3-butadiene and styrene.
- Qstn #6Arrange the following polymers in increasing order of their intermolecular forces.
Ans : Different types of polymers have different intermolecular forces of attraction. Elastomers or rubbers have the weakest while fibres have the strongest intermolecular forces of attraction. Plastics have intermediate intermolecular forces of attraction. Hence, the increasing order of the intermolecular forces of the given polymers is as follows:
- #Section : IISECTION I Page No 437:
- Qstn #1Explain the terms polymer and monomer.
Ans : Polymers are high molecular mass macromolecules composed of repeating structural units derived from monomers. Polymers have a high molecular mass (103 - 107 u). In a polymer, various monomer units are joined by strong covalent bonds. Polymers can be natural as well as synthetic. Polythene, rubber, and nylon 6, 6 are examples of polymers.
Monomers are simple, reactive molecules that combine with each other in large numbers through covalent bonds to give rise to polymers. For example, ethene, propene, styrene, vinyl chloride.