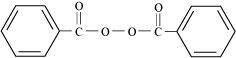NEET-XII-Chemistry
06: Polymers
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
No item to list.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- Qstn #2What are natural and synthetic polymers? Give two examples of each type.
Ans : Natural polymers are polymers that are found in nature. They are formed by plants and animals. Examples include protein, cellulose, starch, etc.
Synthetic polymers are polymers made by human beings. Examples include plastic (polythene), synthetic fibres (nylon 6, 6), synthetic rubbers (Buna - S).
- Qstn #3Distinguish between the terms homopolymer and copolymer and give an example of each.
Ans :-
Homopolymer
Copolymer
The polymers that are formed by the polymerization of a single monomer are known as homopolymers. In other words, the repeating units of homopolymers are derived only from one monomer. For example, polythene is a homopolymer of ethene.
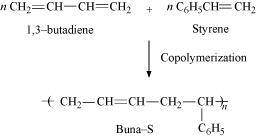
The polymers whose repeating units are derived from two types of monomers are known as copolymers. For example, Buna-S is a copolymer of 1, 3-butadiene and styrene.
-
- Qstn #4How do you explain the functionality of a monomer?
Ans : The functionality of a monomer is the number of binding sites that is/are present in that monomer.
For example, the functionality of monomers such as ethene and propene is one and that of 1, 3-butadiene and adipic acid is two.
- Qstn #5Define the term polymerisation.
Ans : Polymerization is the process of forming high molecular mass (103 - 107 u) macromolecules, which consist of repeating structural units derived from monomers. In a polymer, various monomer units are joined by strong covalent bonds.
- Qstn #6Is
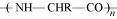 , a homopolymer or copolymer?
, a homopolymer or copolymer?
Ans :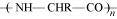 is a homopolymer because it is obtained from a single monomer unit, NH2-CHR-COOH.
is a homopolymer because it is obtained from a single monomer unit, NH2-CHR-COOH.
- Qstn #7In which classes, the polymers are classified on the basis of molecular forces?
Ans : On the basis of magnitude of intermolecular forces present in polymers, they are classified into the following groups:
(i) Elastomers
(ii) Fibres
(iii) Thermoplastic polymers
(iv) Thermosetting polymers
- Qstn #8How can you differentiate between addition and condensation polymerisation?
Ans : Addition polymerization is the process of repeated addition of monomers, possessing double or triple bonds to form polymers. For example, polythene is formed by addition polymerization of ethene.
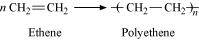
Condensation polymerization is the process of formation of polymers by repeated condensation reactions between two different bi-functional or tri-functional monomers. A small molecule such as water or hydrochloric acid is eliminated in each condensation. For example, nylon 6, 6 is formed by condensation polymerization of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.
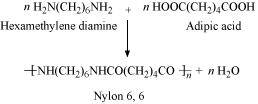
- Qstn #9Explain the term copolymerisation and give two examples.
Ans : The process of forming polymers from two or more different monomeric units is called copolymerization. Multiple units of each monomer are present in a copolymer. The process of forming polymer Buna-S from 1, 3-butadiene and styrene is an example of copolymerization
Nylon 6, 6 is also a copolymer formed by hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.

- Qstn #10Write the free radical mechanism for the polymerisation of ethene.
Ans : Polymerization of ethene to polythene consists of heating or exposing to light a mixture of ethene with a small amount of benzoyl peroxide as the initiator.
The reaction involved in this process is given below:
.png)
.png)
- Qstn #11Define thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers with two examples of each.
Ans : Thermoplastic polymers are linear (slightly branched) long chain polymers, which can be repeatedly softened and hardened on heating. Hence, they can be modified again and again. Examples include polythene, polystyrene.
Thermosetting polymers are cross-linked or heavily branched polymers which get hardened during the molding process. These plastics cannot be softened again on heating. Examples of thermosetting plastics include bakelite, urea-formaldehyde resins.
- Qstn #13Write the name and structure of one of the common initiators used in free
radical addition polymerisation.
Ans : One common initiator used in free radical addition polymerization is benzoyl peroxide. Its structure is given below.