NEET-XII-Chemistry
05: Biomolecules
- #16How do you explain the amphoteric behaviour of amino acids?
Ans : In aqueous solution, the carboxyl group of an amino acid can lose a proton and the amino group can accept a proton to give a dipolar ion known as zwitter ion.
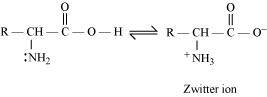
Therefore, in zwitter ionic form, the amino acid can act both as an acid and as a base.

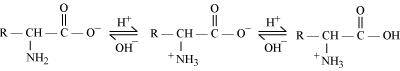
Thus, amino acids show amphoteric behaviour.