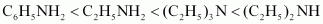NEET-XII-Chemistry
04: Amines
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
No item to list.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #4 - Amines
- #Section : ISECTION I Page No 384:
- Qstn #1Classify the following amines as primary, secondary or tertiary:
Ans : Primary: (i) and (iii)
Secondary: (iv)
Tertiary: (ii)
- Qstn #2( i) Write structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula, C4H11N
(ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers.
(iii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by different pairs of amines?
Ans : (i), (ii) The structures and their IUPAC names of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula, C4H11N are given below:
(a) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-NH2
Butanamine (10)
(b)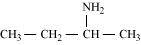
Butan-2-amine (10)
(c)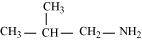
2-Methylpropanamine (10)
(d)
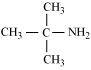
2-Methylpropan-2-amine (10)
(e) CH3-CH2-CH2-NH-CH3
N-Methylpropanamine (20)
(f) CH3-CH2-NH-CH2-CH3
N-Ethylethanamine (20)
(g)
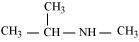
N-Methylpropan-2-amine (20)
(h)
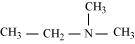
N,N-Dimethylethanamine (3°)
(iii) The pairs (a) and (b) and (e) and (g) exhibit position isomerism.
The pairs (a) and (c); (a) and (d); (b) and (c); (b) and (d) exhibit chain isomerism.
The pairs (e) and (f) and (f) and (g) exhibit metamerism.
All primary amines exhibit functional isomerism with secondary and tertiary amines and vice-versa.
SECTION I SECTION I Page No 387:
- Qstn #4-iC2H5NH2, C6H5NH2, NH3, C6H5CH2NH2 and (C2H5)2NHAns : Considering the inductive effect of alkyl groups, NH3, C2H5NH2, and (C2H5)2NH can be arranged in the increasing order of their basic strengths as:

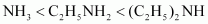
Again, C6H5NH2 has proton acceptability less than NH3. Thus, we have:
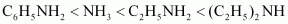
Due to the -I effect of C6H5 group, the electron density on the N-atom in C6H5CH2NH2 is lower than that on the N-atom in C2H5NH2, but more than that in NH3. Therefore, the given compounds can be arranged in the order of their basic strengths as:
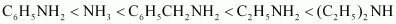
- Qstn #4-iiC2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N, C6H5NH2Ans : Considering the inductive effect and the steric hindrance of the alkyl groups, C2H5NH2, (C2 H5)2NH2, and their basic strengths as follows:
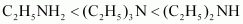
Again, due to the -R effect of C6H5 group, the electron density on the N atom in C6H5 NH2 is lower than that on the N atom in C2H5NH2. Therefore, the basicity of C6H5NH2 is lower than that of C2H5NH2. Hence, the given compounds can be arranged in the increasing order of their basic strengths as follows: