NEET-XII-Chemistry
03: Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
03-Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- Qstn #4Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions.
- Qstn #4-iEthanal, Propanal, Propanone, Butanone.Ans :
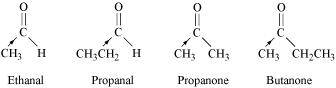
The +I effect of the alkyl group increases in the order:
Ethanal < Propanal < Propanone < Butanone
The electron density at the carbonyl carbon increases with the increase in the +I effect. As a result, the chances of attack by a nucleophile decrease. Hence, the increasing order of the reactivities of the given carbonyl compounds in nucleophilic addition reactions is:
Butanone < Propanone < Propanal < Ethanal
- Qstn #4-iiBenzaldehyde, p-Tolualdehyde, p-Nitrobenzaldehyde, Acetophenone.
Hint:Consider steric effect and electronic effect.
Ans :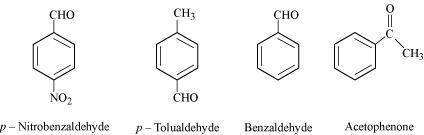
The +I effect is more in ketone than in aldehyde. Hence, acetophenone is the least reactive in nucleophilic addition reactions. Among aldehydes, the +I effect is the highest in p-tolualdehyde because of the presence of the electron-donating -CH3 group and the lowest in p-nitrobezaldehyde because of the presence of the electron-withdrawing -NO2 group. Hence, the increasing order of the reactivities of the given compounds is:
Acetophenone < p-tolualdehyde < Benzaldehyde < p-Nitrobenzaldehyde