NEET-XII-Chemistry
03: Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
03-Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- Qstn #8-iCH3CO2H or CH2FCO2HAns :
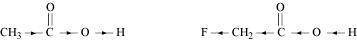
The +I effect of -CH3 group increases the electron density on the O-H bond. Therefore, release of proton becomes difficult. On the other hand, the -I effect of F decreases the electron density on the O-H bond. Therefore, proton can be released easily. Hence, CH2FCO2H is a stronger acid than CH3CO2H.
- Qstn #8-iiCH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2HAns :

F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
- Qstn #8-iiiCH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2HAns :

Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
- Ans :

Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
- #Section : IISECTION I Page No 377:
- Qstn #1-iCyanohydrinAns : Cyanohydrin:
Cyanohydrins are organic compounds having the formula RR′C(OH)CN, where R and R′ can be alkyl or aryl groups.
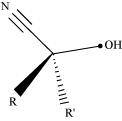
Aldehydes and ketones react with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the presence of excess sodium cyanide (NaCN) as a catalyst to field cyanohydrin. These reactions are known as cyanohydrin reactions.

Cyanohydrins are useful synthetic intermediates.
- Qstn #1-iiAcetalAns : Acetal:
Acetals are gem-dialkoxy alkanes in which two alkoxy groups are present on the terminal carbon atom. One bond is connected to an alkyl group while the other is connected to a hydrogen atom.

When aldehydes are treated with two equivalents of a monohydric alcohol in the presence of dry HCl gas, hemiacetals are produced that further react with one more molecule of alcohol to yield acetal.
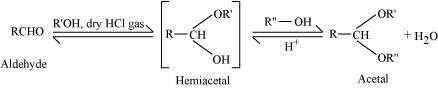
- Qstn #1-iiiSemicarbazoneAns : Semicarbarbazone:
Semicarbazones are derivatives of aldehydes and ketones produced by the condensation reaction between a ketone or aldehyde and semicarbazide.
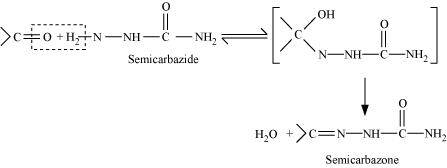
Semicarbazones are useful for identification and characterization of aldehydes and ketones.
- Qstn #1-ivAldolAns : Aldol:
A β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone is known as an aldol. It is produced by the condensation reaction of two molecules of the same or one molecule each of two different aldehydes or ketones in the presence of a base.
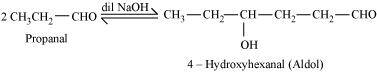
- Qstn #1-ix2,4-DNP-derivativeAns : 2, 4-DNP-derivative:
2, 4-dinitrophenylhydragones are 2, 4-DNP-derivatives, which are produced when aldehydes or ketones react with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine in a weakly acidic medium.
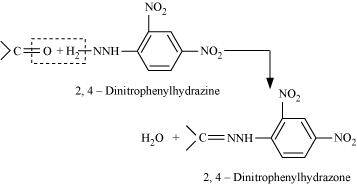
To identify and characterize aldehydes and ketones, 2, 4-DNP derivatives are used.