NEET-XI-Biology
22: Chemical Coordination and Integration
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
No item to list.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #22 - Chemical Coordination and Integration
- #Section : IPage No 341:
- #1-aExocrine glandAns : Exocrine glands: Glands that discharge secretions into ducts are known as exocrine glands. Sebaceous gland in the skin, salivary gland in the buccal cavity, etc. are examples of exocrine glands.
- #1-bEndocrine glandAns : Endocrine glands: Glands that do not discharge their secretions into ducts are known as endocrine glands. Instead, these glands discharge their secretions directly into the blood. Pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, etc. are examples of endocrine glands.
- #1-cHormoneAns : Hormones: Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate physiological processes in living organisms. They act upon specific cells/tissues/organs which are called target cells/tissues/organs.
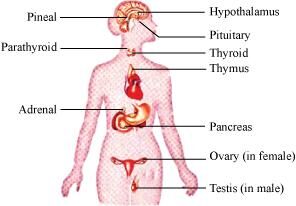
- Qstn #2Diagrammatically indicate the location of the various endocrine glands in our body.
Ans : The location of various endocrine glands in the human body can be illustrated as follows:
- #3-aHypothalamusAns : Hypothalamus: Hormones secreted by the hypothalamus include:
(1) Releasing hormones: These hormones stimulate the secretions of the pituitary hormone. Examples of these hormones are:
(i) Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone
(ii) Thyrotrophin-releasing hormone
(iii) Somatotropin-releasing hormone
(iv) Adrenocorticotrophin-releasing hormone
(2) Inhibiting hormones: These hormones inhibit the secretions of the pituitary hormone. Examples of these hormones are:
(i) Somatostatin
(ii) Growth-inhibiting hormone
(iii) Melanocyte-inhibiting hormone
- #3-bPituitaryAns : Pituitary: The pituitary gland has two components i.e., adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis.
Hormones secreted by the adenohypophysis are:
(i) Growth hormone (GH)
(ii) Prolactin
(iii) Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
(iv) Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
(v) Luteinizing hormone (LH)
(vi) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
(vii) Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
Hormones secreted by the neurohypophysis are:
(i) Oxytocin
(ii) Vasopressin
- #3-cThyroidAns : Thyroid: The thyroid gland secretes three hormones namely, thyroxin, triiodothyronin, and calcitonin.
- #3-dParathyroidAns : Parathyroid: The parathyroid gland secretes a hormone known as the parathyroid hormone.
- #3-eAdrenalAns : Adrenal: The adrenal gland is divided into two parts, the outer adrenal cortex and the inner adrenal medulla.
Hormones of adrenal cortex include the following:
(i) Mineralocorticoids: The hormone secreted is known as aldosterone.
(ii) Glucocorticoids: The hormone secreted is cortisol.
Hormones of adrenal medulla are adrenaline and nor-adrenalin.
- #3-fPancreasAns : Pancreas: Hormones secreted by the pancreas are insulin and glucagon.
- #3-gTestisAns : Testis: The hormone secreted by the testis is testosterone.