NEET-XI-Biology
10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
No item to list.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #10 - Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- #Section : IPage No 171:
- Qstn #1What is the average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell?
Ans : The average cell cycle span for a mammalian cell is approximately 24 hours.
- Qstn #2Distinguish cytokinesis from karyokinesis.
Ans :
Cytokinesis
Karyokinesis
(i)
Cytokinesis is the biological process involving the division of a cell’s cytoplasm during mitosis or meiosis.
(i)
Karyokinesis is the biological process involving the division of a cell’s nucleus during mitosis or meiosis.
(ii)
Stages such as prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase are not present in cytokinesis.
(ii)
It is divided into four stages –prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
- Qstn #3Describe the events taking place during interphase.
Ans : Interphase involves a series of changes that prepare a cell for division. It is the period during which the cell experiences growth and DNA replication in an orderly manner. Interphase is divided into three phases.
(i) G1 phase
(ii) S phase
(iii) G2 phase
G1 phase - It is the stage during which the cell grows and prepares its DNA for replication. In this phase, the cell is metabolically active.
S phase - It is the stage during which DNA synthesis occurs. In this phase, the amount of DNA (per cell) doubles, but the chromosome number remains the same.
G2 phase - In this phase, the cell continues to grow and prepares itself for division. The proteins and RNA required for mitosis are synthesised during this stage.
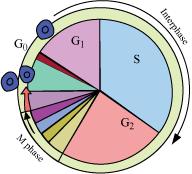
- Qstn #4What is G0 (quiescent phase) of cell cycle?
Ans : G0 or quiescent phase is the stage wherein cells remain metabolically active, but do not proliferate unless called to do so. Such cells are used for replacing the cells lost during injury.
- Qstn #5Why is mitosis called equational division?
Ans : Mitosis is the process of cell division wherein the chromosomes replicate and get equally distributed into two daughter cells. The chromosome number in each daughter cell is equal to that in the parent cell, i.e., diploid. Hence, mitosis is known as equational division.
- Qstn #7Describe the following:
(a) synapsis (b) bivalent (c) chiasmata
Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
Ans : null (a) Synapsis
The pairing of homologous chromosomes is called synapsis. This occurs during the second stage of prophase I or zygotene.
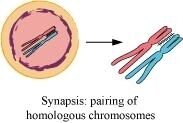
(b) Bivalent
Bivalent or tetrad is a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes. They are formed during the zygotene stage of prophase I of meiosis.

(c) Chiasmata
Chiasmata is the site where two non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes have crossed over. It represents the site of cross-over. It is formed during the diplotene stage of prophase I of meiosis.

- #7-asynapsisAns : Synapsis
The pairing of homologous chromosomes is called synapsis. This occurs during the second stage of prophase I or zygotene.

- #7-bbivalentAns : Bivalent
Bivalent or tetrad is a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes. They are formed during the zygotene stage of prophase I of meiosis.
