NEET-XI-Biology
08: Cell: The Unit of Life
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
No item to list.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- Qstn #13-iNucleus () Centrosome
() CentrosomeAns : Nucleus
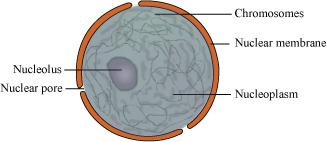
Nucleus controls all the cellular activities of the cell. It is spherical in shape. It is composed of the following structures:
Nuclear membrane: It is a double membrane separating the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm. The narrow space between the two membranes is called the perinuclear space. Nuclear membrane has tiny holes called nuclear pores. These holes allow specific substances to be transferred into a cell and out from it.
Nucleoplasm/Nuclear matrix: It is a homogenous granular fluid present inside the nucleus. It contains the nucleolus and chromatin. Nucleolus is a spherical structure that is not bound by any membrane. It is rich in protein and RNA molecules, and is the site for ribosome formation. Chromatin is an entangled mass of thread-like structures. It contains DNA and some basic proteins called histones.
() Centrosome
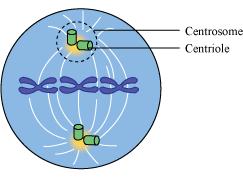
Centrosome consists of two cylindrical structures called centrioles. Centrioles lie perpendicular to each other. Each has a cartwheel-like organisation.
A centriole is made up of microtubule triplets that are evenly spaced in a ring. The adjacent triplets are linked together. There is a proteinaceous hub in the central part of a centriole. The hub is connected to the triplets via radial spokes. These centrioles help in organising the spindle fibres and astral rays during cell division. They form the basal body of cilia and flagella.
() Centrosome
Centrosome consists of two cylindrical structures called centrioles. Centrioles lie perpendicular to each other. Each has a cartwheel-like organisation.
A centriole is made up of microtubule triplets that are evenly spaced in a ring. The adjacent triplets are linked together. There is a proteinaceous hub in the central part of a centriole. The hub is connected to the triplets via radial spokes. These centrioles help in organising the spindle fibres and astral rays during cell division. They form the basal body of cilia and flagella.

- Qstn #13-iiCentrosomeAns : Centrosome
Centrosome consists of two cylindrical structures called centrioles. Centrioles lie perpendicular to each other. Each has a cartwheel-like organisation.
A centriole is made up of microtubule triplets that are evenly spaced in a ring. The adjacent triplets are linked together. There is a proteinaceous hub in the central part of a centriole. The hub is connected to the triplets via radial spokes. These centrioles help in organising the spindle fibres and astral rays during cell division. They form the basal body of cilia and flagella.

- Qstn #14What is a centromere? How does the position of centromere form the basis of classification of chromosomes. Support your answer with a diagram showing the position of centromere on different types of chromosomes.
Ans : Centromere is a constriction present on the chromosomes where the chromatids are held together.
Chromosomes are divided into four types based on the position of the centromere.
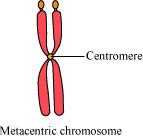
(i) Metacentric chromosome
The chromosomes in which the centromere is present in the middle and divides the chromosome into two equal arms is known as a metacentric chromosome.
(ii) Sub-metacentric chromosome
The chromosome in which the centromere is slightly away from the middle region is known as a sub-metacentric chromosome. In this, one arm is slightly longer than the other.
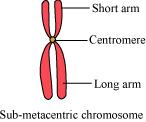
(iii) Acrocentric chromosome
The chromosome in which the centromere is located close to one of the terminal ends is known as an acrocentric chromosome. In this, one arm is extremely long and the other is extremely short.
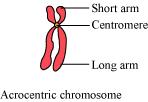
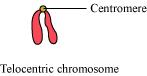
(iv) Telocentric chromosome
The chromosome in which the centromere is located at one of the terminal ends is known as a telocentric chromosome.