ICSE-X-Biology
Previous Year Paper year:2012
Qstn# 1 Next-Qstn
- #1: (a) Name the following : (a) The phenomenon by which living or dead plant cells absorb water by surface attraction. (a) The phase of cardiac cycle in which the auricles contract. (a) The organ where urea is produced. (a) The hormone that helps increase the reabsorption of water from the kidney tubules. (a) Chemical substances produced by micro organisms that can kill or inhibit
the growth of other micro organisms. (b) Choose the correct answer from the four options given below each statement: (b) BCG vaccine is used to build immunity against :
(A) Poliomyelitis (B) Tuberculosis (C) Malaria (D) Whooping cough (b) A plant is kept in a dark cupboard for about 48 hours before conducting any experiment on photosynthesis to :
(A) Remove starch from the plant
(B) Ensure that starch is not translocated from the leaves
(C) Remove chlorophyll from the leaf of the plant
(D) Remove starch from the experimental leaf (b) The part of the human eye where rod cells and cone cells are located is the :
(A) Retina (B) Cornea (C) Choroid (D) Sclera (b) A reflex arc in man is best described as movement of stimuli from :
(A) Receptor cell, sensory neuron, relaying neuron, effector muscles.
(B) Receptor cell, efferent nerve, relaying neuron, muscles of the body
(C) Receptor cell, spinal cord, motor neuron, relaying neuron.
(D) Receptor cell, synapse, motor neuron, relaying neuron. (b) NADP is expanded as :
(A) Nicotinamide, adenosine dinucleostide phosphate
(B) Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleotide phosphate
(C) Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleous phosphate
(D) Nicotinamide, adenosine dinucleous phosphate (c) State the main function of the following : (c) Chordae tendinae (c) Lymphocytes (c) Seminiferous tubule (c) Thylakoids (c) Beta cells of pancreas (d) Give the exact location of the : (d) Lenticels (d) Prostate gland (d) Thyroid gland (d) Centrosome (d) Mitral valve (e) Given below are sets office terms each. In each case rewrite the terms in logical sequence as directed at the end of each statement. An example has been done for you :
Example :
Cortical cells, Root hair, xylem, Soil water, endodermis (absorption of water by the plants)
Answer-: Soil water, Root hair, cortical cells, endodermis, xylem. (e) Active immunity, Antigen, Antibody, Bacteria, Lymphocytes (defence mechanism of the body). (e) Implantation, Parturition, Ovulation, Gestation, Fertilisation (stages leading to formation of foetus and birth). (e) Oval window, Tympanum, Cochlea, Auditory canal, Ear ossicles (path through which a vibration of sound is transferred in the human ear). (e) Karyokinesis, S-phase, Cytokinesis, G1 phase, G2-phase (cell cycle). (e) Renal vein, Renal artery, Afferent arteriole, Efferent arteriole, Glomerulus
(pathway of blood through glomerulus). (f) Study the following diagram carefully and then answer the questions that follow. The diagram is depicting a defect of the human eye :
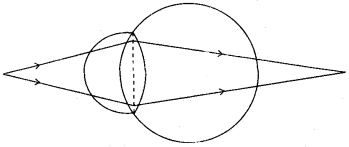 (f) Identify the defect shown in the diagram. (f) Give two possible reasons for the above defect. (f) Draw a neat labelled diagram to show how the above defect can be rectified. (g) Match the items in Column A with that which is most appropriate in Column B. Rewrite the matching pairs :
(f) Identify the defect shown in the diagram. (f) Give two possible reasons for the above defect. (f) Draw a neat labelled diagram to show how the above defect can be rectified. (g) Match the items in Column A with that which is most appropriate in Column B. Rewrite the matching pairs :
 (h) Given below are six sets with four terms each. In each set a term is an odd one and cannot be grouped in the same category to which the other three belong. Identify the odd one in each set and name the category to which the remaining three belong. The first has been done for you as an example.
(h) Given below are six sets with four terms each. In each set a term is an odd one and cannot be grouped in the same category to which the other three belong. Identify the odd one in each set and name the category to which the remaining three belong. The first has been done for you as an example.
 (a) Name the following : (a) The phenomenon by which living or dead plant cells absorb water by surface attraction. (a) The phase of cardiac cycle in which the auricles contract. (a) The organ where urea is produced. (a) The hormone that helps increase the reabsorption of water from the kidney tubules. (a) Chemical substances produced by micro organisms that can kill or inhibit
(a) Name the following : (a) The phenomenon by which living or dead plant cells absorb water by surface attraction. (a) The phase of cardiac cycle in which the auricles contract. (a) The organ where urea is produced. (a) The hormone that helps increase the reabsorption of water from the kidney tubules. (a) Chemical substances produced by micro organisms that can kill or inhibit
the growth of other micro organisms. (b) Choose the correct answer from the four options given below each statement: (b) BCG vaccine is used to build immunity against :
(A) Poliomyelitis (B) Tuberculosis (C) Malaria (D) Whooping cough (b) A plant is kept in a dark cupboard for about 48 hours before conducting any experiment on photosynthesis to :
(A) Remove starch from the plant
(B) Ensure that starch is not translocated from the leaves
(C) Remove chlorophyll from the leaf of the plant
(D) Remove starch from the experimental leaf (b) The part of the human eye where rod cells and cone cells are located is the :
(A) Retina (B) Cornea (C) Choroid (D) Sclera (b) A reflex arc in man is best described as movement of stimuli from :
(A) Receptor cell, sensory neuron, relaying neuron, effector muscles.
(B) Receptor cell, efferent nerve, relaying neuron, muscles of the body
(C) Receptor cell, spinal cord, motor neuron, relaying neuron.
(D) Receptor cell, synapse, motor neuron, relaying neuron. (b) NADP is expanded as :
(A) Nicotinamide, adenosine dinucleostide phosphate
(B) Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleotide phosphate
(C) Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleous phosphate
(D) Nicotinamide, adenosine dinucleous phosphate (c) State the main function of the following : (c) Chordae tendinae (c) Lymphocytes (c) Seminiferous tubule (c) Thylakoids (c) Beta cells of pancreas (d) Give the exact location of the : (d) Lenticels (d) Prostate gland (d) Thyroid gland (d) Centrosome (d) Mitral valve (e) Given below are sets office terms each. In each case rewrite the terms in logical sequence as directed at the end of each statement. An example has been done for you :
Example :
Cortical cells, Root hair, xylem, Soil water, endodermis (absorption of water by the plants)
Answer-: Soil water, Root hair, cortical cells, endodermis, xylem. (e) Active immunity, Antigen, Antibody, Bacteria, Lymphocytes (defence mechanism of the body). (e) Implantation, Parturition, Ovulation, Gestation, Fertilisation (stages leading to formation of foetus and birth). (e) Oval window, Tympanum, Cochlea, Auditory canal, Ear ossicles (path through which a vibration of sound is transferred in the human ear). (e) Karyokinesis, S-phase, Cytokinesis, G1 phase, G2-phase (cell cycle). (e) Renal vein, Renal artery, Afferent arteriole, Efferent arteriole, Glomerulus
(pathway of blood through glomerulus). (f) Study the following diagram carefully and then answer the questions that follow. The diagram is depicting a defect of the human eye :
 (f) Identify the defect shown in the diagram. (f) Give two possible reasons for the above defect. (f) Draw a neat labelled diagram to show how the above defect can be rectified. (g) Match the items in Column A with that which is most appropriate in Column B. Rewrite the matching pairs :
(f) Identify the defect shown in the diagram. (f) Give two possible reasons for the above defect. (f) Draw a neat labelled diagram to show how the above defect can be rectified. (g) Match the items in Column A with that which is most appropriate in Column B. Rewrite the matching pairs :
 (h) Given below are six sets with four terms each. In each set a term is an odd one and cannot be grouped in the same category to which the other three belong. Identify the odd one in each set and name the category to which the remaining three belong. The first has been done for you as an example.
(h) Given below are six sets with four terms each. In each set a term is an odd one and cannot be grouped in the same category to which the other three belong. Identify the odd one in each set and name the category to which the remaining three belong. The first has been done for you as an example.
 Ans : (a) (a) Imbibition (a) Auricular systole (a) Liver (a) Antidiuretic hormone/Vasopressin (a) Antibiotics (b) (b) (B) - Tuberculosis (b) (D) - Remove starch from the experimental leaf (b) (A) - Retina (b) (A) - Receptor cell, sensory neuron, relaying neuron, effector muscles (b) (B) - Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleotide phosphate (c) (c) Chordae tendinae - Holds the valves in position. (c) Lymphocytes - Produce antibodies to defend the body against infection. (c) Seminiferous tubule - Produce sperms (c) Thylakoids - Chlorophyll is located on the wall of thylakoids so light reaction of photosynthesis begins here. (c) Beta cells of pancreas - Secrete insulin that helps to lower the level of glucose in blood. (d) (d) Lenticels - On the older stens (d) Prostate gland - Between the urinary bladder and the point where sperm ducts join the urethra. (d) Thyroid gland - In the front part in the neck (d) Centrosome - Above the nucleus in animal cells. (d) Mitral value - Between the left auricle and left ventricle. (e) (e) Active immunity, Bacteria, Antigen, Lymphocytes, Antibody. (e) Ovulation, Fertilisation, Implantation, Gestation, Parturition. (e) Auditory canal, Tympanum, Ear ossicles, Oval window, Cochlea. (e) G1-phase, S-phase, G2-phase, Karyokinesis, Cytokinesis. (e) Renal artery, Afferent arteriole, Glomerulus, Efferent arteriole, Renal vein. (f) (f) Hypermetropia (f) 1. The eye ball is too short from front to back.
Ans : (a) (a) Imbibition (a) Auricular systole (a) Liver (a) Antidiuretic hormone/Vasopressin (a) Antibiotics (b) (b) (B) - Tuberculosis (b) (D) - Remove starch from the experimental leaf (b) (A) - Retina (b) (A) - Receptor cell, sensory neuron, relaying neuron, effector muscles (b) (B) - Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleotide phosphate (c) (c) Chordae tendinae - Holds the valves in position. (c) Lymphocytes - Produce antibodies to defend the body against infection. (c) Seminiferous tubule - Produce sperms (c) Thylakoids - Chlorophyll is located on the wall of thylakoids so light reaction of photosynthesis begins here. (c) Beta cells of pancreas - Secrete insulin that helps to lower the level of glucose in blood. (d) (d) Lenticels - On the older stens (d) Prostate gland - Between the urinary bladder and the point where sperm ducts join the urethra. (d) Thyroid gland - In the front part in the neck (d) Centrosome - Above the nucleus in animal cells. (d) Mitral value - Between the left auricle and left ventricle. (e) (e) Active immunity, Bacteria, Antigen, Lymphocytes, Antibody. (e) Ovulation, Fertilisation, Implantation, Gestation, Parturition. (e) Auditory canal, Tympanum, Ear ossicles, Oval window, Cochlea. (e) G1-phase, S-phase, G2-phase, Karyokinesis, Cytokinesis. (e) Renal artery, Afferent arteriole, Glomerulus, Efferent arteriole, Renal vein. (f) (f) Hypermetropia (f) 1. The eye ball is too short from front to back.
2. The lens is too flat. (f) (g)
(g)  (h)
(h) 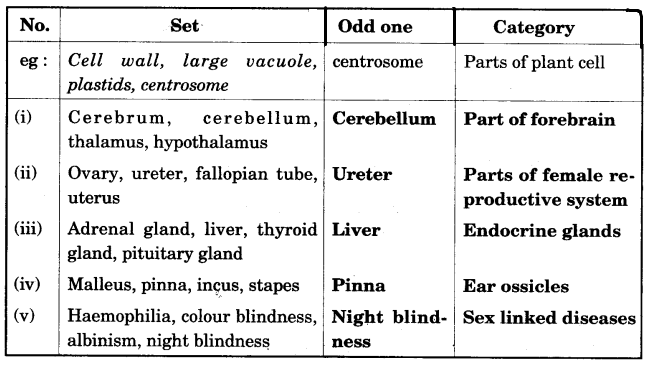 (a) (a) Imbibition (a) Auricular systole (a) Liver (a) Antidiuretic hormone/Vasopressin (a) Antibiotics (b) (b) (B) - Tuberculosis (b) (D) - Remove starch from the experimental leaf (b) (A) - Retina (b) (A) - Receptor cell, sensory neuron, relaying neuron, effector muscles (b) (B) - Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleotide phosphate (c) (c) Chordae tendinae - Holds the valves in position. (c) Lymphocytes - Produce antibodies to defend the body against infection. (c) Seminiferous tubule - Produce sperms (c) Thylakoids - Chlorophyll is located on the wall of thylakoids so light reaction of photosynthesis begins here. (c) Beta cells of pancreas - Secrete insulin that helps to lower the level of glucose in blood. (d) (d) Lenticels - On the older stens (d) Prostate gland - Between the urinary bladder and the point where sperm ducts join the urethra. (d) Thyroid gland - In the front part in the neck (d) Centrosome - Above the nucleus in animal cells. (d) Mitral value - Between the left auricle and left ventricle. (e) (e) Active immunity, Bacteria, Antigen, Lymphocytes, Antibody. (e) Ovulation, Fertilisation, Implantation, Gestation, Parturition. (e) Auditory canal, Tympanum, Ear ossicles, Oval window, Cochlea. (e) G1-phase, S-phase, G2-phase, Karyokinesis, Cytokinesis. (e) Renal artery, Afferent arteriole, Glomerulus, Efferent arteriole, Renal vein. (f) (f) Hypermetropia (f) 1. The eye ball is too short from front to back.
(a) (a) Imbibition (a) Auricular systole (a) Liver (a) Antidiuretic hormone/Vasopressin (a) Antibiotics (b) (b) (B) - Tuberculosis (b) (D) - Remove starch from the experimental leaf (b) (A) - Retina (b) (A) - Receptor cell, sensory neuron, relaying neuron, effector muscles (b) (B) - Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleotide phosphate (c) (c) Chordae tendinae - Holds the valves in position. (c) Lymphocytes - Produce antibodies to defend the body against infection. (c) Seminiferous tubule - Produce sperms (c) Thylakoids - Chlorophyll is located on the wall of thylakoids so light reaction of photosynthesis begins here. (c) Beta cells of pancreas - Secrete insulin that helps to lower the level of glucose in blood. (d) (d) Lenticels - On the older stens (d) Prostate gland - Between the urinary bladder and the point where sperm ducts join the urethra. (d) Thyroid gland - In the front part in the neck (d) Centrosome - Above the nucleus in animal cells. (d) Mitral value - Between the left auricle and left ventricle. (e) (e) Active immunity, Bacteria, Antigen, Lymphocytes, Antibody. (e) Ovulation, Fertilisation, Implantation, Gestation, Parturition. (e) Auditory canal, Tympanum, Ear ossicles, Oval window, Cochlea. (e) G1-phase, S-phase, G2-phase, Karyokinesis, Cytokinesis. (e) Renal artery, Afferent arteriole, Glomerulus, Efferent arteriole, Renal vein. (f) (f) Hypermetropia (f) 1. The eye ball is too short from front to back.
2. The lens is too flat. (f) (g)
(g)  (h)
(h) 
- #1-a [5]Name the following :
- #1-a-iThe phenomenon by which living or dead plant cells absorb water by surface attraction.Ans : Imbibition
- #1-a-iiThe phase of cardiac cycle in which the auricles contract.Ans : Auricular systole
- #1-a-iiiThe organ where urea is produced.Ans : Liver
- #1-a-ivThe hormone that helps increase the reabsorption of water from the kidney tubules.Ans : Antidiuretic hormone/Vasopressin
- #1-a-vChemical substances produced by micro organisms that can kill or inhibit
the growth of other micro organisms.Ans : Antibiotics
- #1-b [5]Choose the correct answer from the four options given below each statement:
- #1-b-iBCG vaccine is used to build immunity against :
(A) Poliomyelitis (B) Tuberculosis (C) Malaria (D) Whooping coughAns : (B) - Tuberculosis
- #1-b-iiA plant is kept in a dark cupboard for about 48 hours before conducting any experiment on photosynthesis to :
(A) Remove starch from the plant
(B) Ensure that starch is not translocated from the leaves
(C) Remove chlorophyll from the leaf of the plant
(D) Remove starch from the experimental leafAns : (D) - Remove starch from the experimental leaf
- #1-b-iiiThe part of the human eye where rod cells and cone cells are located is the :
(A) Retina (B) Cornea (C) Choroid (D) ScleraAns : (A) - Retina
- #1-b-ivA reflex arc in man is best described as movement of stimuli from :
(A) Receptor cell, sensory neuron, relaying neuron, effector muscles.
(B) Receptor cell, efferent nerve, relaying neuron, muscles of the body
(C) Receptor cell, spinal cord, motor neuron, relaying neuron.
(D) Receptor cell, synapse, motor neuron, relaying neuron.Ans : (A) - Receptor cell, sensory neuron, relaying neuron, effector muscles
- #1-b-vNADP is expanded as :
(A) Nicotinamide, adenosine dinucleostide phosphate
(B) Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleotide phosphate
(C) Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleous phosphate
(D) Nicotinamide, adenosine dinucleous phosphateAns : (B) - Nicotinamide, adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- #1-c [5]State the main function of the following :
- #1-c-iChordae tendinaeAns : Chordae tendinae - Holds the valves in position.