NEET-XII-Chemistry
03: Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- #8-iCH3CO2H or CH2FCO2H
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()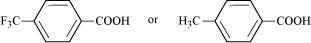
Ans :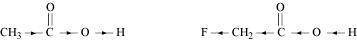
The +I effect of -CH3 group increases the electron density on the O-H bond. Therefore, release of proton becomes difficult. On the other hand, the -I effect of F decreases the electron density on the O-H bond. Therefore, proton can be released easily. Hence, CH2FCO2H is a stronger acid than CH3CO2H.
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
- #8-iiCH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2HAns :

F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
- #8-iiiCH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2HAns :

Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
- #8-iv
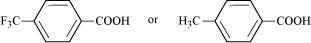
Ans :
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).