NEET-XII-Chemistry
03: Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- #8Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
() CH3CO2H or CH2FCO2H
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()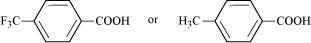
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()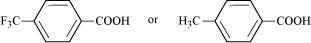
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()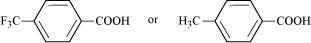
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()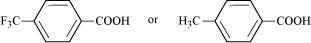
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()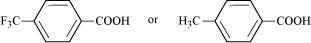
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()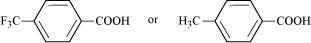
() CH3CO2H or CH2FCO2H
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()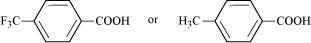
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()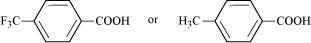
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()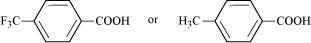
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()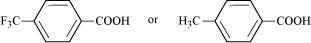
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()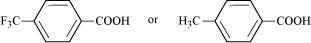
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()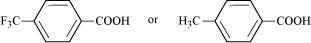
Ans : null ()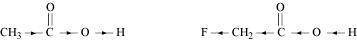
The +I effect of -CH3 group increases the electron density on the O-H bond. Therefore, release of proton becomes difficult. On the other hand, the -I effect of F decreases the electron density on the O-H bond. Therefore, proton can be released easily. Hence, CH2FCO2H is a stronger acid than CH3CO2H.
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()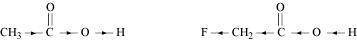
The +I effect of -CH3 group increases the electron density on the O-H bond. Therefore, release of proton becomes difficult. On the other hand, the -I effect of F decreases the electron density on the O-H bond. Therefore, proton can be released easily. Hence, CH2FCO2H is a stronger acid than CH3CO2H.
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
- #8-iCH3CO2H or CH2FCO2H
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()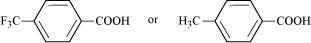
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()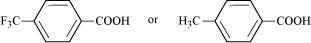
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()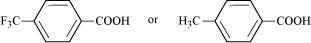
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()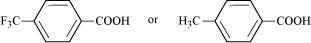
() CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
() CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
()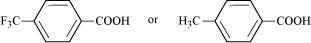
Ans :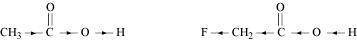
The +I effect of -CH3 group increases the electron density on the O-H bond. Therefore, release of proton becomes difficult. On the other hand, the -I effect of F decreases the electron density on the O-H bond. Therefore, proton can be released easily. Hence, CH2FCO2H is a stronger acid than CH3CO2H.
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
()
F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
()
Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
()
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).
- #8-iiCH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2HAns :

F has stronger -I effect than Cl. Therefore, CH2FCO2H can release proton more easily than CH2ClCO2H. Hence, CH2FCO2H is stronger acid than CH2ClCO2H.
- #8-iiiCH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2HAns :

Inductive effect decreases with increase in distance. Hence, the +I effect of F in CH3CHFCH2CO2H is more than it is in CH2FCH2CH2CO2H. Hence, CH3CHFCH2CO2H is stronger acid than CH2FCH2CH2CO2H.
- #8-iv
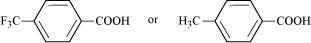
Ans :
Due to the -I effect of F, it is easier to release proton in the case of compound (A). However, in the case of compound (B), release of proton is difficult due to the +I effect of -CH3 group. Hence, (A) is a stronger acid than (B).