Loading…
NEET-XII-Chemistry
06: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Qstn #22Out of C and CO, which is a better reducing agent for ZnO ?
Ans :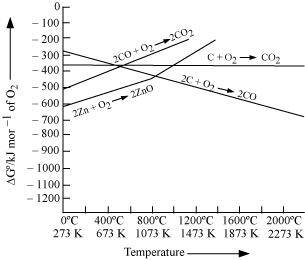
Reduction of ZnO to Zn is usually carried out at 1673 K. From the above figure, it can be observed that above 1073 K, the Gibbs free energy of formation of CO from C and above 1273 K, the Gibbs free energy of formation of CO2 from C is lesser than the Gibbs free energy of formation of ZnO. Therefore, C can easily reduce ZnO to Zn.
On the other hand, the Gibbs free energy of formation of CO2 from CO is always higher than the Gibbs free energy of formation of ZnO. Therefore, CO cannot reduce ZnO. Hence, C is a better reducing agent than CO for reducing ZnO.
- Qstn #23The choice of a reducing agent in a particular case depends on
thermodynamic factor. How far do you agree with this statement? Support
your opinion with two examples.
Ans :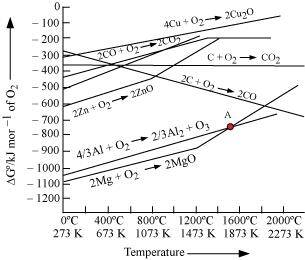
The above figure is a plot of Gibbs energy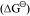 vs. T for formation of some oxides.
vs. T for formation of some oxides.
It can be observed from the above graph that a metal can reduce the oxide of other metals, if the standard free energy of formation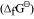 of the oxide of the former is more negative than the latter. For example, since
of the oxide of the former is more negative than the latter. For example, since 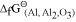 is more negative than
is more negative than 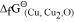 , Al can reduce Cu2O to Cu, but Cu cannot reduce Al2O3. Similarly, Mg can reduce ZnO to Zn, but Zn cannot reduce MgO because
, Al can reduce Cu2O to Cu, but Cu cannot reduce Al2O3. Similarly, Mg can reduce ZnO to Zn, but Zn cannot reduce MgO because 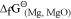 is more negative than
is more negative than 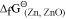 .
.
- Qstn #24Name the processes from which chlorine is obtained as a by-product. What
will happen if an aqueous solution of NaCl is subjected to electrolysis?
Ans : In the electrolysis of molten NaCl, Cl2 is obtained at the anode as a by product.
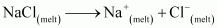
At cathode: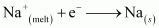
At anode: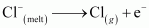

The overall reaction is as follows:
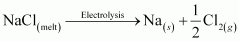
If an aqueous solution of NaCl is electrolyzed, Cl2 will be obtained at the anode but at the cathode, H2 will be obtained (instead of Na). This is because the standard reduction potential of Na (E°= - 2.71 V) is more negative than that of H2O (E° = - 0.83 V). Hence, H2O will get preference to get reduced at the cathode and as a result, H2 is evolved.
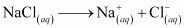
At cathode: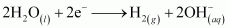
At anode:

- Qstn #25What is the role of graphite rod in the electrometallurgy of aluminium?
Ans : In the electrometallurgy of aluminium, a fused mixture of purified alumina (Al2O3), cryolite (Na3AlF6) and fluorspar (CaF2) is electrolysed. In this electrolysis, graphite is used as the anode and graphite-lined iron is used as the cathode. During the electrolysis, Al is liberated at the cathode, while CO and CO2 are liberated at the anode, according to the following equation.
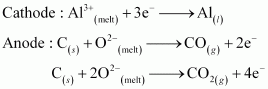
If a metal is used instead of graphite as the anode, then O2 will be liberated. This will not only oxidise the metal of the electrode, but also convert some of the Al liberated at the cathode back into Al2O3. Hence, graphite is used for preventing the formation of O2 at the anode. Moreover, graphite is cheaper than other metals.
- Qstn #26-iZone refiningAns : Zone refining:
This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the rod also moves along with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass to the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times, which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. Then, the end with the impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, gallium, indium etc. can be purified by this process.
.jpg)
- Qstn #26-iiElectrolytic refiningAns : Electrolytic refining;
Electrolytic refining is the process of refining impure metals by using electricity. In this process, impure metal is made the anode and a strip of pure metal is made the cathode. A solution of a soluble salt of the same metal is taken as the electrolyte. When an electric current is passed, metal ions from the electrolyte are deposited at the cathode as pure metal and the impure metal from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte in the form of ions. The impurities present in the impure metal gets collected below the anode. This is known as anode mud.
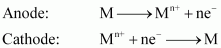
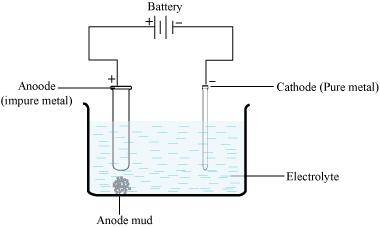
- Qstn #26-iiiVapour phase refiningAns : Vapour phase refining
Vapour phase refining is the process of refining metal by converting it into its volatile compound and then, decomposing it to obtain a pure metal. To carry out this process,
(i) the metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent, and
(ii) the volatile compound should be easily decomposable so that the metal can be easily recovered.
Nickel, zirconium, and titanium are refined using this method.
- Qstn #27Predict conditions under which Al might be expected to reduce MgO.
Ans : Above 1350°C, the standard Gibbs free energy of formation of Al2O3 from Al is less than that of MgO from Mg. Therefore, above 1350°C, Al can reduce MgO.