ICSE-X-Mathematics
Previous Year Paper year:2011
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #ICSE X| Mathematics
ICSE Board
Class X Mathematics
Board Question Paper 2011
(Two and a half hours)
Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the Question Paper.
The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
Attempt all questions from Section A and any four questions from Section B.
All working, including rough work, must be clearly shown and must be done on the same
sheet as the rest of the answer.
Omission of essential working will result in loss of marks.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
Mathematical tables are provided.
- # [40]Section : AAttempt all questions from this Section.
- #1
- #1-a [3]Find the value of .k. if (x . 2) is a factor of ``x^3 + 2x^2 . kx + 10``.
Hence determine whether (x + 5) is also a factor.Ans : Let ``f(x) = x^3+2x^2-kx+10`` .
Since given that (x-2) is a factor f(2) = 0
Substituting the value of x =2 in the above function we get:
f(2) = 0
``f(2) = 2^3 + 2\times 2^2 -kx+10 = 8+8-2k+10=0 ``
``\Rightarrow k=13 ``
For (x + 5) to be a factor f(-5) = 0
Substituting the value of x =-5 in the above function we get:
``f(-5) = (-5)^3+2(-5)^2-k(-5)+10 = -125+50+65+10=0 ``
Hence (x+5 ) is a factor of ``x^3+2x^2-kx+10 ``
- #1-b [3]If A = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 5 \\ 4 & -2 \\\end{bmatrix}
and B \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ 4 \\\end{bmatrix}
,
is the product AB possible? Give a reason. If yes, find
AB.Ans : The order of matrix ``A = 2 \times 2`` and the order of matrix ``B \ is \ 2 \times 1`` .
Since the number of columns in A is equal to the number of rows in B , the product AB is possible.
``AB = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 5 \\ 4 & -2 \end{bmatrix} . \begin{bmatrix} 4 \\ 2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 6+20 \\ 8-8 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 26 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} ``
- #1-c [4]Mr. Kumar borrowed Rs. 15000 for two years. The rates of interest for two
successive years are 8% and 10% respectively. If he repays Rs. 6200 at the end of
first year, find the outstanding amount at the end of second year.Ans : Principal ``= 15000 \ Rs ``
The rate of interest for the two successive years are ``8\% and 10\%`` respectively.
Formula: ``A = P(1+\frac{r}{100})^n``
Therefore Amount after ``1^{st}`` year ``= 15000 \times (1+\frac{8}{100})^1 = 16200 \ Rs.``
Principal at the start of ``2^{nd}`` year after repayment ``= 16200 - 6200 = 10000 \ Rs.``
Amount outstanding at the end of second year ``= 10000 \times (1+\frac{10}{100})^1 = 11000 \ Rs.``
- #2
- #2-a [3]From a pack of 52 playing cards all cards whose numbers are multiples of 3 are
removed. A card is now drawn at random.Ans : Total number of cards = 52
Number of cards which are multiples of 3 = 12
Total number of cards left = 52 - 12 = 40
- #2-a-ia face card (King, Jack or Queen) (ii) an even numbered red cardAns : Number of face cards = 12
Probability (of a face card) ``= \frac{12}{40} = 0.3 ``
(ii) Even numbered red cards = 10
Probability (of a even number red card) ``= \frac{10}{40} = 0.25``
- #2-b [3]Solve the following equation:
$$x- \frac{18}{x} = 6$$
. Give your answer correct to two significant figures.Ans : Given ``x - \frac{18}{x} = 6 ``
Simplifying: ``x^2 - 6x - 18 = 0 ``
Compare with equation ``ax^2 + bx + c = 0 , \ we get \ a =1 b = -6 and c = -18``
We know, ``x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}``
``= \frac{6 \pm \sqrt{36 + 72 }}{2} ``
``= \frac{6 \pm 6\sqrt{3}}{2} = 3 \pm 3 \sqrt{3} ``
Therefore ``x = 8.196 \ or \ -2.196 ``
Answer correct to two significant figures: ``x = 8.2 \ or \ -2.2 ``
- #2-cIn the given figure O is the centre of the circle. Tangents A and B meet at C. If
∠ACO = 30°, find
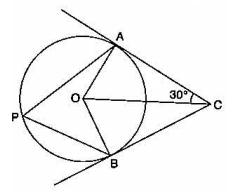 Ans : Consider ``\triangle AOC`` and ``\triangle BOC ``
Ans : Consider ``\triangle AOC`` and ``\triangle BOC ``
``\angle OAC = \angle OBC = 90°``
OC is common
AC = BC (two tangents drawn from a point on a circle are of equal lengths)
Therefore ``\triangle AOC \cong \triangle BOC`` (RHS postulate)
- #2-c-i [4]∠BCO (ii) ∠AOB (iii) ∠APBAns : ``\angle ACO = \angle BCO = 30°``
(ii) ``\angle AOC = 180° - 90° - 30° = 60°``
``\angle BOC = 180° - 90° - 30° = 60°``
``\therefore \angle AOB = \angle AOC + \angle BOC = 120°``
(iii) ``\angle AOB = 2 \angle APB`` (chord subtends twice the angle at the center than that it subtends on the circumference)
``\Rightarrow \angle AOB = 2 \angle APB``
``\Rightarrow \angle APB = 60° ``
- #3
- #3-a [3]Ahmed has a recurring deposit account in a bank. He deposits Rs. 2,500 per month
for 2 years. If he gets Rs. 66,250 at the time of maturity, findAns : ``P = Rs. \ 2500, \ no \ of \ months = 24, \\ \ rate = r\% \ Maturity Amount = Rs. 66250 ``
Maturity ``\ Value = P \times n + P \times \frac{n(n+1)}{2 \times 12} \times \frac{r}{100} ``
``66250 =2500 \times 24 +2500 \times \frac{24(24+1)}{2 \times 12} \times \frac{r}{100} \Rightarrow r=10\% ``
Interest ``= P \times \frac{n(n+1)}{2 \times 12} \times \frac{r}{100} ``
``= 2500 \times \frac{24(24+1)}{2 \times 12} \times \frac{10}{100} = 6250``
- #3-a-iThe interest paid by the bank