ICSE-X-Mathematics
Previous Year Paper year:2014
- #Board Paper . 2014
ICSE Board
Class X Mathematics
Board Question Paper 2014
(Two and a half hours)
Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the Question Paper.
The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
Attempt all questions from Section A and any four questions from Section B.
All working, including rough work, must be clearly shown and must be done on the same
sheet as the rest of the answer.
Omission of essential working will result in loss of marks.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
Mathematical tables are provided.
- # [40]Section : AAttempt all questions from this Section.
- #1
- #1-a [3]Ranbir borrows Rs. 20,000 at 12% per annum compound interest. If he repays Rs.
8400 at the end of the first year and Rs. 9680 at the end of the second year, find the
amount of loan outstanding at the beginning of the third year.Ans : Given: Principal for the first year (P)= ``Rs. \ 20000, \ Rate (r)=12\% ``
We known that ``A=P( 1+\frac{1}{100})^n `` [Reference Link]
Amount after the 1st year = ``20000 (1+\frac{12}{100})^1 = 20000 (\frac{112}{100}) = Rs. \ 22400 ``
Money repaid at the end of 1st year ``Rs. \ 8400``
Principle for the 2nd year ``22400 - 8400 = Rs. \ 14000 ``
Amount after 2nd year ``14000 ( 1+\frac{12}{100} )^1= Rs. \ 15680 ``
Money repaid at the end of the second year ``= Rs. \ 9680 ``
The loan amount outstanding at the beginning of the third year ``15680-9680 = Rs. \ 6000 ``
- #1-b [3]Find the values of x, which satisfy the inequation
$$-2\frac56 \lt \frac12 -\frac23 x \le 2 , x\epsilon W $$
Graph the solution set on the number line.Ans : Given ``-2\frac{5}{6}<\frac{1}{2}-\frac{2x}{3}\le 2``
``\Rightarrow - \frac{17}{6} < \frac{3-4x}{6} \le 2 ``
Multiplying throughout by 6
``- 17 <3-4x \le 12 ``
``-17<3-4x \ and \ 3-4x \le 12 ``
``\Rightarrow 4x<3+17 \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \Rightarrow 3-12 \le 4x ``
``\Rightarrow 4x < 20 \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \Rightarrow - 9 \le 4x ``
``\Rightarrow x < 5 \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \Rightarrow - \frac{9}{4} < x ``
Therefore ``(5>x\ge \frac{-9}{4}) ``
Hence the solution set is ``\{x \in W, - \frac{9}{4} \le x<5 \}``
Therefore the values of x are ``\{0,1,2,3,4 \} ``
The graph of the solution set is shown by dots on the number line.

- #1-cA die has 6 faces marked by the given numbers as shown below:
The die is thrown once. What is the probability of getting
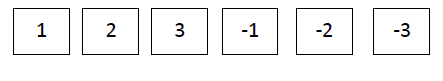 Ans : No. of sample space n(S) =6
Ans : No. of sample space n(S) =6
A positive integer = ``\{1,2,3\}``
No. of favorable cases n(E) = 3
Probability = ``\frac{n(E)}{n(S)}=\frac{3}{6}= \frac{1}{2} ``
An integer greater than -3 = ``\lbrace 1,2,3,-1,-2\rbrace ``
No. of favorable cases n(E)=5
Probability = ``\frac{n(E)}{n(S)}=\frac{5}{6}``
Smallest integer = -3
Probability of smallest integer = ``\frac{n(E)}{n(S)}=\frac{1}{6}``
- #1-c-ia positive integer.
- #1-c-iian integer greater than -3.
- #1-c-iii [4]the smallest integer.
- #2
- #2-a [3]Find x, y if $$ \begin{bmatrix}-2 & 0 \\ 3 & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} -1 \\-2x\end{bmatrix} + 3\begin{bmatrix} -2 \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = 2\begin{bmatrix} y \\ 3 \\ \end{bmatrix} $$Ans : Given ``\begin{bmatrix} -2 & 0 \\ 3 & 1 \end{bmatrix} . \begin{bmatrix} -1 \\ 2x \end{bmatrix} + 3 \begin{bmatrix} -2 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = 2 \begin{bmatrix} y \\ 3 \end{bmatrix}``
``\Rightarrow \begin{bmatrix} -2 \times -1+0 \times 2x \\ 3 \times - 1 + 1 \times 2x \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} -6 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 2y \\ 6 \end{bmatrix} ``
``\Rightarrow \begin{bmatrix} 2 \\ -3+2x \end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix} -6 \\ 3 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 2y \\ 6 \end{bmatrix} ``
``\Rightarrow \begin{bmatrix} 2-6 \\ -3+2x+3 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 2y \\ 6 \end{bmatrix} ``
``\Rightarrow \begin{bmatrix} -4 \\ 2x \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 2y \\ 6 \end{bmatrix} ``
``2y = 4 \ or \ y = -2 \ and \ 2x = 6 \ or \ x = 3 ``
- #2-b [3]Shahrukh opened a .Recurring Deposit. account in a bank and deposited Rs. 800 per
month for ``1\frac12`` years. If he received Rs. 15,084 at the time of maturity, find the rate of
interest per annum.Ans : Here, Principal (P) = money deposited per month =``Rs. \ 800 ``
N= Time for which the money is deposited = ``1\frac{1}{2} \ years =18 \ months ``
Let the rate of interest be r\% per annum, then
Interest= ``P\times \frac{n(n+1)}{2\times 12}\times \frac{r}{100}`` [Reference Link]
= ``800 \times \frac{18\times 19}{2\times 12}\times \frac{r}{100} = 114r \ Rs. ``
Total money deposited = ``18 \times 800= Rs. \ 14400 ``
Since money deposited +Interest = Maturity value
``14400+114r=15084 ``
``114r=15084-14400 ``
``114r=684 ``
``r=\frac{684}{114}=6 ``
Hence rate of interest = ``6\% p.a``.
- #2-c [4]Calculate the ratio in which the line joining A(-4, 2) and B(3, 6) is divided by a
point P(x, 3). Also find (i) x (ii) Length of AP.Ans : Let P(x, 3) divide the line segment joining the points A (-4, 2) and B (3, 6) in the ratio k :1
Coordinate of P is: [Reference Link]
(`` \frac{m_1. x_2+m_2.x_1}{m_1+m_2}, \frac{m_1. y_2+m_2.y_1}{m_1+m_2} = \frac{3k-4}{k+1}, \frac{6k+2}{k+1}) ``
But Coordinate of ``P \ is \ (x,3) ``
``\frac{6k+2}{k+1}=3 ``
``6k+2=3k+3 ``
``3k=1 \Rightarrow k=\frac{1}{3} ``
The required ratio is ``\frac{1}{3}:1 \ i.e. \ 1:3`` , (Divides Internally)
(i) Therefore ``x= \frac{3k-4}{k+1} ``
Substituting ``k =\frac{1}{3}``
``x= \frac{3\times \frac{1}{3}-4}{\frac{1}{3}+1}= \frac{1-4}{\frac{1+3}{3}} = \frac{-3}{\frac{4}{3}}= \frac{-9}{4}``
(ii) Coordinate of P is ``(\frac{-9}{4}, 3) ``
Length of AP = ``\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2} ``
= ``\sqrt{(-\frac{9}{4}+4)^2+(3-2)^2} ``
= ``\sqrt{(\frac{-9+16}{4})^2+(3-2)^2} = \sqrt{\frac{49}{16}+1}``
= ``\sqrt{\frac{49+16}{16}}= \sqrt{\frac{65}{16}}=\sqrt{\frac{65}{4}} ``
- #3
- #3-a [3]Without using trigonometric tables, evaluate
$$ \sin^2 34° + \sin^2 56° + 2\tan 18°tan 72° - \cot^2 30° $$Ans : Given ``sin^2 \ 34° + sin^2 \ 56° + 2 \ tan \ 18° tan \ 72° - cot ^2 \ 30° ``
= ``sin^2 \ 34° + sin^2 \ (90° - 34°) + 2 \ tan \ 18° \ tan \ (90°-18°) - cot ^2 \ 30° ``
= ``sin^2 \ 34° + cos^2 \ 34° + 2 \ tan \ 18° \ cot \ 18° - (\sqrt{3})^2 ``
= ``1+ 2 \ tan \ 18° \times \frac{1}{tan \ 18°}-3 ``
= ``1+2-3 = 0 ``