ICSE-X-Mathematics
Previous Year Paper year:2015
- #5-a-iiiWrite the coordinates of B., C., D. and E..Ans : Coordinates : B', (-2, 5), C', (-5 ,2), D', (-5 , -2),E', (-2, -5)
- #5-a-ivName the figure formed by B C D E E. D. C. B..Ans : Octagon
- #5-a-v [5]Name a line of symmetry for the figure formed.Ans : ``x-axis \ or \ y-axis ``.
- #5-b [5]
Virat opened a Savings Bank account in a bank on ``16^{th}`` April 2010. His pass book
shows the following entries :Date Particulars Withdrawal (Rs.) Deposit (Rs.) Balance (Rs.) April 16, 2010 By cash - 2500 2500 April 28th By cheque - 3000 5500 May 9th To cheque 850 - 4650 May 15th By cash - 1600 6250 May 24th To cash 1000 - 5250 June 4th To cash 500 - 4750 June 30th To cheque - 2400 7150 July 3rd By cash - 1800 8950
Calculate the interest Virat earned at the end of 31st July, 2010 at 4% per annum
interest. What sum of money will he receive if he closed the account on 1st August,
2010?Ans :Qualifying principal for various months:
Total = 18350Month Principal (Rs.) April 0 May 4650 June 4750 July 8950
P = ``Rs. \ 18350 \ R = 4\% \ and \ T= \frac{1}{12} ``
I = ``P \times R \times T = 18350 \times \frac{4}{100} \times \frac{1}{12} = Rs. \ 61.16 ``
Amount = ``8950+61.16= Rs. \ 9011.16 ``
\\
- #6
- #6-a [3]If a, b, c are in continued proportion, prove that (a + b + c) (a . b + c) = a2 + b2 + c2.Ans : To prove: ``(a + b + c) (a - b + c) = a^2 + b^2 + c^2``
Given ``a, b \ and\ c `` are in continued proportion
Therefore ``\frac{a}{b} = \frac{b}{c} = k ``
``\Rightarrow a = bk \ and \ b = ck``
This also implies ``a = (ck)k = ck^2``
LHS ``= (a + b + c) (a - b + c) ``
``= (ck^2+ck+c)(ck^2-ck+c) ``
``= c^2(k^2+k+1)(k^2-k+1)``
``= c^2 \{ (k^2+1)+k \} \{ (k^2+1)-k \} ``
``=c^2 \{ (k^2+1)^2-k^2 \} ``
``= c^2 \{ k^4+1+2k^2-k^2 \} ``
``= c^2 \{ k^4+k^1+1 \} ``
RHS ``= a^2 + b^2 + c^2 ``
``= (ck^2)^2+(ck)^2+c^2 ``
``= c^2k^4+c^2k^2+c^2 ``
``=c^2(k^4+k^2+1) ``
Hence LHS = RHS
Therefore Proved
- #6-bIn the given figure ABC is a triangle and BC is parallel to the y . axis. AB and AC intersect
the y.axis at P and Q respectively.
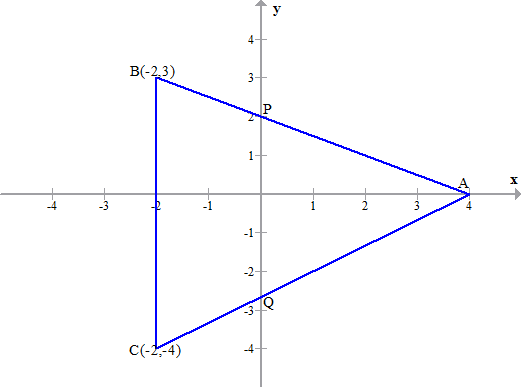 Ans : (i) Coordinates of A (4, 0)
Ans : (i) Coordinates of A (4, 0)
- #6-b-iWrite the coordinates of A.
- #6-b-iiFind the length of AB and AC.Ans : Coordinates of ``A (4, 0) \ and \ B (-2, 3)``
Note: The distance between any two points ``(x_1, y_1) and (x_2, y_2) is = \sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2 + (y_2-y_1)^2} ``
Length ``AB = \sqrt{(-2-4)^2+(3-0)^2} = \sqrt{36+9} = \sqrt{45} = 3 \sqrt{5} \ units ``
Coordinates of ``A (4, 0) \ and \ C (-2, -4) ``
Length ``AC = \sqrt{(-2-4)^2+(-4-0)^2} = \sqrt{36+16} = \sqrt{52} = 2 \sqrt{13} \ units ``
- #6-b-iiiFind the ratio in which Q divides AC.Ans : Let the required ratio be k:1
Let the coordinate of`` P \ be \ (0, y)`` , since it lies on the y axis.
Since ``x = \frac{kx_2+x_1}{k+1} ``
``\Rightarrow 0 = \frac{k \times (-2) +4}{k+1} ``
``\Rightarrow -2k+4=0 ``
``\Rightarrow k = 2 ``
``\Rightarrow m_1:m_2 = 2:1 ``
- #6-b-iv [4]Find the equation of the line ACAns : Equation of AC through Coordinates of ``A(4, 0) \ and \ C(-2, -4)``
Required equation of the line: `` (y-y_1)=m(x-x_1) ``
``y-0= (\frac{0+4}{4+2}) (x-4) ``
``\Rightarrow 3y=2x-8 ``
``\Rightarrow \ or \ 3y-2x+8=0 ``
- #6-c [3]Calculate the mean of the following distribution :
Class Interval 0-10 10-20 20-30 30-40 40-50 50-60 Frequency 8 5 12 35 24 16 Ans :Class Mid Value x f fx 0-10 5 8 40 10-20 15 5 75 20-30 25 12 300 30-40 35 35 1225 40-50 45 24 1080 50-60 55 16 880
Total``\Sigma f=100 \Sigma fx=3600 ``
Mean = ``\bar{x} = \frac{\mathcal{E}fx}{ \mathcal{E}f} = \frac{3600}{100} = 36 ``
\\
- #7
- #7-a [3]Two solid spheres of radii 2 cm and 4 cm are melted and recast into a cone of height 8
cm. Find the radius of the cone so formed.Ans : Volume of two spheres = Volume of cone
``\frac{4}{3}\pi \left(2^3\right)+\frac{4}{3}\pi \left(4^3\right)=\ \frac{1}{3}{\pi r}^2h
32+256=r^2\times 8 ``
``r^2 = \frac{288}{8}``
``r^2 = 36 \Rightarrow r = 6 \ cm``
- #7-b [3]Find 'a' of the two polynomials ``ax^3 + 3x^2 . 9`` and ``2x^3 + 4x + a``, leaves the same remainder
when divided by x + 3.Ans : Let ``f(x) = {ax}^3+{3x}^2-9 \ and \ g(x) = {2x}^3+4x+a``
Putting x = -3 in both the expressions
``f(-3) = {a(-3)}^3+{3(-3)}^2-9 ``
``g(-3) ={2(-3)}^3+4(-3)+a ``
Given ``f(-3) = g(-3) ``
Therefore ``{a(-3)}^3+{3(-3)}^2-9 = {2(-3)}^3+4(-3)+a ``
``-27a+27 -9 = -54-12+a ``
``27a+a = 27-9+54+12 ``
``28a=84 \Rightarrow a = 3 ``