NEET-XII-Physics
07: Alternating Current
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- Qstn #26Do the same exercise as above with the replacement of the earlier transformer by a 40,000-220 V step-down transformer (Neglect, as before, leakage losses though this may not be a good assumption any longer because of the very high voltage transmission involved). Hence, explain why high voltage transmission is preferred?
Ans : The rating of a step-down transformer is 40000 V-220 V.
Input voltage, V1 = 40000 V
Output voltage, V2 = 220 V
Total electric power required, P = 800 kW = 800 × 103 W
Source potential, V = 220 V
Voltage at which the electric plant generates power, V‘ = 440 V
Distance between the town and power generating station, d = 15 km
Resistance of the two wire lines carrying power = 0.5 ``\Omega``/km
Total resistance of the wire lines, R = (15 + 15)0.5 = 15 ``\Omega``
P = V1I
Rms current in the wire line is given as:
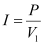
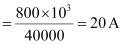
(a) Line power loss = I2R
= (20)2 × 15
= 6 kW
(b) Assuming that the power loss is negligible due to the leakage of current.
Hence, power supplied by the plant = 800 kW + 6kW = 806 kW
(c) Voltage drop in the power line = IR = 20 × 15 = 300 V
Hence, voltage that is transmitted by the power plant
= 300 + 40000 = 40300 V
The power is being generated in the plant at 440 V.
Hence, the rating of the step-up transformer needed at the plant is
440 V - 40300 V.
Hence, power loss during transmission =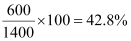
In the previous exercise, the power loss due to the same reason is . Since the power loss is less for a high voltage transmission, high voltage transmissions are preferred for this purpose.
. Since the power loss is less for a high voltage transmission, high voltage transmissions are preferred for this purpose.