NEET-XII-Physics
04: Moving Charges And Magnetism
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #24-b
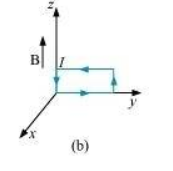
Ans : This case is similar to case (a). Hence, the answer is the same as (a).
- #24-c
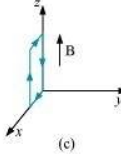
Ans : Torque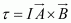
From the given figure, it can be observed that A is normal to the x-z plane and B is directed along the z-axis.
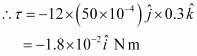
The torque is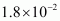 N m along the negative x direction and the force is zero.
N m along the negative x direction and the force is zero.
- #24-d
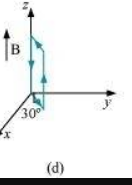
Ans : Magnitude of torque is given as:
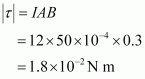
Torque is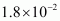 N m at an angle of 240° with positive x direction. The force is zero.
N m at an angle of 240° with positive x direction. The force is zero.
- #24-e
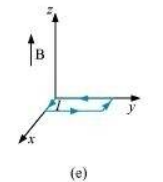
Ans : Torque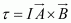
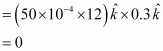
Hence, the torque is zero. The force is also zero.
- #24-f
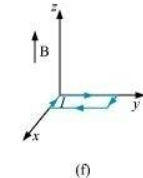
Ans : Torque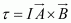
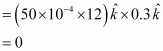
Hence, the torque is zero. The force is also zero.
In case (e), the direction of and
and  is the same and the angle between them is zero. If displaced, they come back to an equilibrium. Hence, its equilibrium is stable.
is the same and the angle between them is zero. If displaced, they come back to an equilibrium. Hence, its equilibrium is stable.
Whereas, in case (f), the direction of and
and  is opposite. The angle between them is 180°. If disturbed, it does not come back to its original position. Hence, its equilibrium is unstable.
is opposite. The angle between them is 180°. If disturbed, it does not come back to its original position. Hence, its equilibrium is unstable.
- Qstn #25A circular coil of 20 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.10 T normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is 5.0 A, what is the
Ans : Number of turns on the circular coil, n = 20
Radius of the coil, r = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Magnetic field strength, B = 0.10 T
Current in the coil, I = 5.0 A
- #25-atotal torque on the coil,
(b) total force on the coil,
(c) average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field?
(The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area 10-5 m2, and the free electron density in copper is given to be about 1029 m-3.)
Ans : The total torque on the coil is zero because the field is uniform.
(b) The total force on the coil is zero because the field is uniform.
(c) Cross-sectional area of copper coil, A = 10-5 m2
Number of free electrons per cubic meter in copper, N = 1029 /m3
Charge on the electron, e = 1.6 × 10-19 C
Magnetic force, F = Bevd
Where,
vd = Drift velocity of electrons
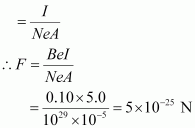
Hence, the average force on each electron is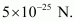
- #25-btotal force on the coil,Ans : The total force on the coil is zero because the field is uniform.
- #25-caverage force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field?
(The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area 10-5 m2, and the free electron density in copper is given to be about 1029 m-3.)
Ans : Cross-sectional area of copper coil, A = 10-5 m2
Number of free electrons per cubic meter in copper, N = 1029 /m3
Charge on the electron, e = 1.6 × 10-19 C
Magnetic force, F = Bevd
Where,
vd = Drift velocity of electrons
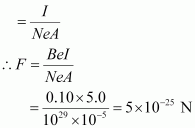
Hence, the average force on each electron is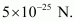
- Qstn #26A solenoid 60 cm long and of radius 4.0 cm has 3 layers of windings of 300 turns each. A 2.0 cm long wire of mass 2.5 g lies inside the solenoid (near its centre) normal to its axis; both the wire and the axis of the solenoid are in the horizontal plane. The wire is connected through two leads parallel to the axis of the solenoid to an external battery which supplies a current of 6.0 A in the wire. What value of current (with appropriate sense of circulation) in the windings of the solenoid can support the weight of the wire? g = 9.8 m s-2
Ans : Length of the solenoid, L = 60 cm = 0.6 m
Radius of the solenoid, r = 4.0 cm = 0.04 m
It is given that there are 3 layers of windings of 300 turns each.
.gif) Total number of turns, n = 3 × 300 = 900
Total number of turns, n = 3 × 300 = 900
Length of the wire, l = 2 cm = 0.02 m
Mass of the wire, m = 2.5 g = 2.5 × 10-3 kg
Current flowing through the wire, i = 6 A
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2
Magnetic field produced inside the solenoid,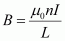
Where,
.gif) = Permeability of free space =
= Permeability of free space = .gif)
I = Current flowing through the windings of the solenoid
Magnetic force is given by the relation,
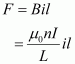
Also, the force on the wire is equal to the weight of the wire.
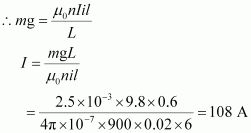
Hence, the current flowing through the solenoid is 108 A.
- Qstn #27A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 12 ``\Omega`` and the metre shows full scale deflection for a current of 3 mA. How will you convert the metre into a voltmeter of range 0 to 18 V?
Ans : Resistance of the galvanometer coil, G = 12 ``\Omega``
Current for which there is full scale deflection, = 3 mA = 3 × 10-3 A
= 3 mA = 3 × 10-3 A
Range of the voltmeter is 0, which needs to be converted to 18 V.
.gif) V = 18 V
V = 18 V
Let a resistor of resistance R be connected in series with the galvanometer to convert it into a voltmeter. This resistance is given as:
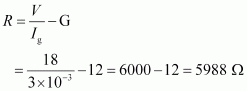
Hence, a resistor of resistance is to be connected in series with the galvanometer.
is to be connected in series with the galvanometer.
- Qstn #28A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 15 ``\Omega`` and the metre shows full scale deflection for a current of 4 mA. How will you convert the metre into an ammeter of range 0 to 6 A?
Ans : Resistance of the galvanometer coil, G = 15 ``\Omega``
Current for which the galvanometer shows full scale deflection,
.gif) = 4 mA = 4 × 10-3 A
= 4 mA = 4 × 10-3 A
Range of the ammeter is 0, which needs to be converted to 6 A.
.gif) Current, I = 6 A
Current, I = 6 A
A shunt resistor of resistance S is to be connected in parallel with the galvanometer to convert it into an ammeter. The value of S is given as:
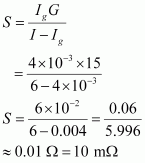
Hence, a shunt resistor is to be connected in parallel with the galvanometer.
shunt resistor is to be connected in parallel with the galvanometer.