NEET-XI-Biology
20: Locomotion and Movement
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
No item to list.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- Qstn #6Match Column I with Column II :
Column I Column II (a) Smooth muscle (i) Myoglobin (b) Tropomyosin (ii) Thin filament (c) Red muscle (iii) Sutures (d) Skull (iv) Involuntary Ans :Column I Column II (a) Smooth muscle (iv) Involuntary (b) Tropomyosin (ii) Thin filament (c) Red muscle (i) Myoglobin (d) Skull (iii) Sutures
- Qstn #7What are the different types of movements exhibited by the cells of human body?
Ans : Movement is a characteristic feature of living organisms. The different types of movement exhibited by cells of the human body are:
- Amoeboid movement: Leucocytes present in the blood show amoeboid movement. During tissue damage, these blood cells move from the circulatory system towards the injury site to initiate an immune response.
- Ciliary movement: Reproductive cells such as sperms and ova show ciliary movement. The passage of ova through the fallopian tube towards the uterus is facilitated by this movement.
- Muscular movement: Muscle cells show muscular movement.
- Qstn #8How do you distinguish between a skeletal muscle and a cardiac muscle?
Ans :Skeletal muscle
Cardiac muscle
1. The cells of skeletal muscles are unbranched. 1. The cells of cardiac muscles are branched. 2. Intercalated disks are absent. 2. The cells are joined with one another by intercalated disks that help in coordination or synchronization of the heart beat. 3. Alternate light and dark bands are present. 3. Faint bands are present. 4. They are voluntary muscles. 4. They are involuntary muscles. 5. They contract rapidly and get fatigued in a short span of time. 5. They contract rapidly but do not get fatigued easily. 6. They are present in body parts such as the legs, tongue, hands, etc. 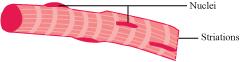
6. These muscles are present in the heart and control the contraction and relaxation of the heart. 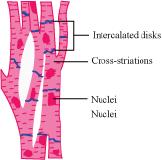
- #9-aatlas/axisAns : atlas/axis: Pivotal joint
- #9-bcarpal/metacarpal of thumbAns : carpal/metacarpal of thumb: Saddle joint
- #9-cbetween phalangesAns : between phalanges: Hinge joint
- #9-dfemur/acetabulumAns : femur/acetabulum: Ball and socket joint
- #9-ebetween cranial bonesAns : between cranial bones: Fibrous joint
- #9-fbetween pubic bones in the pelvic girdleAns : between pubic bones in the pelvic girdle: Cartilaginous joint
- #10-aAll mammals (except a few) have __________ cervical vertebra.Ans : All mammals (except a few) have
 cervical vertebra.
cervical vertebra.
- #10-bThe number of phalanges in each limb of human is __________Ans : The number of phalanges in each limb of a human is
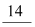 .
.
- #10-cThin filament of myofibril contains 2 ‘F’ actins and two other proteins namely __________ and __________.Ans : Thin filament of myofibril contains 2 ‘F’ actins and two other proteins, namely
 and
and .
.
- #10-dIn a muscle fibre Ca++ is stored in __________Ans : In a muscle fibre, Ca++ is stored in the
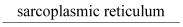 .
.