NEET-XI-Biology
03: Plant Kingdom
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
No item to list.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #3 - Plant Kingdom
- #Section : IPage No 44:
- Qstn #1What is the basis of classification of algae?
Ans : Algae are classified into three main classes - Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, and Rhodophyceae. These divisions are based on the following factors:
(a) Major photosynthetic pigments present
(b) Form of stored food
(c) Cell wall composition
(d) Number of flagella and position of insertion
Class I - Chlorophyceae
Common name - Green algae
Major pigments - Chlorophylls a and b
Stored food - Starch
Cell wall composition - Cellulose
Flagella number and position - 2-8; equal and apical
Class II - Phaeophyceae
Common name- Brown algae
Major pigments - Chlorophylls a and c, and fucoxanthin
Stored food - Mannitol and laminarin
Cell wall composition - Cellulose and algin
Flagella number and position - 2; unequal and lateral
Class III - Rhodophyceae
Common name - Red algae
Major pigments - Chlorophylls a and d, and phycoerythrin
Stored food - Floridean starch
Cell wall - Cellulose, pectin, and polysulphate esters
Flagella number - Absent
- Qstn #2When and where does reduction division take place in the life cycle of a liverwort, a moss, a fern, a gymnosperm and an angiosperm?
Ans : Liverwort - In liverworts, the main plant-body is haploid (gametophytic). It bears the male and female sex organs which produce gametes. These gametes fuse to form a zygote. The zygote develops on the gametophytic plant-body to form a sporophyte. The sporophyte is differentiated into the foot, seta, and capsule. Many haploid spores are produced as a result of the reduction division taking place inside the capsule.
Moss - In mosses, the primary protonema (developed in the first stage) develops into the secondary protonema. Both these stages are haploid or gametophytic. The secondary protonema bears the sex organs which produce gametes. These gametes fuse to form a zygote. The zygote develops into a sporophyte. Many spores are formed as a result of the reduction division taking place in the capsule of this sporophyte.
Fern - In ferns, the main plant-body is sporophytic. Its leaves are known as sporophylls and these bear the sporangia. Reduction division takes place in these sporangia, thereby producing many spores.
Gymnosperm - In gymnosperms, the main plant-body is sporophytic. They bear two types of leaves - microsporophylls and megasporophylls. Reduction division takes place in the microsporangia present on the microsporophylls (producing pollen grains) and on the megasporangia present on the megasporophylls (producing megaspores).
Angiosperm - In angiosperms, the main plant-body is sporophytic and bears flowers. The male sex organ in the flower is the stamen, while the female sex organ is the pistil. Reduction division takes place in the anthers of the stamen (producing haploid pollen grains) and in the ovary of the pistil (producing eggs).
- Qstn #3Name three groups of plants that bear archegonia. Briefly describe the life cycle of any one of them.
Ans : Archegonium is the female sex organ that produces the female gamete or egg. It is present in the life cycles of bryophytes, pteridophytes, and gymnosperms.
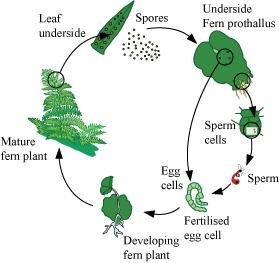
Life cycle of a fern (Dryopteris)
Dryopteris is a common fern with pinnately-compound leaves. The main plant-body is sporophytic. Many sporangia are borne on the lower surfaces of its mature leaves. Each sporangium has spore mother cells which undergo meiosis to produce haploid spores. On maturing, these spores dehisce and germinate to give rise to a heart-shaped gametophyte called prothallus.
The prothallus bears the male and female sex organs called antheridia and archegonia respectively. The antheridia produce sperms that swim in water to reach the archegonia. The egg is produced by the archegonia. As a result of fertilisation, a zygote is formed. The zygote forms an embryo, which in turn develops into a new sporophyte. The young plant comes out of the archegonium of the parent gametophyte.
- #4-aprotonemal cell of a moss;Ans : Protonemal cell of a moss - Haploid
- #4-bprimary endosperm nucleus in dicot,Ans : Primary endosperm nucleus in a dicot - Triploid
- #4-cleaf cell of a moss;Ans : Leaf cell of a moss - Haploid
- #4-dprothallus cell of a fern;Ans : Prothallus of a fern - Haploid
- #4-egemma cell in Marchantia;Ans : Gemma cell in Marchantia - Haploid
- #4-fmeristem cell of monocot,Ans : Meristem cell of a monocot - Diploid
- #4-govum of a liverwort, andAns : Ovum of a liverwort - Haploid
- #4-hzygote of a fern.Ans : Zygote of a fern - Diploid
- Qstn #5Write a note on economic importance of algae and gymnosperms.
Ans : Economic importance of algae
Algae have diverse economic uses. They perform half of the total carbon dioxide-fixation on earth by photosynthesis, acting as the primary producers in aquatic habitats.
(a) Food source: Many species of marine algae such as Porphyra, Sargassum, and Laminaria are edible. Chlorella and Spirulina are rich in proteins. Thus, they are used as food supplements.
(b) Commercial importance: Agar is used in the preparation of jellies and ice-cream. It is obtained from Gelidium and Gracilaria. Carrageenin is used as an emulsifier in chocolates, paints, and toothpastes. It is obtained from the red algae.
(c) Medicines: Many red algae such as Corallina are used in treating worm infections.
Economic importance of gymnosperms
(a) Construction purposes: Many conifers such as pine, cedar, etc., are sources of the soft wood used in construction and packing.
(b) Medicinal uses: An anticancer drug Taxol is obtained from Taxus. Many species of Ephedra produce ephedrine, which can be used in the treatment of asthma and bronchitis.
(c) Food source: The seeds of Pinus gerardiana (known as chilgoza) are edible.
(d) Source of resins: Resins are used commercially for manufacturing sealing waxes and water-proof paints. A type of resin known as turpentine is obtained from various species of Pinus.