ICSE-X-Chemistry
Previous Year Paper year:2012
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
10 minutes can boost your percentage by 10%
Note: Please signup/signin free to get personalized experience.
- #3-bMatch the properties and uses of alloys in List 1 with the appropriate answer from List
2.
List 1 List 2 (i) The alloy containing Cu and Zn is hard, silvery and is used in decorative articles. A. Duralumin (ii) It is stronger than aluminium, light and is used in making light tools. B. Brass (iii) It is lustrous, hard, corrosion resistantand is used in surgical instruments. C. Bronze (iv) Tin lowers the melting point of the alloy and is used for soldering purpose. D. Stainless steel (v) The alloy is hard, brittle, takes up polishand is used for making statues. E. Solder Ans :
(i) (B) Brass
(ii) (A) Duralumin
(iii) (D) Solder
(iv) (D) Stainless steel
(v) (C) Bronze
- #4
- #4-a [4]Identify the anion present in the following compounds:
- #4-a-ii. Compound X on heating with copper turnings and concentrated sulphuric acid
liberates a reddish brown gas.Ans : ``\ce{NO3^-}`` (Nitrate ion)
- #4-a-iiii. When a solution of compound Y is treated with silver nitrate solution, a white
precipitate is obtained which is soluble in excess of ammonium hydroxide solution.Ans : ``\ce{Cl-}`` (Chloride ion)
- #4-a-iiiiii. Compound Z which on reacting with dilute sulphuric acid liberates a gas which
turns lime water milky, but the gas has no effect on acidified potassium dichromate
solution.Ans : ``\ce{CO3^{2-} }``(Carbonate ion)
- #4-a-iviv. Compound L on reacting with barium chloride solution gives a white precipitate
which is insoluble in dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute nitric acid.Ans : ``\ce{SO4^{2-} }``(Sulphate ion)
- #4-b [3]State one chemical test between each of the following pairs:Ans :
1. Test Sodium Carbonate Sodium Sulphite Add dil. HCl or dil. ``\ce{H2SO4}`` Colourless, odourless gas that turn lime water milky but has no effect on acidified potassium dichromate solution is released i.e., ``\ce{CO2}`` Colourless gas with smell of burning sulphur, turn lime water milky and also turn acidified potassium dichromate green is released i.e., ``\ce{SO2}`` gas. 2. Test Ferrous Nitrate Lead Nitrate Add few drops of NaOH Dirty green ppt of Ferrous hydroxide Chalky white ppt of lead hydroxide. 3. Test Manganese dioxide Copper (II) oxide Heat with cone. HCl Greenish yellow gas with irritating smell and acidic nature is released i.e., chlorine gas. No reaction.
- #4-b-ii. Sodium carbonate and sodium sulphite
- #4-b-iiii. Ferrous nitrate and lead nitrate
- #4-b-iiiiii. Manganese dioxide and copper (II) oxide
- #4-c [10]Draw an electron dot diagram to show the structure of hydronium ion. State the type of
bonding present in it.
Question 5Ans :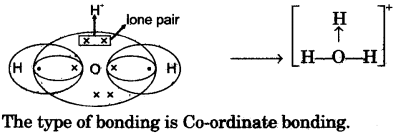
- #5-aAns :
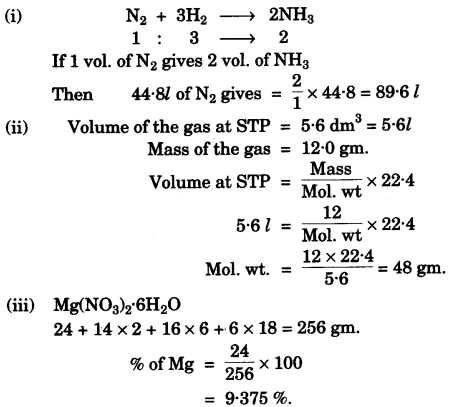
- #5-a-ii. 67.2 litres of hydrogen combines with 44.8 litres of nitrogen to form ammonia under specific conditions as
$$\ce{ N2(g) + 3H2(g) -> 2NH3(g)}$$
Calculate the volume of ammonia produced. What is the other substance, if any,
which remains in the resultant mixture?
- #5-a-iiii. The mass of ``\pu{5.6 dm324 g }`` of a certain gas at STP is ``\pu{12.0 g}``. Calculate the relative molecular
mass of the gas.